LTE (Long Term Evolution) is a data transmission technology that currently makes it possible to connect to the Internet at "high speed" from a mobile device. Officially it has been accepted that LTE is considered as a fourth generation or 4G technology. That should mean that it offers a speed higher than 3G, but this is not necessarily true. If we spin finer we will find that some versions of LTE are slower than 3G..
First of all you have to understand that «4G» is not a technology, but only a label used to classify fourth generation technologies, such as LTE (or at least that is what is supposed when cellular operators speak of « 4G LTE »). The same applies to the label "3G", "2G" and the UMTS and GSM technologies, respectively.
Globally, although on a commercial level, operators are allowed to label LTE as a 4G technology (remember their advertising "4G LTE") this is not technically correct in all cases, and this is where users can get confused. For a mobile phone technology to be called 4G, it must meet several requirements: perhaps the most important of all is that it must offer a download speed of at least 100 Mbps [1] ..

The speed of the LTE data connection varies from country to country and from one operator to another, but on average, the actual download speed of the LTE connection worldwide is currently only 13.5 Mbps [2] , a value very far from the 100 Mbps that at least 4G technology should have. This 13.5 Mbps value is equivalent to four times the speed of 3G, one hundred thirty-five times the speed of 2G, and approximately two times the speed of WiFi.
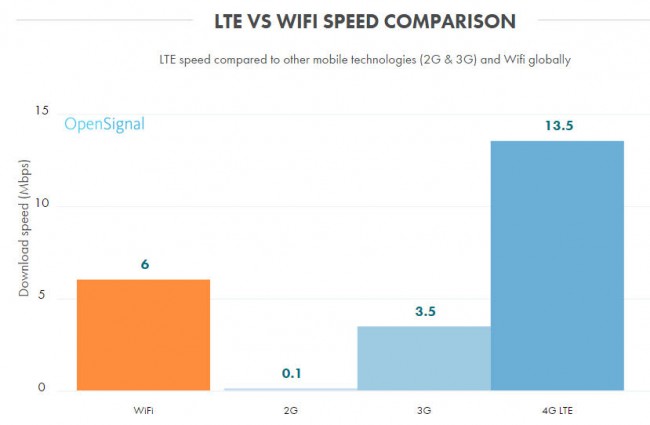
4G LTE vs. other technologies. Source: Open Signal
Una de las razones para que la velocidad LTE varíe de un país a otro es el uso de distintas versiones o categorías de LTE. Actualmente hay 16 categorías [3] , cada una con capacidades de red diferentes. Por ejemplo, mientras que una red LTE categoría 3 (que es la categoría más usada en el mundo ahora mismo [4] ) puede alcanzar una velocidad máxima de aproximadamente 100 Mbps, una red LTE categoría 4 puede conseguir una velocidad máxima de alrededor de 150 Mbps. Por supuesto, estos son solo valores teóricos, pues los valores reales son mucho menores como se indicó antes. Una red LTE categoría 0 puede alcanzar una velocidad máxima de solo 1 Mbps, un valor que podría ser superado por la mejor red 3G..
In conclusion, the 4G LTE that is being sold right now is not actually 4G technically speaking. The International Telecommunications Union (ITU) itself accepted the relationship of both terms in 2010. It is not surprising that cellular operators have taken advantage of this for marketing purposes, something for which they cannot be blamed. Users will be surprised to realize that the "4G" that is currently sold to them by the operators, and that is reinforced by the press stating that they can download files at "150 megabytes" [5] , is actually only a fraction of the authentic 4G (that's LTE certainly). Not even more modern technology like LTE Advanced (also known as 4G +), which was implemented in a few countries, could reach such figures: in real conditions it is barely enough to scratch the minimum speed required by 4G [6] . Currently with the hype for 5G , a similar situation should come as no surprise.
4G LTE in Ecuador: Everything you need to know
How to configure the APN (3G, 4G Mobile Internet) on Android
How to know if my cell phone works in another COUNTRY