If you are a system administrator and you have under your control teams that have been in the organization for several years, the most normal thing is that for compatibility, security and scalability issues it is time to update or migrate certain functions and roles talking specifically about Windows Server servers ..
The world of servers can become complex because of the number of processes and roles that can be used, but it is something that really has a positive impact on the administration if we know how to take them centrally, Windows Server is the offer that Microsoft launches for organizations looking for a way to have a reliable and high-performance secure system for each of the tasks that we must perform as administrators and in this world one of the most delicate and important concepts is the domain controller .
In Windows Server we handle the concept of directory, especially Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) , which provide the necessary tools to host and manage directory data and make this data available to the client computers of the organization..
Active Directory makes use of a structured data warehouse with which the logical and hierarchical organization of each directory element is achieved, in this structure the domain controller (DC - Domain Controller) stands out, which manages authentication requests at the level of security in a specific domain, hence its name "controller", within its main functions we have:
- Authenticate users for access to computers.
- Apply domain security policies .
- Host and control user account information
Many organizations still have computers integrated by Windows Server 2008 and after more than 10 years there have been many changes not only in the design of the system but in the roles, functions and parameters so that a good decision is to update the system but like everything It is a cycle linked to each other, we cannot simply buy a new license and install everything from scratch, for these cases the ideal is to perform a domain controller migration from one system to another and in this case it will be migrating from Windows Server 2008 to Windows Server 2019
Today TechnoWikis will explain how to carry out this in a functional and safe way.
For this case we have a Windows Server 2008 R2 server and this can be validated in the Server Manager:
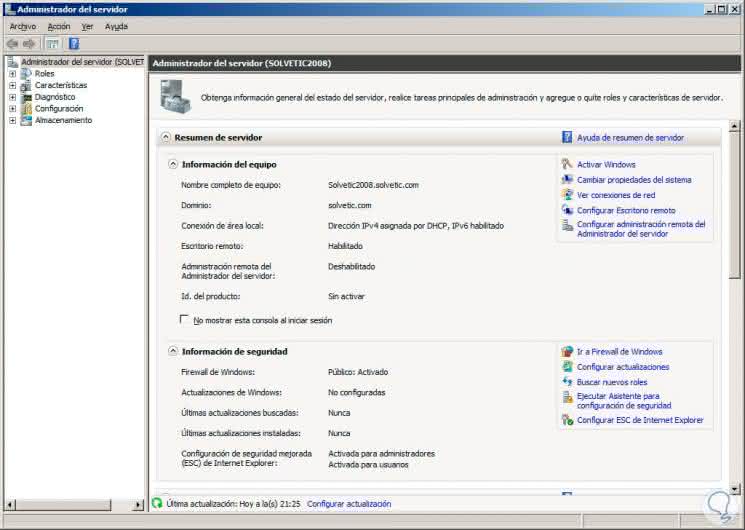
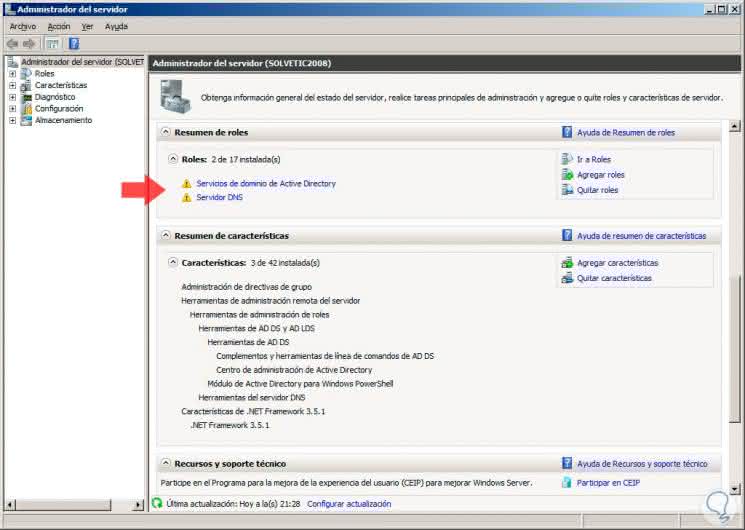
In the case of this server, count on the roles:
- Active Directory Domain Services .
