One of the issues that have always been discussed before, today and in the next times, is the duration and performance that the battery must have in our equipment and around this there are hundreds of points of view both for and against, either that we leave it connected, that we remove it from the equipment, that we use performance software, etc., but a common goal is always sought: to extend the life of this to the maximum..
Although there are many tips on this topic, do not use the maximum brightness of the screen, do not leave the computer on if we are not going to use it, configure the hard disk to turn off and more, today TechnoWikis will analyze in detail a utility called TLP the which will be of great help in the whole topic associated with the battery.
What is TLP?
TLP is an open source utility that has been developed thinking about optimizing the battery power of our Linux machines in an advanced way.
TLP is compatible for systems:
TLP runs on all brands of laptops, setting the battery charge thresholds is only available for IBM / Lenovo ThinkPads computers..
TLP offers energy saving tasks to be able to configure the energy use of the portable equipment. It is also a command line tool with automated background tasks and does not contain a GUI or graphical interface.
If you want to know more features about TLP you can visit its official website at the following link:
TLP
1. Install TLP on Linux
Step 1
For this case we will use Ubuntu 17.10 Server and for this we can use the TLP-PPA repository as follows:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa: linrunner / tlp
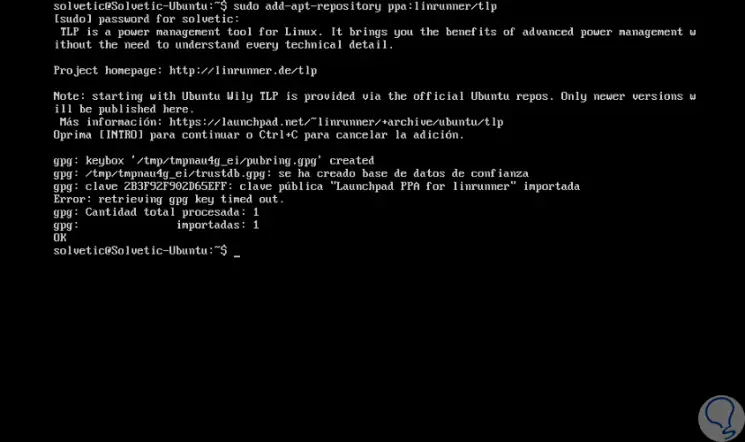
Step 2
Later we update the repository packages by executing the following line:
sudo apt-get update
Step 3
Finally we install TLP by running the following command:
sudo apt install tlp tlp-rdw
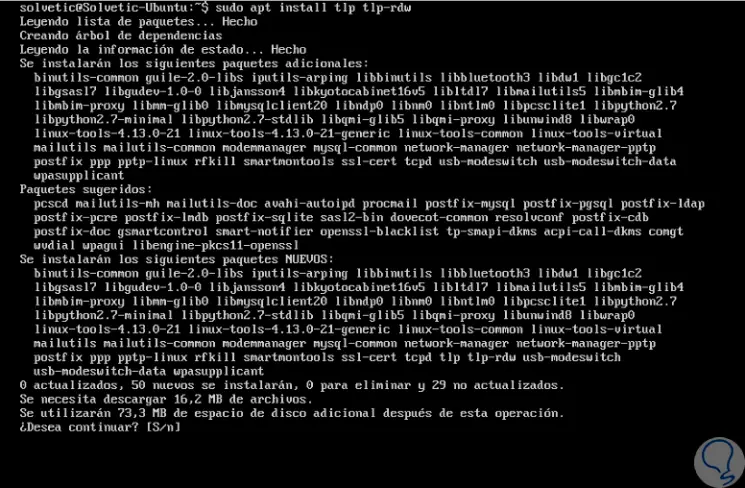
Step 4
Enter the letter S to confirm the download and installation of the TLP packages. The packages that are installed are the following:
tlp (PPA or universal)
Energy saving.
tlp-rdw (PPA or universal)
It is optional, it is a radio device assistant.
tp-smapi-dkms (PPA or universal)
Applies only in ThinkPad, tp-smapi is necessary for thresholds of battery charge, recalibration and specific status output of tlp-stat.
acpi-call-dkms (PPA or universal)
Applies only with ThinkPad, acpi-call is required for battery charge thresholds and recalibration in Sandy Bridge and newer models (X220 / T420, X230 / T430 and others).
