There is no doubt that users and processes are two of the fundamental elements in any operating system ; since the users are the ones that manage and carry out the actions on the whole system with certain permissions while the processes allow the applications, services and the operating system itself to fulfill its usage roles..
There are certain tools that have been developed to allow us to keep track of each of these elements, since it is important that we centrally administer both users and processes to know which users have permissions on the computer, which are active and what processes are being executed there for support or control reasons.
It is for this reason that today TechnoWikis will talk about a tool called whowatch and we will learn how to install and use it on Linux to know in real time everything that happens with users and processes..
What is whowatch?
Whowatch is an interactive utility similar to ncurses through which it will be possible to display information about users who have permissions to log on to the computer and all this in real time. In addition to this, whowatch generates standard information (username, tty, host, user process) and also displays the type of connection used as telnet or ssh.
Some users may be selected and access the process tree either individually or as the tree of all system processes, this tree can be visualized with an additional column in which the owner of each process is displayed, if we use the Process tree mode, SIGINT and SIGKILL signals can be sent to the selected process to execute tasks on it.
Whowatch has no command line options or a configuration file like other utilities, so all actions are performed in real time by pressing the following keys:
Cursor movement
up and down
Allows you to toggle between the user's command line and idle time
Refers to the command line activated or deactivated
Displays the process tree of the selected user.
Access all system processes (startup tree)
Send an INT signal to the selected process
Send a KILL signal to the selected process
1. How to install whowatch on Linux
It will be possible to install whowatch from the default repositories using the package manager based on the Linux distribution used as follows:
Ubuntu / Debian
sudo apt install whowatch
CentOS / RHEL
sudo yum install whowatch
Fedora
sudo dnf install whowatch
2. How to use whowatch on Linux
Step 1
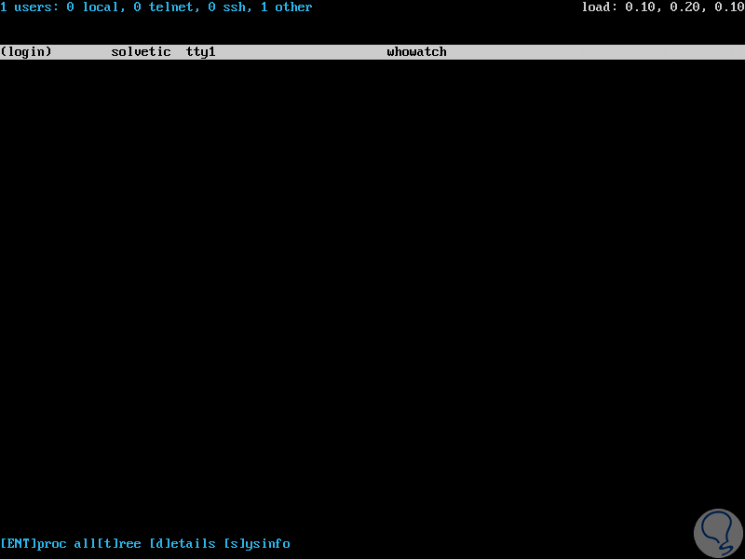
Once installed, just run whowatch on the command line, where we will see the user who is logged in and their type of connection.
Step 2
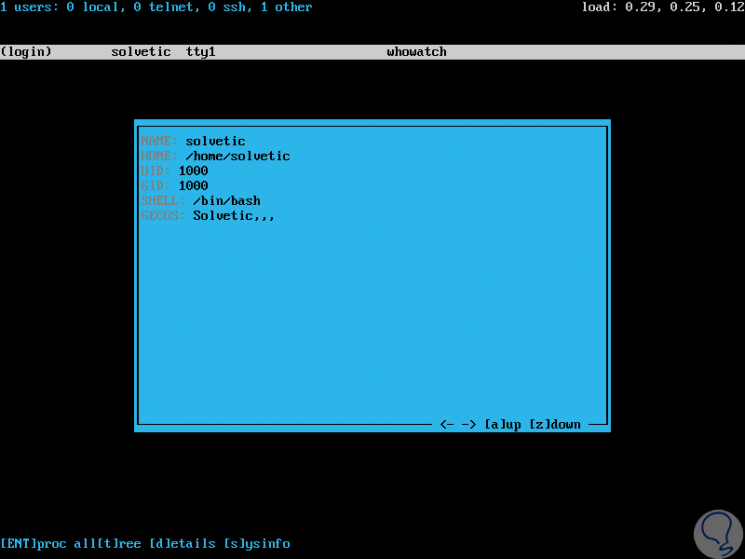
To see the details of a specific user, we will highlight the user using the up and down arrows to navigate) and then press the d key to display the user information, the result will be as follows:
There we see details like
Step 3
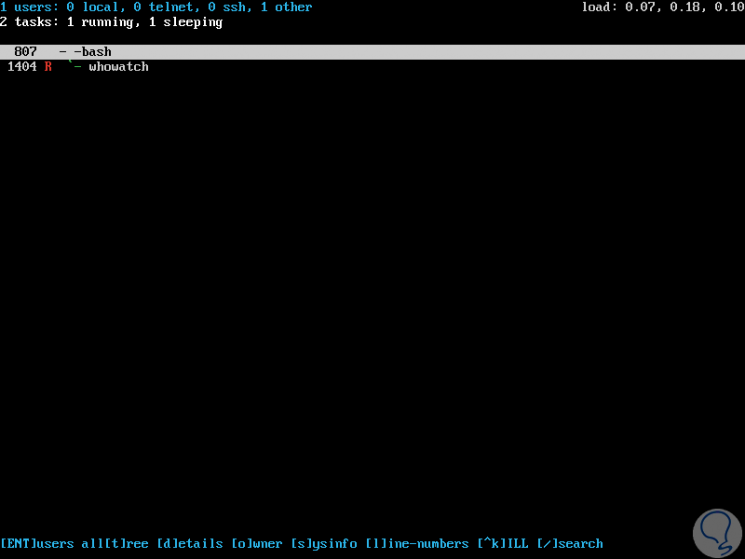
To see the process tree of a particular user, press "Enter" after highlighting that user and we will see the following:
Step 4
If we want to see all the user's processes in tree format, press the "t" key
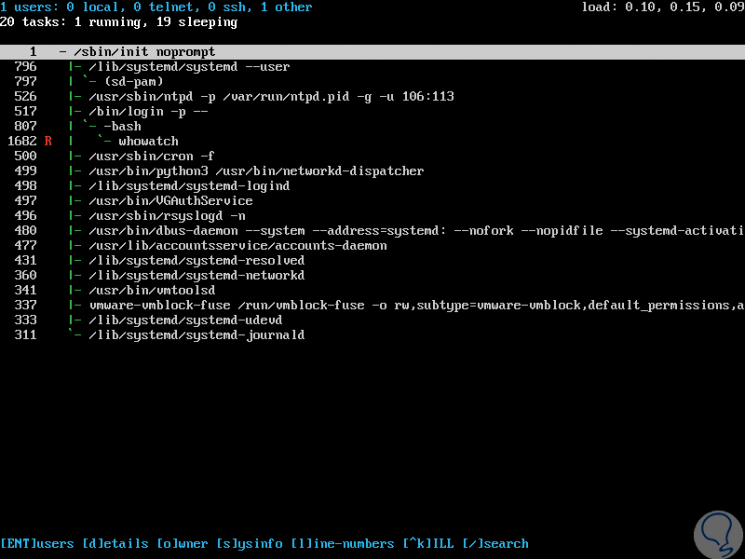
Step 5
Another option is to view the Linux system information using the "s" key. There we see full details about memory usage, disk, swap memory, free space, etc.
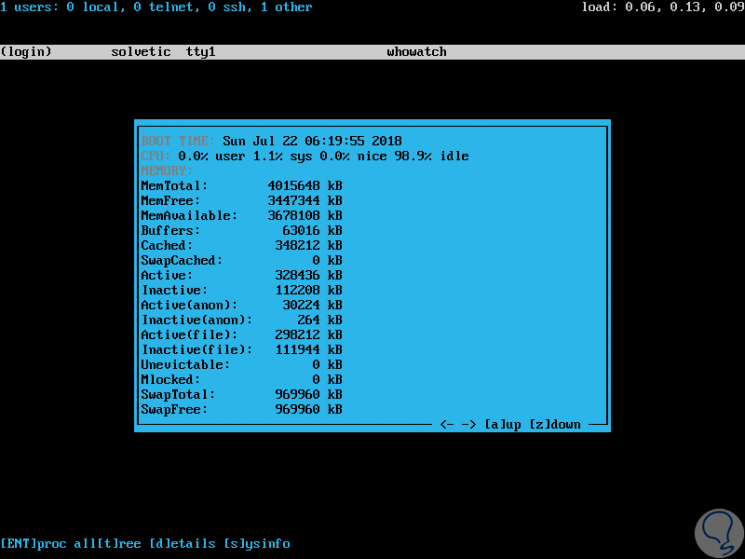
To access the help of the command we will execute the following command:
man whowatch
Thus, with whowatch we have the option of accessing all the information in real time of a user and its associated processes for a better management of these.