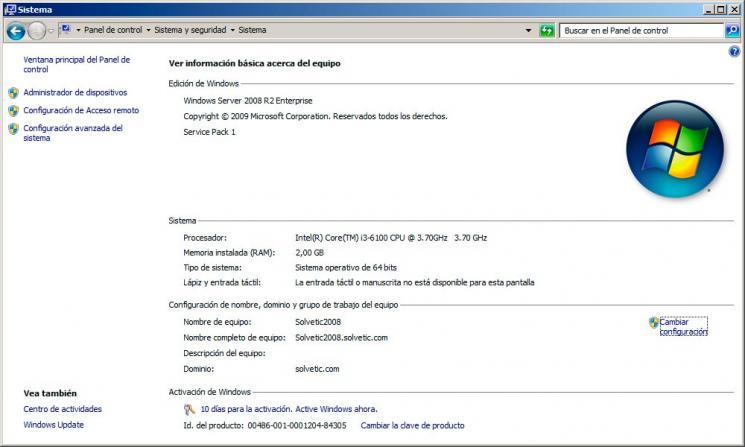
To validate the system edition we go to the equipment properties:
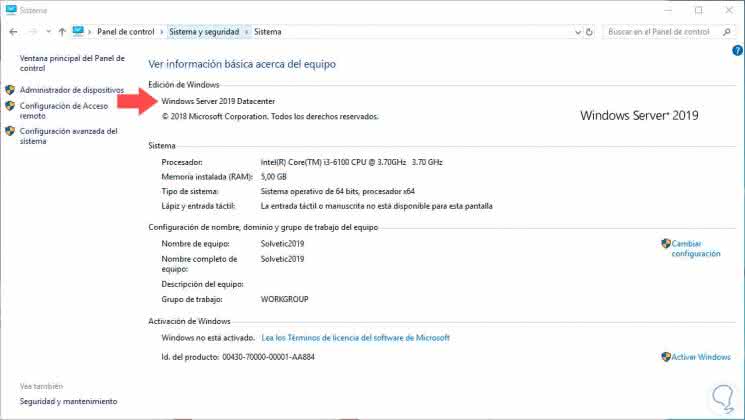
In the case of Windows Server 2019 we can check the edition used:
From the "Administrator" of the Server 2019 server we can see their roles and settings:
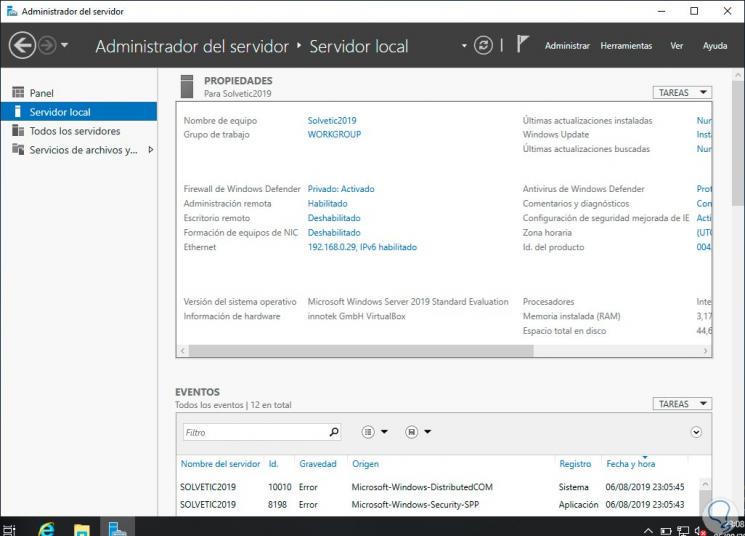
Previous Validations
To begin, we will go to Windows Server 2008 and at the command prompt we will execute the following:
netdom query fsmo
This command is responsible for displaying on screen the Flexible Single Master Operation Roles (FSMO) or Flexible Single Master Operation Roles which are essential for optimal operation of domain controllers.
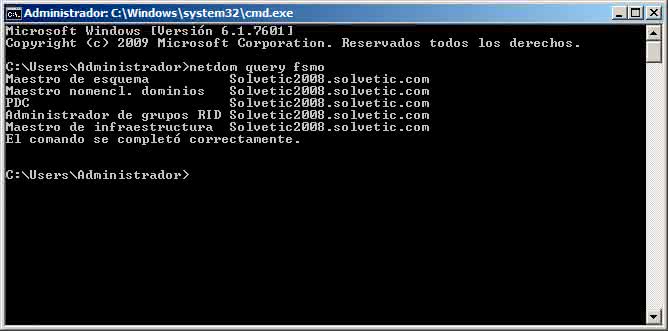
As we see there are 5 FSMO roles..
