When working with Linux operating systems we can frequently hear about a term called swap but at some times we do not understand its use and functionality..
Swap, or swap memory, is a part of the system that we can allocate during or after the installation process and in this way the system structure is left with the system space and another for the swap.
Swap itself is an exchange space that can be represented by a file or a partition, thus, swap uses hard disk space instead of using RAM space and in that space it houses temporary files allowing memory RAM is used to its fullest potential ..
On Linux systems, both physical RAM and swap are combined and create more virtual memory than is set by default.
With the rise of solid state hard drives, we can have much greater access to the system and we have RAM greater than 8 GB physical, it is possible to disable the swap partitioning of the distro, in this case CentOS 7, and thus optimize Better system resources..
To keep up, remember to subscribe to our YouTube channel! SUBSCRIBE
1. See the amount of swap memory in CentOS 7
Step 1
First of all we must verify how much swap memory is defined for the device, this can be verified using the following command:
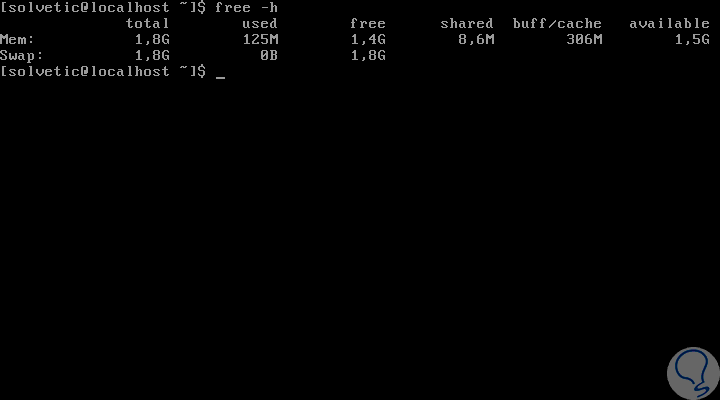
free -h
Step 2
In this example we can see that although we have 1.8 GB available for swap memory, the use is in 0 bytes, so there is an indication that physical memory is more than enough for the tasks carried out in CentOS. Now, to identify the path where swap is located, we must execute the
