The use of databases has become an essential point in many organizations due to their functions, scalability and dynamism when it comes to managing and managing large amounts of data, offering the administrator control over each one of them. reason that we can find different solutions in the market (both free and paid) to manage the databases but today in TechnoWikis we will talk about two in particular and they are MySQL and MariaDB..
What is MySQL?
MySQL has become over time one of the most used open source SQL database management systems and managed by thousands of users, MySQL has been developed and supported by Oracle Corporation which gives us one more point of reliability.
The databases that we implement in MySQL are relational, that is, MySQL stores the data in separate tables but does not place all the data registered in a single store, this is done for availability and integrity issues, in addition to this with MySQL we can configure various rules by which we will manage the relationships between data fields.
MySQL handles an aspect called Structured Query Language (SQL) which is a standardized language that allows us to access databases directly, embed SQL statements in written code using a different language or make use of APIs for working in the bases..
MySQL works normally on both client / server or embedded systems which consists of a multi-threaded SQL server which supports different back-end, multiple programs and libraries of multiple clients and many more advantages.
features
Among the different features that we find in MySQL we have:
- It is written in the C and C ++ language
- You can work smoothly on different platforms such as CentOS, SUSE, RedHat, Ubuntu, Solaris, Debian, Windows Server, FreeBSD and macOS.
- MySQL makes use of the design of multilayer servers which have independent modules.
- It has multi-threaded technology to make use of multiple CPUs if they exist in the physical equipment.
- Offers transactional and non-transactional storage engines.
- MySQL has a memory allocation system which is based on threads to streamline operations.
- It implements hash tables in the memory sectors which are subsequently used as temporary tables.
- MySQL manages multiple types of data such as signed / unsigned integers of 1, 2, 3, 4 and 8 bytes long, floating, double, char, varchar, binary, varbinary, text, blob, date, time, date, hour, hour, hours, date, time, set and more.
- Execute SQL functions by taking an optimized class library.
- It has better password security levels as it uses encryption for all password traffic when we connect to a server.
- Compatible with large databases.
- Support up to 64 indexes per table and many more features.
What is MariaDB
Another of the most popular database engines today is MariaDB which has been conceived by the initial MySQL developers and is open source to be accessible by everyone.
MariaDB is responsible for converting the data into structured information taking as criteria different methodologies and integrated features, in addition, MariaDB has a relational database which integrates an SQL interface to access the data in a simple and secure way and as a point Extra MariaDB has GIS and JSON features..
features
Some of the features of MariaDB are:
- It has dynamic columns such as COLUMN_ADD, COLUMN_CHECK, COLUMN_CREATE, COLUMN_DELETE, COLUMN_EXISTS, COLUMN_GET, COLUMN_JSON, COLUMN_LIST
- MariaDB makes use of a standard query language.
- It can be run on various operating systems such as Linux, FreeBSD, macOS and more.
- MariaDB has a selection of storage engines, where you will find high performance storage engines, which will allow us to work with other RDBMS data sources.
- MariaDB offers us Galera cluster technology.
On this day TechnoWikis will explain in detail how to install both MySQL and MariaDB in the new Debian edition which you can download for free at the following link:
Debian 10
1. How to install MySQL on Debian 10
Step 1
For this process we will execute the commands as root users or in such case we must have the sudo permissions for this purpose.