Step 5
- In the case that we use some ThinkPad equipment it will be necessary to run the following additional line:
sudo apt-get install tp-smapi-dkms acpi-call-dkms
- In the case of using Debian it will be necessary to add the following line in the /etc/apt/sources.list directory:
echo "deb http://ftp.debian.org/debian jessie-backports main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list
- Then, we can update the packages and carry out the TLP installation process:
apt-get update apt-get install tlp tlp-rdw
- In the case of using Debian BackPorts we must execute the following additional line:
apt-get install -t jessie-backports tlp tlp-rdw
- In case of having other distributions we can execute the following:
dnf install tlp tlp-rdw (Fedora) pacman -S tlp tlp-rdw (Arch Linux) zypper install tlp tlp-rdw (OpenSUSE)
2. Use TLP to increase battery efficiency in Linux
When the installation process is finished, your configuration file is / etc / default / tlp and we will have the opportunity to use the following commands to manage the battery in Linux:
tlp
It allows to generate the energy saving configuration of the portable device.
tlp-stat
Display all energy saving settings.
tlp-pcilist
It generates data from the PCI device (e).
tlp-usblist -
View data from USB devices.
3. Verify battery TLP service in Linux
Step 1
We can validate the current status of the TLP service by running the following line:
sudo systemctl status tlp
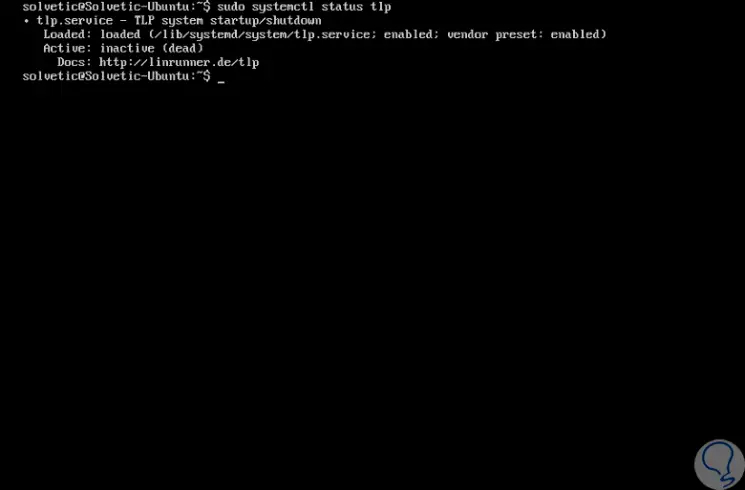
Step 2
We can see that its initial state is inactive, so that the service is active we can restart the system or run the following line:
sudo tlp start
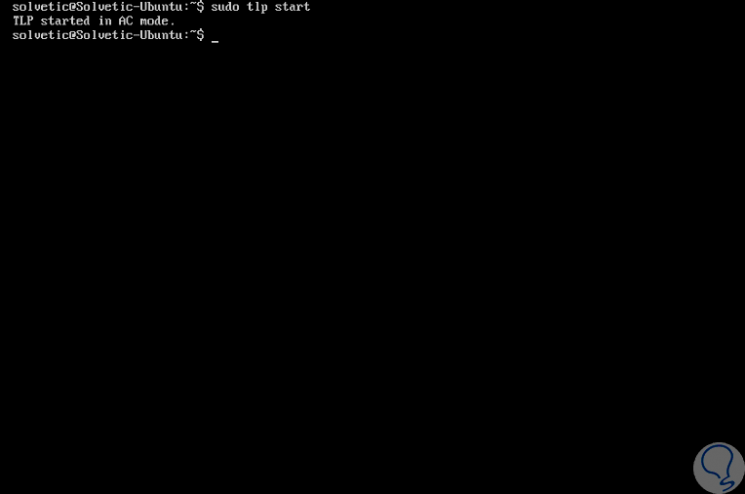
Step 3
We can validate that it is being executed using the following command which displays system information and the status of TLP:
sudo tlp-stat -s
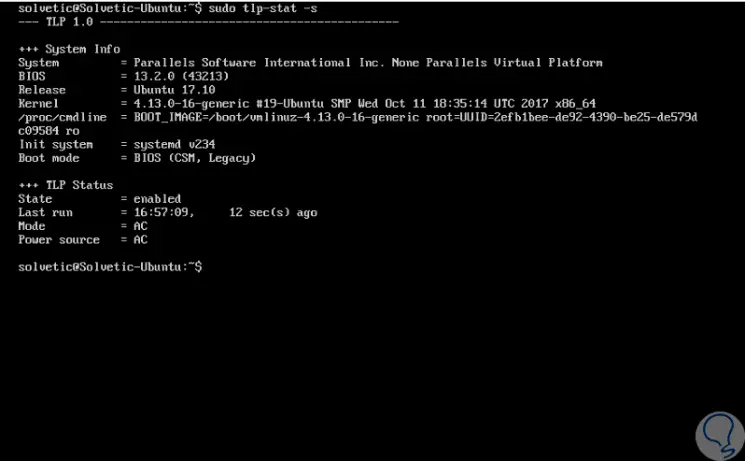
Step 4
We can find detailed system information, TLP status, last execution, etc.