blkid command
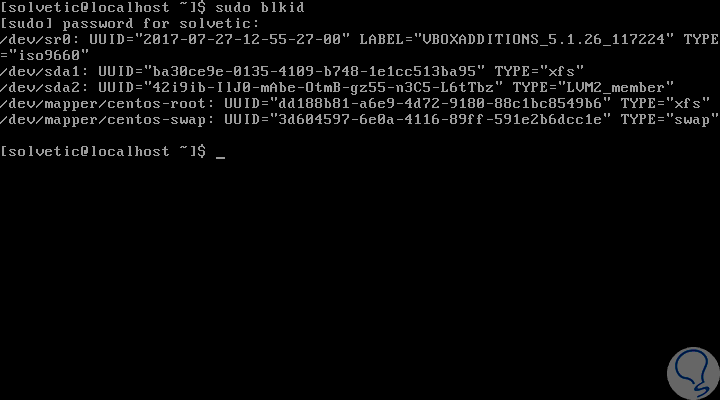
: sudo blkid
Step 3
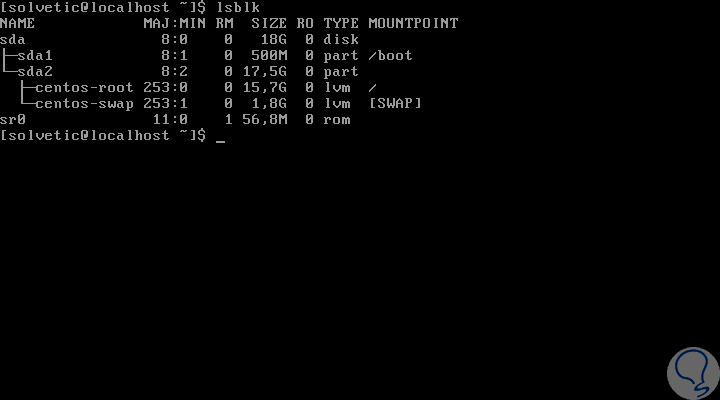
We can observe the line TYPE = "swap" to define and identify the swap partition. Now, we will execute the lsblk command and see the following:
Step 4
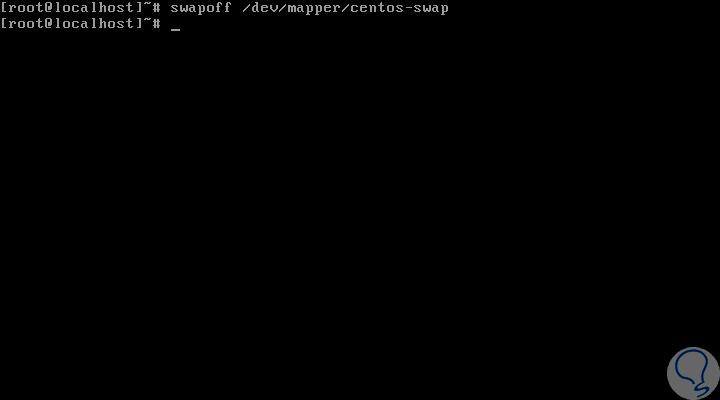
There we can determine that the swap partition is hosted on sda2. Once we identify the partition where swap is located, we proceed to execute the following command to disable swap in CentOS 7:
swapoff / dev / mapper / centos-swap
Note
If we want to disable all swap partitions of / proc / swaps we must execute the following command:
swapoff -a
Step 5
Run the free -h command again to verify that swap has been disabled correctly:
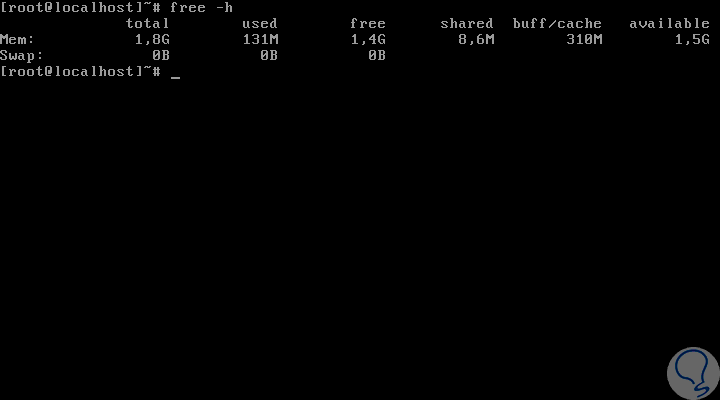
2. Permanently disable swap memory in CentOS 7
Step 1
If the goal is to permanently disable the swap partition in the system, we must access the / etc / fstab file using the desired editor:
nano / etc / fstab
Step 2
Once there, we must comment on the swap line by putting the sign # like this:
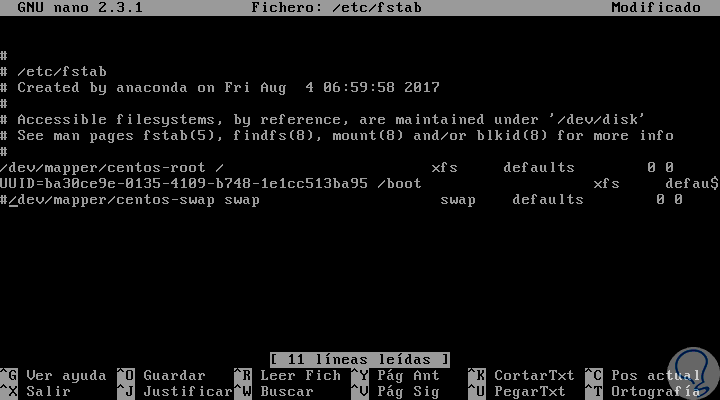
Step 3
We save the changes using the following key combination:
+ O Ctrl + O
We leave the editor using:
+ X Ctrl + X
Step 4
Then we can restart the operating system, or use the mount -a command to apply the changes.
After this we can execute the following commands to verify that swap has been permanently disabled:
free -h blkid lsblk
In this way we have disabled swap in CentOS 7.