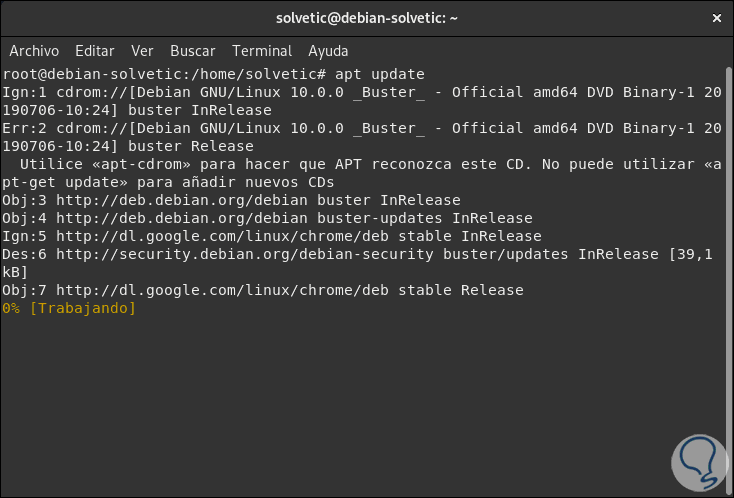
First, let's update the system packages by running:
apt update
Step 2
Then we will upgrade the libraries, packages and repositories by running:
apt upgrade
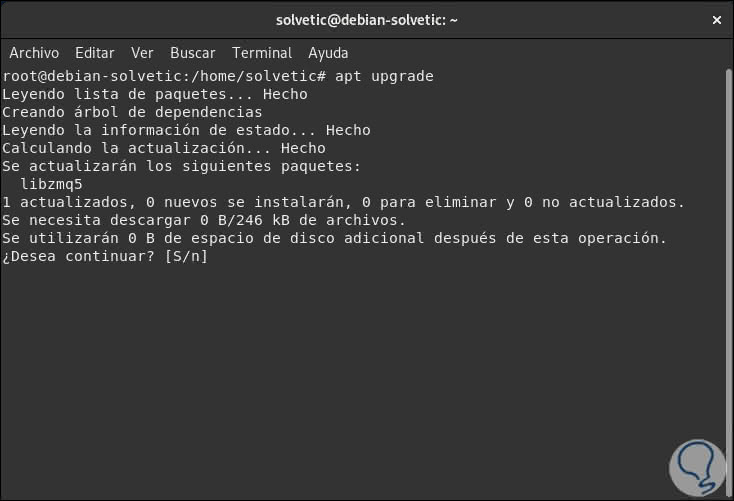
Enter the letter S to confirm the action.
2. How to configure MySQL PPA repositories in Debian 10
Step 1
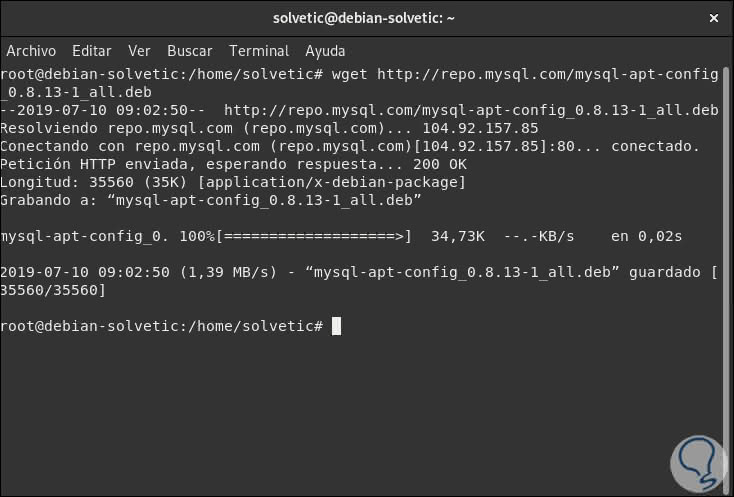
Once this process is completed correctly, we will configure the official MySQL PPA repositories which will allow us to carry out the installation tasks properly, for this we will execute the following:
wget http://repo.mysql.com/mysql-apt-config_0.8.13-1_all.deb
