One of the actions that we carry out daily, regardless of the role or position we have, is accessing multiple websites. Although many times we access and perform the tasks that are necessary, work, study, entertainment, etc., we do not know that behind all this there is a giant machinery that allows the response of an internet site to be optimal or not.
There is nothing more annoying, in some cases it brings out the anger, than going to a web address and waiting minutes for said site to load , which can be detrimental if it is a special website, such as paying taxes, identity validation, etc.
The speed with which a website responds to a request is crucial for that site to gain reputation, users feel comfortable and everything runs smoothly.
In this tutorial we will see how it is possible to test the speed at which a website is deployed through the Linux terminal . There are some parameters that play a fundamental role there such as:
- The time it takes to resolve the domain name.
- The TCP connection to the server.
- Transferred files and more.
For this we will use a tool called CURL.
What is CURL
CURL is a command line tool designed to transfer data using URLs. It is very versatile since it supports DICT, FILE, FTP, FTPS, Gopher, HTTP, HTTPS, IMAP, IMAPS, LDAP, LDAPS, POP3, POP3S, RTMP, RTSP, SCP, SFTP, SMB, SMBS, SMTP, SMTPS, Telnet and TFTP., HTTP POST, HTTP PUT and many more.
The main use of CURL is to transfer data through command lines or scripts and in some cases, to download elements from the network.
But this command goes much further and has other functions that we haven't fully explored yet, and TechnoWikis will teach how we can use CURL to determine the loading speed of a website.
We achieve this thanks to some additional parameters that we can add to the command.
To stay up to date, remember to subscribe to our YouTube channel! SUBSCRIBE
Check the loading speed of a website in Linux
Step 1
For this we open the terminal console and execute the following line with the name of the desired website:
curl -s -w 'Testing Website Response Time for:% {url_effective} \ n \ nLookup Time: \ t \ t% {time_namelookup} \ nConnect Time: \ t \ t% {time_connect} \ nPre-transfer Time: \ t % {time_pretransfer} \ nStart-transfer Time: \ t% {time_starttransfer} \ n \ nTotal Time: \ t \ t% {time_total} \ n '-o / dev / null http://www.technowikis.com
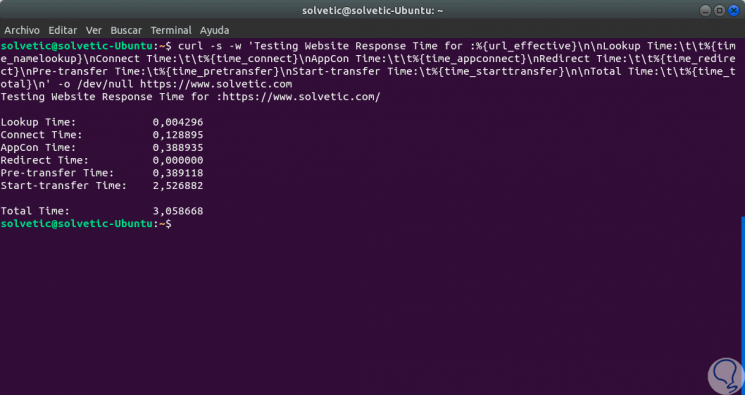
Step 2
In this command the variables that we have used are:
time_namelookup
Refers to the time, measured in seconds, of the total time the request was sent until it received a response.
time_connect
It covers the entire time, in seconds, that the TCP protocol connection to the remote computer was completed.
time_pretransfer
Refers to the time, also in seconds, that the file transfer was started.
time_starttransfer
It includes the time when the first byte was about to be transmitted to the remote equipment.
time_total
It indicates the total time it took, in seconds, to complete the response action by the remote team.
Step 3
We can see that this executed line is extensive and, therefore, prone to some type of typing error. If we lean towards something more summarized we can execute the following:
curl -s -w "@ format.txt" -o / dev / null http://www.technowikis.com
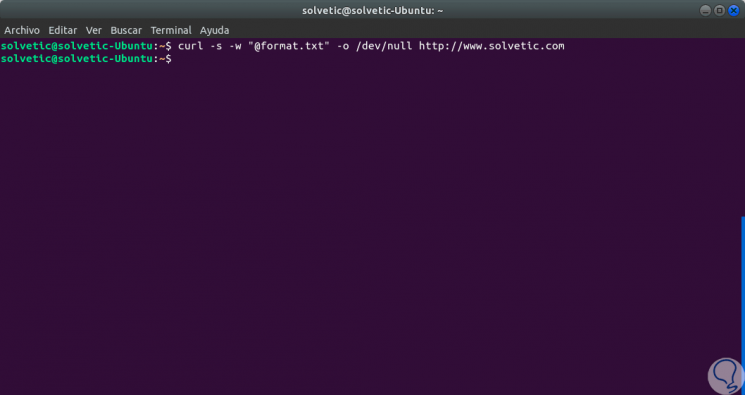
Step 4
In this case we have used the following parameters:
-s
Run CURL silent working mode.
-w
Stores the information in stdout.
-or
It is in charge of redirecting the results to the indicated route.
Step 5
In the case of HTTPS protected sites, we can execute the following:
curl -s -w 'Testing Website Response Time for:% {url_effective} \ n \ nLookup Time: \ t \ t% {time_namelookup} \ nConnect Time: \ t \ t% {time_connect} \ nAppCon Time: \ t \ t % {time_appconnect} \ nRedirect Time: \ t \ t% {time_redirect} \ nPre-transfer Time: \ t% {time_pretransfer} \ nStart-transfer Time: \ t% {time_starttransfer} \ n \ nTotal Time: \ t \ t % {time_total} \ n '-o / dev / null https://www.technowikis.com
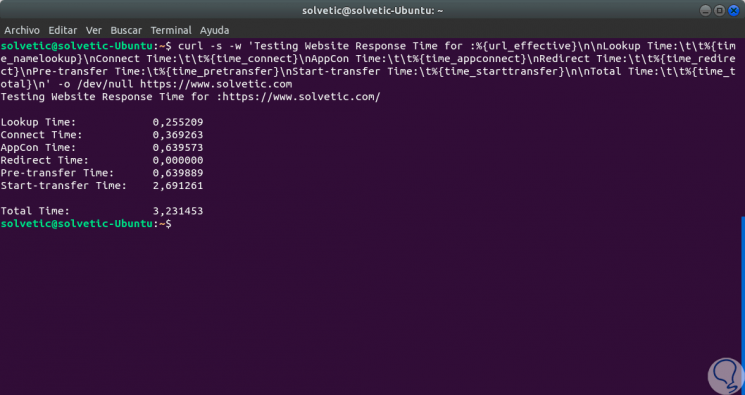
Step 6
In this HTTPS case we have used the following variables:
time_appconnect
This value refers to the time measured in seconds of the entire SSL communication process between the source computer and the remote computer.
time_redirect
It's the time where the redirect process was involved, including actions like connection, name analysis, and more.
Every time we execute the command we will receive a new time due to the loads that the server may or may not be executing at that time.
Step 7
We can use these options to know, in real time, what the loading time of a website is and we emphasize that it will always take a little longer, for security, to load a secure site. In case you know more about CURL we can execute the following command:
man curl
As we see through these commands we can verify the loading speed on a website in Linux