To see the current TLP configuration, we can execute the following command with the -c option :
sudo tlp-stat -c
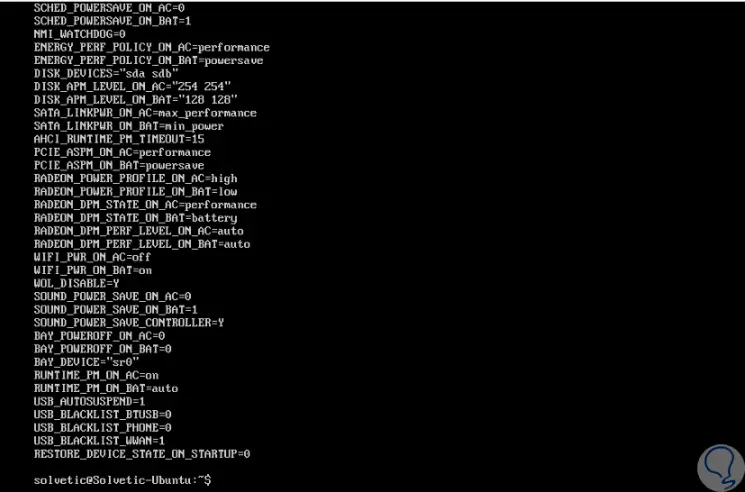
Step 5
To deploy all power settings, we will execute the following command:
sudo tlp-stat
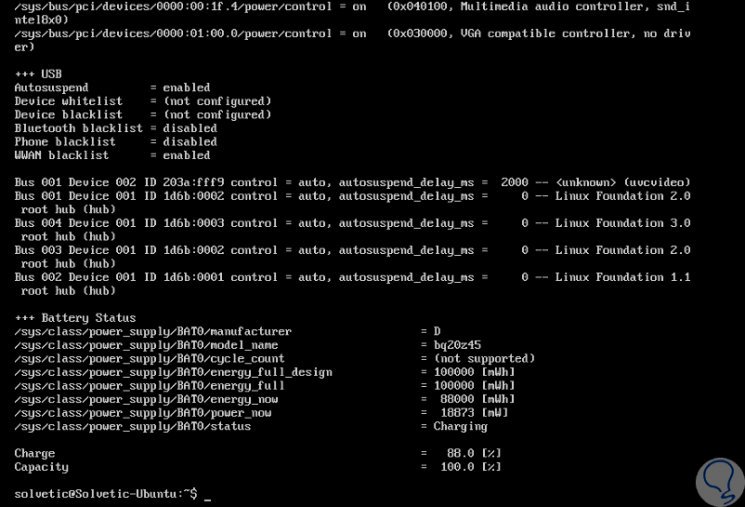
Step 6
To visualize in real time the battery information of the Linux system, we must execute the following command with the -b parameter:
sudo tlp-stat -b
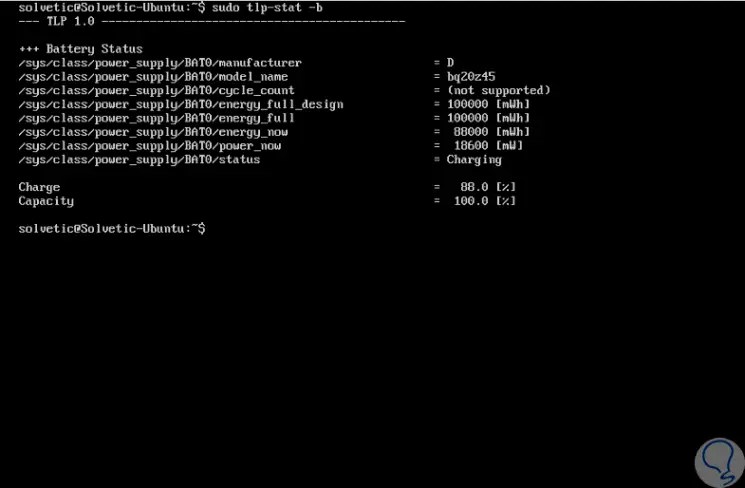
Step 7
We see in detail the current state of the battery, whether it is in charge or not as well as its current capacity.