1. Join Windows Server 2019 to the domain
Once we validate the previous steps, we will proceed to join the server with Windows Server 2019 to the server with the Domain Solvent.com in Server 2008 R2, to achieve this, we will go to the following route:
There we will right click on the server adapter and select "Properties":
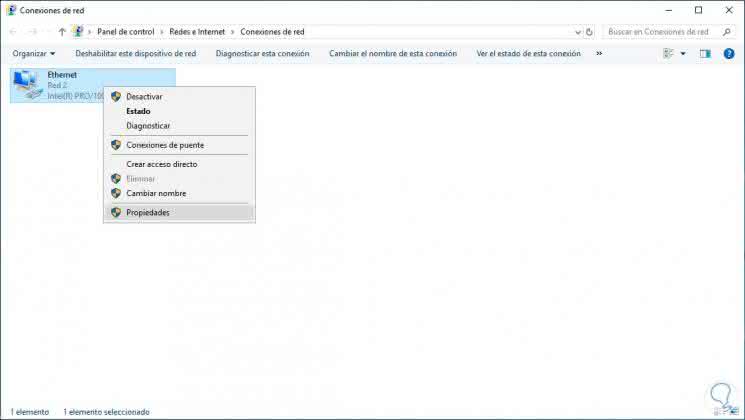
In the window that is displayed, uncheck the “Internet Protocol version 6†box and select the “Internet Protocol version 4†line:
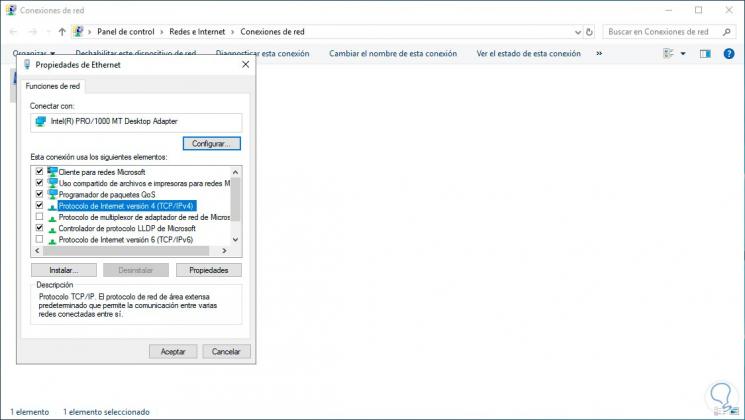
We click on "Properties" and there we define the fixed IP address next to the subnet mask and the gateway, in the field "Preferred DNS server" it is important that we enter the IP address of the Windows Server 2008 server:
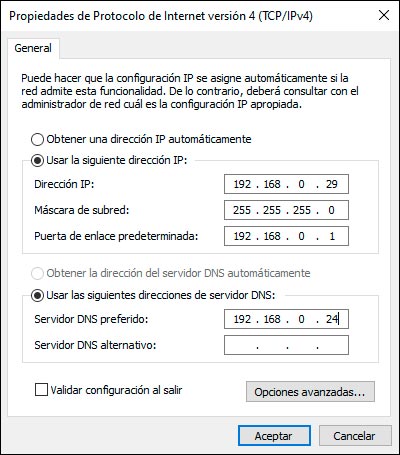
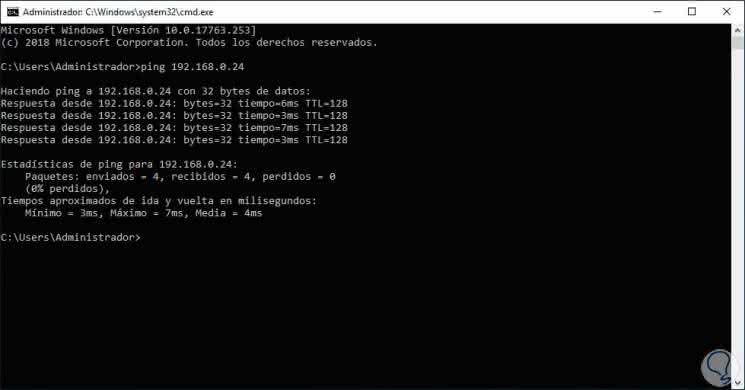
Once this is defined, we click on OK to save the changes and we can check the connectivity by pinging from Windows Server 2019 to Server 2008 R2:
ping 192.168.0.24
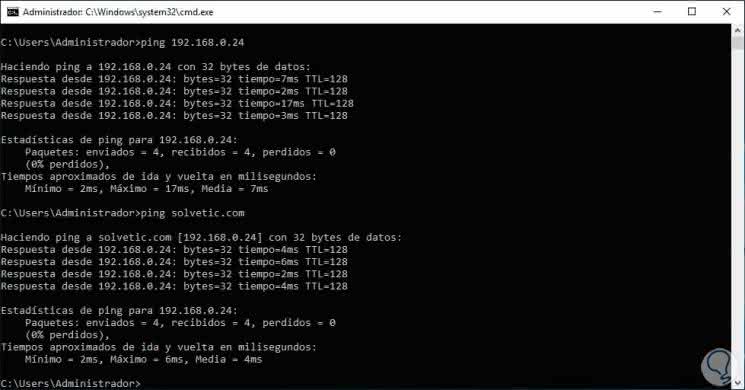
Also we can ping directly to the domain:
ping solvetic.com