Step 2
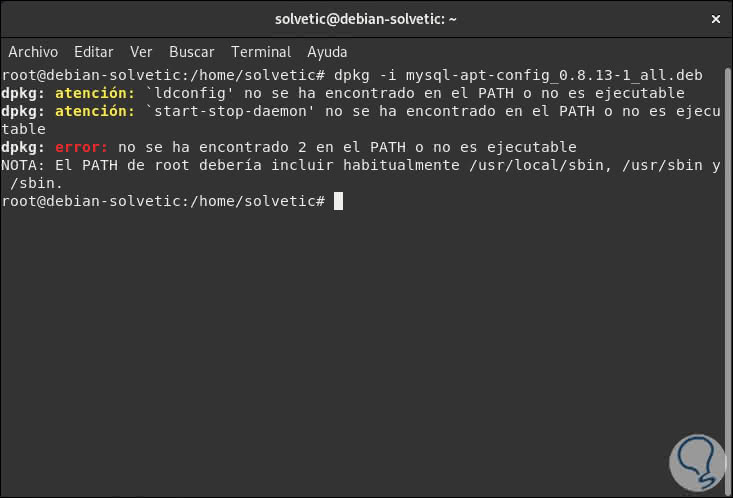
Once downloaded we will decompress it by running:
dpkg -i mysql-apt-config_0.8.13-1_all.deb
You may encounter the following error:
Step 3
To correct this you must edit the following:
nano / etc / profile
There you will see the following:
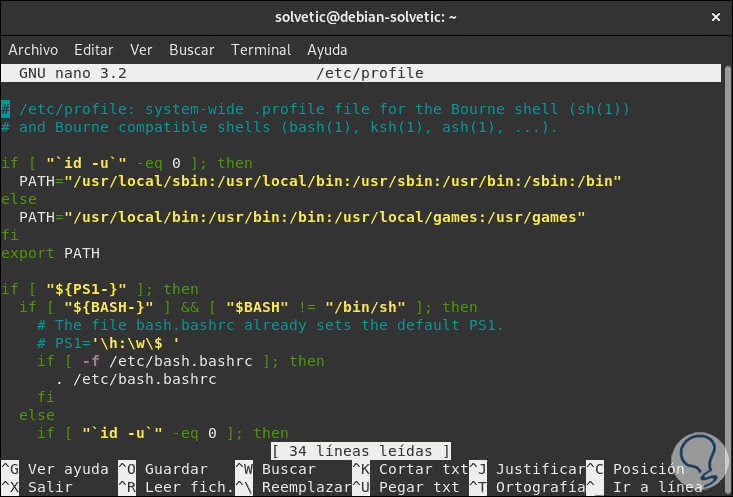
Step 4
The if line determines whether the user is root or not and the PATH = line will modify the value of the variable, to correct this error we will edit the second line of the variable which will be as follows:
PATH = "/ usr / local / sbin: / usr / local / bin: / usr / sbin: / usr / bin: / sbin: / bin: / usr / local / games: / usr / games"
