The use of
MySQL or MariaDB databases
is very common in web applications. It is a system that allows us to store large amounts of data in a database and then make inquiries. Both MariaDB and MySQL use the so-called storage engines and can sometimes bring us the odd problem. Therefore, we will gather in this article
different ways to find out which storage engine MySQL or MariaDB uses
.

Storage engines are responsible for managing the operations that are performed on the different tables.
Each table can be assigned a different storage engine. In addition, there is always a default storage system in the system that uses the MySQL or MariaDB server. To follow this tutorial we will rely primarily on the use of the console, although everything can be done through database managers such as phpMyAdmin or
Adminer
.
How to check which storage engine uses by default our MySQL or MariaDB server.
We will start by checking the default storage engine. When a table is created and the storage engine to use is not specified, the default storage engine will be used. Some time ago the MyISAM engine was the most used, but thanks to the advantages offered by InnoDB, this is the most used today. There are other types of storage engines but it is not the purpose of this tutorial to review them all.
To
determine which is the default storage engine on a MySQL or MariaDB server
, simply access the server with the
mysql -u root -p
command, as explained in
this tutorial
. You will ask us to enter the password.
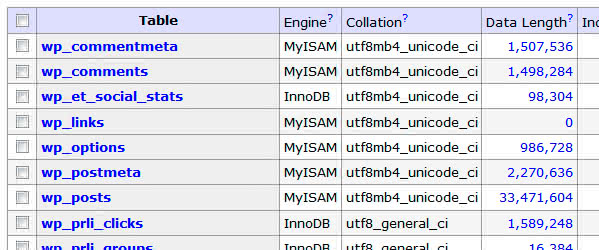
Then we execute the
SHOW engines;
query
SHOW engines;
where we will be shown a list with all supported storage engines. The engine configured by default in the system is assigned the
DEFAULT
value as we see in the following image.
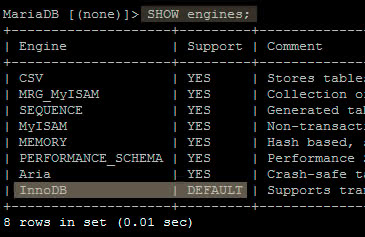
See the storage engine of a specific table through its creation statement.
This method allows us to
see the creation statement of an existing table
, where among other things the storage engine is specified. It is a quick way to
check the storage engine of a single table through the console
. We access the server as indicated in the previous section and execute the query:
SHOW create table basededatos.nombretabla;
As an example I have made this query based on the
TechnoWikis
name
TechnoWikis
and the
usuarios
name table:
SHOW create table TechnoWikis.usuarios;
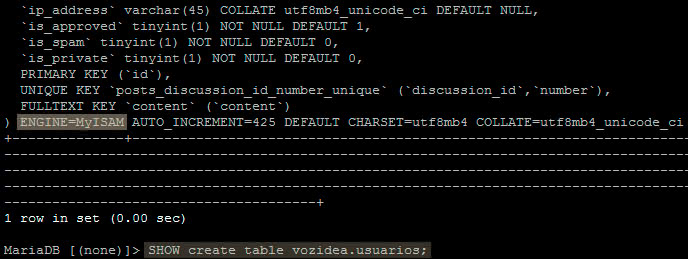
Consult the storage engine of several tables simultaneously.
If we want to see the storage engine of several tables at once to avoid going one by one, we have to resort to the system information database called
information_schema
. This database contains information on all databases and server tables.
Now we are going to
list the storage engine of all the tables in a database
. To do this we execute the following command:
SELECT table_name,engine from information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema='nombredb';
For example I will see the storage engine of all the tables in my WordPress blog:
SELECT table_name,engine from information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema='TechnoWikis';
Alternative method to obtain information from tables in a database.
Finally, I want to mention the possibility of using
SHOW table status
to see the status of a table. Within the information that this command returns, the storage engine used by the table is included.
Its use is very simple, first we have to define the database we use and then execute the command. We achieve this by executing a single line like the following:
USE nombrebasedatos; SHOW table status where name='nombretabla';
As we said at the beginning, if you have a database manager with a graphical interface such as
phpMyAdmin
or Adminer, consulting this information is very simple since the properties of the tables are shown directly.