You often come across the term “format” when you are more concerned with computers and want to do more specific things. But what does the term actually mean? What does formatting do? And which data carriers can be formatted and how? We explain all of this to you in this tip.
What does "formatting" mean?
Basically, formatting is the preparation of a data carrier for the reception of new data. Sounds complicated, but it basically just means that a disk is reset, which deletes the files on it. There are two types of formatting that differ in what happens to the files on the disk.
To show exactly what the difference is, we first have to explain what a filesystem is is: There are innumerable small areas on a data carrier in which information can be stored. There are file systems so that a computer can find the data again later. As with a table of contents, these indicate where which information has been stored. Different computer operating systems work with different file systems. This means that the way the tables of contents work are different.
Very simply and figuratively speaking, one can imagine a hard drive like a chessboard: Small files occupy one field, larger files several. So that the computer knows what a file fragment in a field belongs to, there is a table of contents of a file system. This means that five fragments on different fields can then be put together to form an image file, for example. However, different file systems have different ways of assigning the files to the fields, which is why, for example, a hard drive that has been formatted for a Mac cannot simply be used with a Windows computer.
If a data carrier is now formatted, the table of contents of the file system is relocated to the hard disk. Depending on which file system is selected, a different table of contents is also used in the process. The files on the data carrier are then also deleted - but “deleted” does not mean “deleted” in this context: With quick formatting only the table of contents is deleted and reinserted. The data that was stored on the data carrier, however, remains physically until it is overwritten at some point - so only the link is removed that shows what was stored where. In this case, a computer assumes that the hard drive is empty, but you could still access the data that has not yet been overwritten with special software. On the other hand, there are normal formatting in which not only the table of contents is deleted, but also all data that was stored on the hard drive. Then no more data can be restored either..
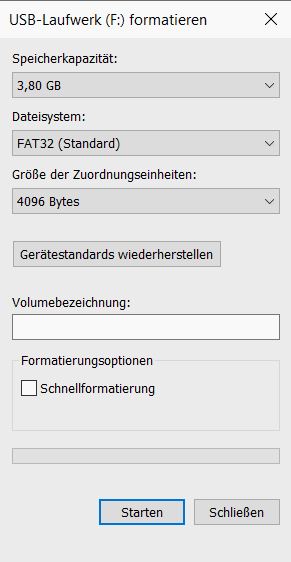 Formatting assistant in Windows Explorer
Formatting assistant in Windows Explorer There is also a special form of formatting: partitioning . A data carrier is divided into different areas. Each of these areas then behaves like its own hard drive; the areas cannot communicate with one another. This means that different file systems can be installed in the different areas. For example, you can use a hard drive with a Windows PC and a Mac at the same time, or you can install two operating systems at the same time.
Which data carriers can be formatted?
In principle, all data carriers can be formatted, but hard drives, USB sticks, SD cards or even some DVDs are particularly common. For example, you have to format hard drives and USB sticks if you want to use them on a Mac instead of a Windows computer. And with SD cards, for example, you can use the formatting function of your camera if you want to erase the card in order to be able to take more photos.
In a number of tips, we will show you the easiest way to apply formatting in different situations:
- Format hard drive in Windows
- Format hard drive on Mac
- Format hard drive in Linux
- Format the USB stick in Windows
- Format the USB stick on the Mac
- Format SD card in Windows
- Format SD card on Mac
- Format the SD card on the Android smartphone
What formatting is there?
As explained above, the different formats differ in their file systems. Today, different types of devices often have different file systems..
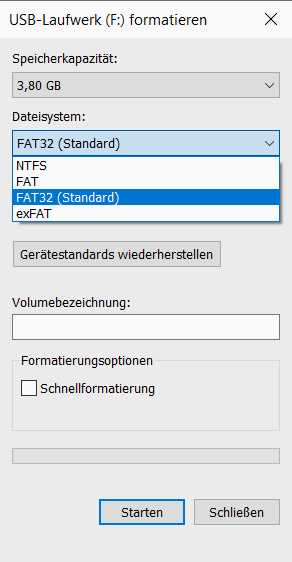 Available file systems in the Format Assistant in Windows Explorer
Available file systems in the Format Assistant in Windows Explorer FAT32
The only file system that can be used on almost every operating system is FAT32 . This is already quite old and is therefore supported by the three major computer operating systems as well as by many mobile devices. This means that SD memory cards can not only be read by cameras, but also by Windows devices or Macs. However, the disadvantage of the file system is that it can only create files up to 4 GB in size and that copy and move operations are relatively slow.
NTFS
The most common file system on Windows devices is NTFS . Compared to older file systems, it is significantly faster, especially with large data carriers and files, and offers additional features such as compression or encryption of data. This file system is ideal if data carriers are only used on Windows devices. On devices that use macOS and Linux, however, you need additional tools or drivers in order to be able to fully access the data carriers.
APFS
On the Mac, HFS + was used as a file system for a long time , which is particularly specialized for mechanical data carriers. However, with the spread of SSDs, Apple released the new APFS file system, which is specially tailored to the new flash disks. A special feature here is that several partitions with variable storage space can be created - so that all partitions can simply access the space that is still available as required, without the data carrier having to be reformatted. Both file systems can only be used with additional software on other operating systems.
ext4
Most Linux systems have used the ext4 file system for years . Compared to previous versions, ext4 offers optimized speeds and the option of encrypting files. In addition, partitions can be enlarged or reduced directly during use. However, ext4 can only be used on other operating systems with special tools.