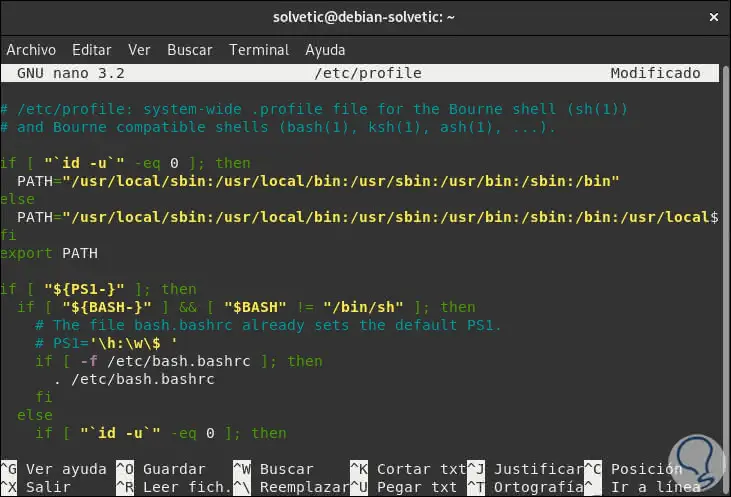
Step 5
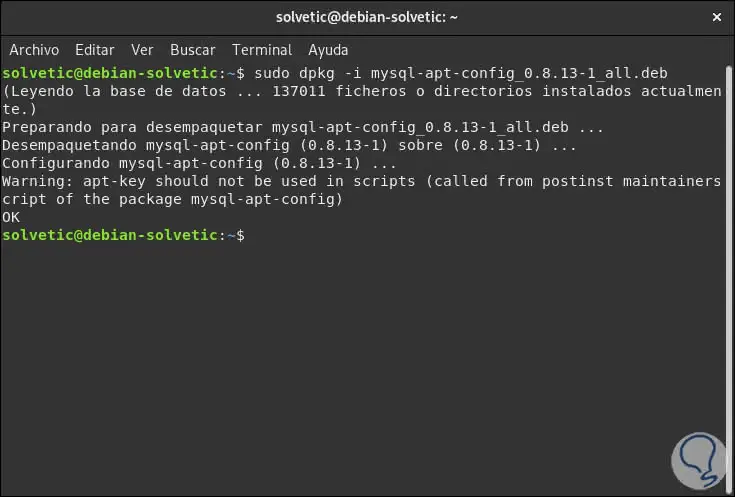
We save the changes using the Ctrl + O keys and exit the editor using the Ctrl + X keys. Now, if we repeat the sudo command
During dpkg -i mysql-apt-config_0.8.13-1_all.deb we will see that it is executed correctly:
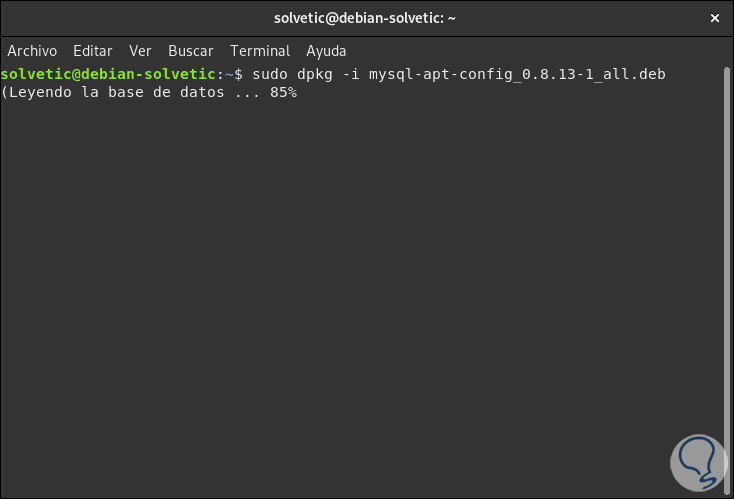
Step 6
During this process the following window will be displayed where we will select the type of product to be installed:
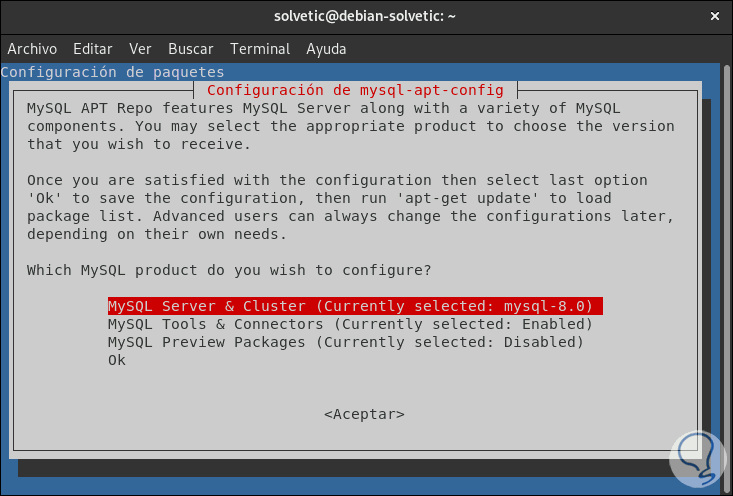
Step 7
We give Enter and now we select the version:
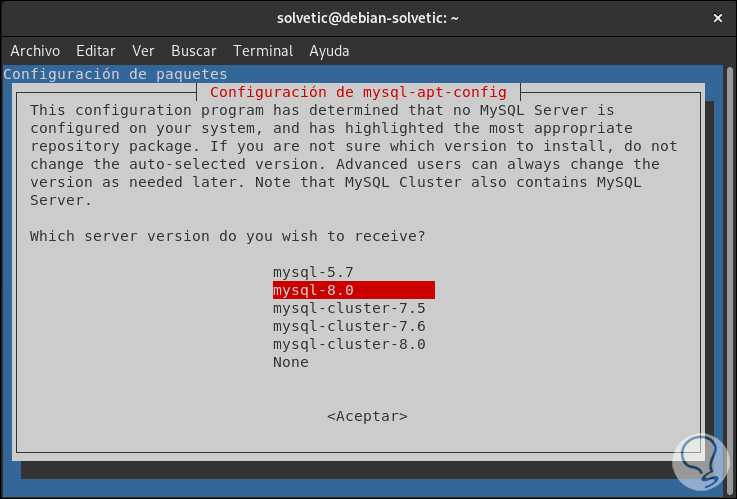