Now from the Server Manager we click on the WORKGROUP line and the following window will be displayed:
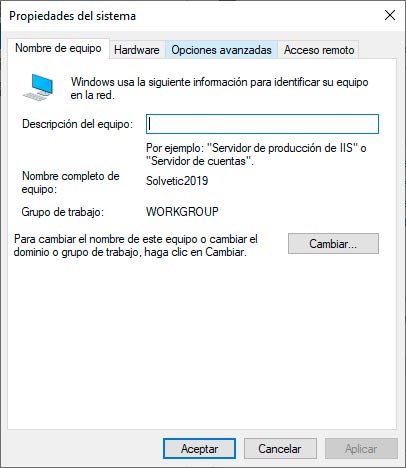
There we click on "Change" and in the following window we activate the "Domain" box and enter the Windows Server 2008 R2 domain:
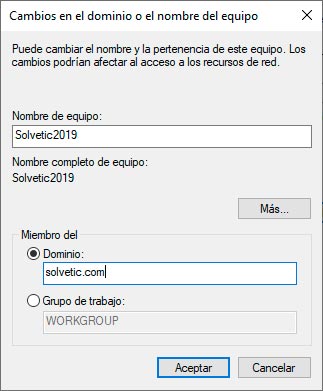
We click OK and the following pop-up window will appear where we enter the credentials with permissions for connection:
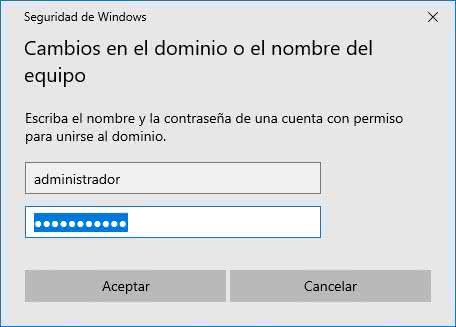
We click on Accept and after a moment we will see the following:
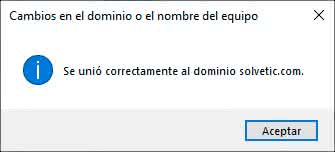
We click on Accept and we will see the following:
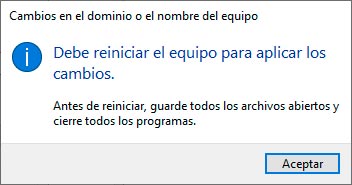
Again we click on Accept and it will ask if we want to restart immediately or later:
We click on "Restart now" and after the process we go to the login screen, there we click on "Other user" and enter the following syntax:
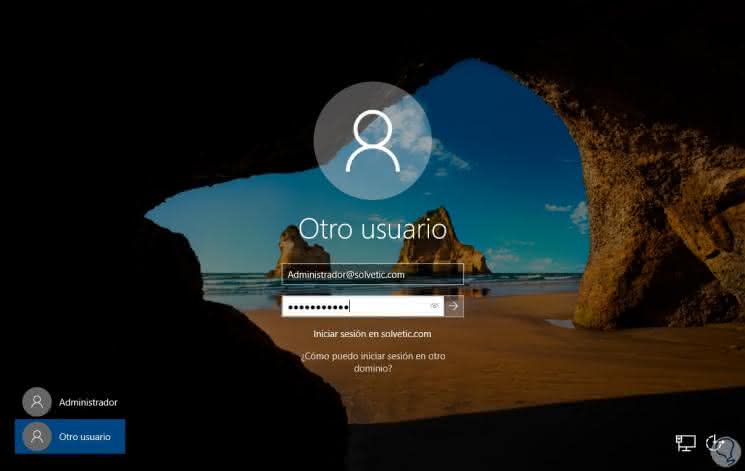
By pressing Enter we access the system and we can see that it has been added correctly to the Windows Server 2008 R2 domain:
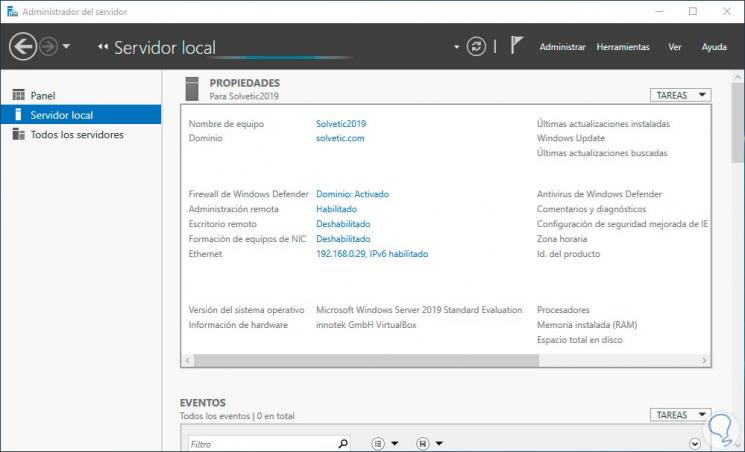

Login Join up!