When we work on Linux environments and distributions, we know that we have numerous commands that help us make administration tasks a truly satisfying experience. One of these commands is Nmap which, at the network level , is quite broad and gives us multiple features in order to carry out centralized management on multiple aspects of the system used..
In this opportunity we will analyze some of the best uses that Nmap offers us in Linux.
What is Nmap
Nmap (Network Mapper) is a free and open source utility which was created for the detection of networks and security audit issues offering relevant details about the network.
By using Nmap we can be sure of having a practical command to carry out tasks such as network inventory, administration of service update schedules and monitoring of host or service activity time..
The Nmap command makes use of unprocessed IP packets to determine what hosts are available on the network , what services (name and version of the application) these hosts offer, what operating systems (and versions of the operating system) are running, what kind of packet filters / firewalls are in use , and dozens of other features. In this way, especially if we manage networks, have complete and detailed information on each network point at the source and destination.
The Nmap command was designed to quickly scan large networks, but this does not mean that it does not work optimally on small networks or on single computers..
Another of the great advantages of using Nmap, is that it can be run on all current operating systems , and its official binary packages are available for Linux, Windows and Mac OS X. In addition to these great advantages, the Nmap suite includes a GUI Advanced and a result viewer (Zenmap). A flexible data transfer , redirection and debugging tool (Ncat), a utility to compare scan results (Ndiff) and a packet generation and response analysis (Nping) tool with which we have multiple options for complete administration.
1. How to install Nmap on Linux
In Debian and Ubuntu distributions, Nmap can be installed by running the following command.
sudo apt-get install nmap
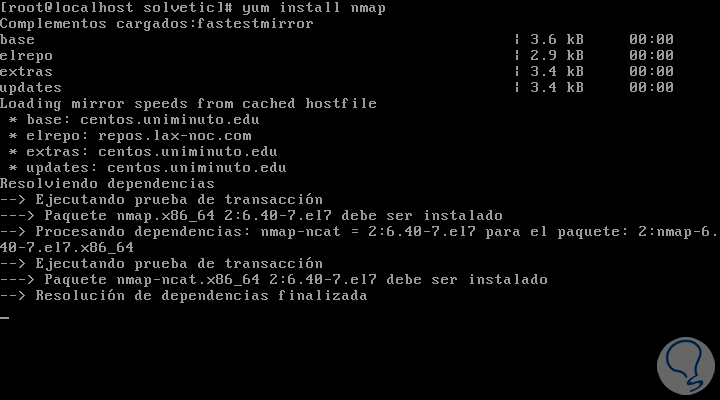
In the case of CentOS and RedHat we will use the following command:
yum install nmap
If we use OpenBSD we can install it by executing the following:
export PKG_PATH = http: //mirror.esc7.net/pub/OpenBSD/`uname -r` / packages / `machine -a` / pkg_add -v nmap
Now we will see some practical examples of how to use Nmap in Linux.

Login Join up!