If we want to display the temperature and fan speed, we must add the -t parameter like this:
sudo tlp-stat -t
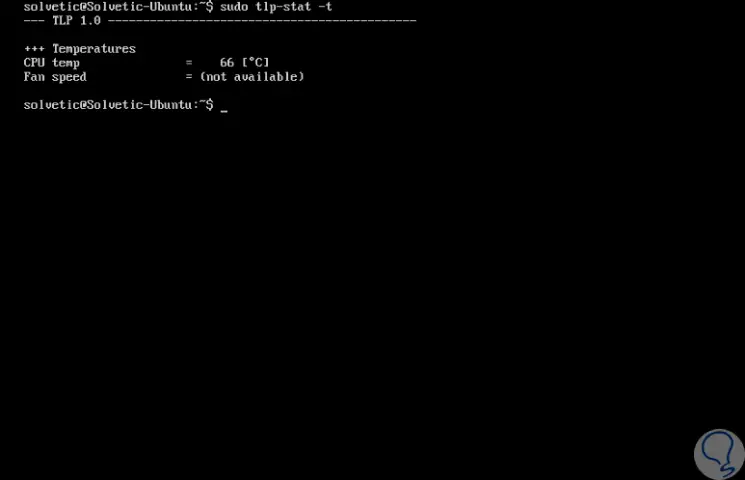
Step 8
If we want to display processor data, we must use the -p parameter:
sudo tlp-stat -p
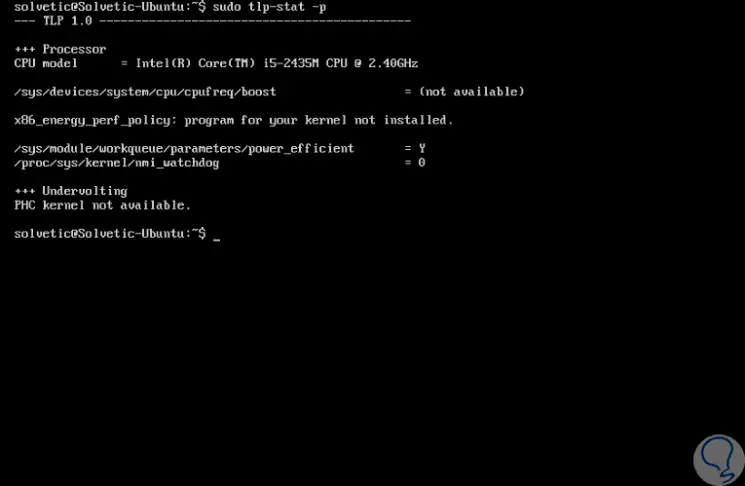
Step 9
If we want to see the energy warnings we can use the -w parameter:
sudo tlp-stat -w
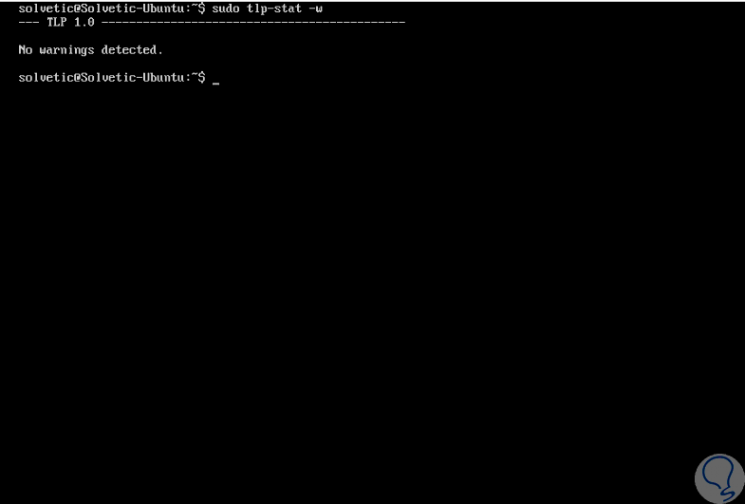
Step 10
Other additional options are:
View disk information
tlp-stat -d tlp-stat –disk
View graphics card information
tlp-stat -g tlp-stat –graphics
Get information from PCI devices
tlp-stat -e tlp-stat –pcie
Check the status of radio devices
tlp-stat -r tlp-stat –rfkill
Check USB devices
tlp-stat -u tlp-stat –usb
Step 11
We can apply the following settings:
sudo tlp start
sudo tlp bat
sudo tlp ac
- Apply auto suspension of all USB devices:
sudo tlp usb
- Turn off the optical drive:
sudo tlp bayoff
- Finally, to get help we can run the following line:
man command
TLP is an ideal solution for all battery management in Linux systems and thus achieve much more precise control over this fundamental hardware element.