Some time ago we explained what
VPN networks
were and what their uses were. One of the main disadvantages faced by users of a VPN is the
slow connection
. Let's see how to try to improve a slow VPN.

This slowness can have its origin in many causes. In this article we will try to diagnose them to propose solutions and
improve the speed of the VPN
. The management of a VPN network may seem superficially very simple, but behind these hide many protocols and technical issues that we will try to approach the end user in an affordable way.
Diagnosing problems in a slow VPN.
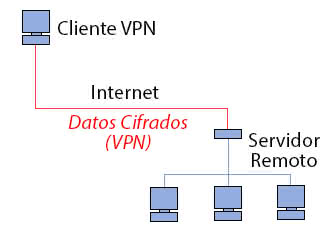
First of all, we must be clear that
when we use a VPN network to access the internet the connection is not direct, but there is an intermediate machine that we call a server
. This fact alone causes the connections cannot be established with the usual fluidity, generally finding a latency of milliseconds in each connection.
This VPN server is where we usually find the causes of a VPN slow.
Type of service chosen: free or paid VPN.
When we use a
free VPN service
,
in 99% of cases the connection will be slow because the intermediate servers are saturated
. In this case there is no solution, just wait for a time slot in which the number of users is lower.
On the other hand, when we are facing a paid VPN service, we should not have the previous problem, since they generally offer a professional service with certain guarantees. In spite of this, that it is of payment neither guarantees us low latencies and high transfer speeds. Keep reading and you will see that there are more factors to consider.
The chosen encryption affects the speed of the VPN.
One of the first aspects that we must find out is the type of encryption that our VPN uses, since some are faster than others.
It is also true that slower encryption usually offers greater security, since they perform data integrity checks.
The encryption systems ordered from highest to lowest speed would be the following:
-
PPTP
(the fastest)
.
-
L2TP / IPSec
.
-
OpenVPN
-
SSTP
-
IKEv2 / IPSec
(the slowest)
.
In this section I want to emphasize that
sometimes it is better to choose a slower protocol but that is considered safe
. For example, in the case of PPTP it is the oldest protocol and is currently considered unsafe. Instead IKEv2 is one of the safest, but it can also give us higher latencies.
Each
VPN protocol
has its advantages and disadvantages, so it is convenient to inform yourself well before. Personally, both in SMEs and in home networks, I usually opt for
OpenVPN
, because it is a very extended, secure and cross-platform solution.
Limited hardware, make sure the intermediate server is powerful enough.
Another reason why a VPN can go slow is because of limited hardware on the intermediate server, so that a bottleneck is produced.
Computers with limited resources acting as VPN servers, are another of the main causes of
slow connections
.
Remember that to manage the reception and sending of data with its corresponding encryption / decryption, these are tasks that need minimal resources to be executed quickly. If we do not have these resources, the latency of the connection will be affected.
Geographical location of the VPN server.
The geographic location of the server is another fundamental aspect.
The general rule is that the further the server is from our location, the slower the connection will be.
If we are in Spain and our VPN server is in China, it will generally have more latency than a server located in France.
Check the fine print of the VPN provider's terms of service.
A fundamental aspect when hiring a paid VPN service is to review the terms of the service thoroughly.
Many times we get surprises when reading the fine print of the contracted service and we find that the provider limits the transfer of data at a certain speed after a certain consumption. So be careful, carefully check the small print of the service.