Step 8
We will continue with the installation process:
3. How to install the MySQL server on Debian 10
Step 8
Now, in Debian 10 buster we will execute the following command to install the MySQL server:
sudo apt install default-mysql-server
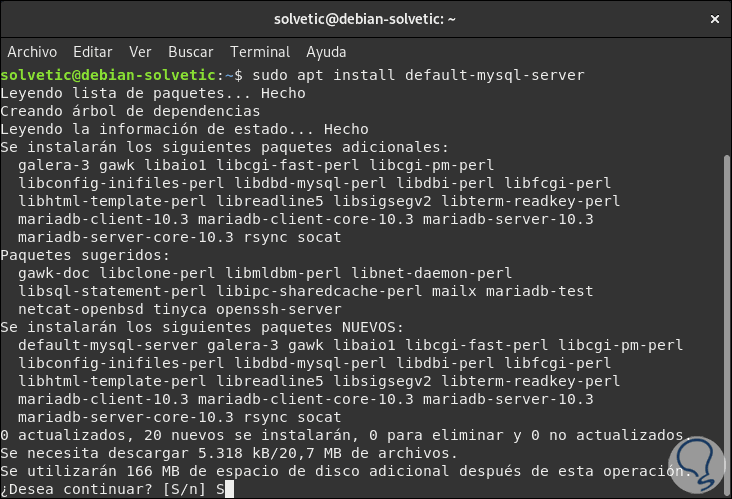
Step 9
There we enter the letter S to confirm the action and the following window will be displayed where we will assign the MySQL root password:
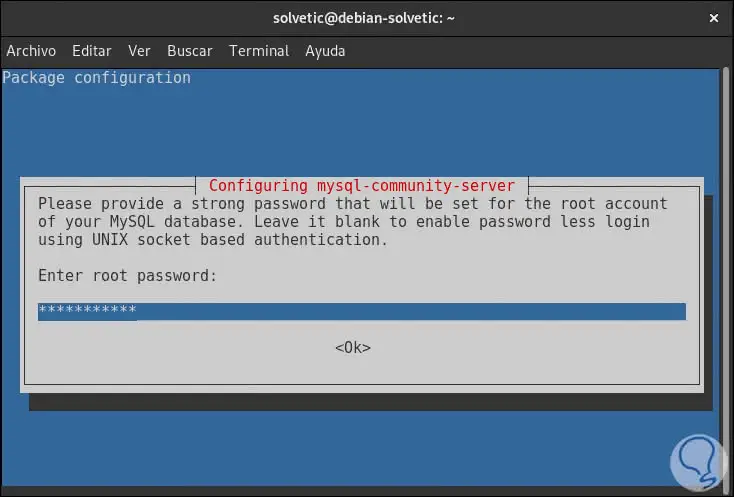
Step 10
Press Enter and we must confirm the password entered:
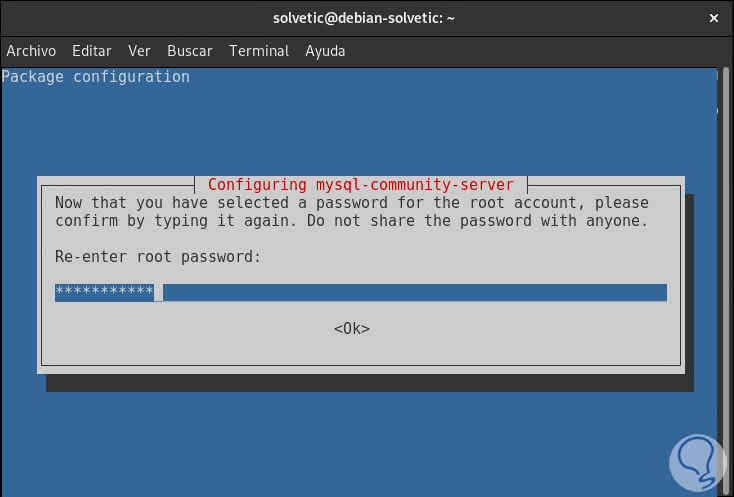
Step 11
Press Enter and we will see the following information:
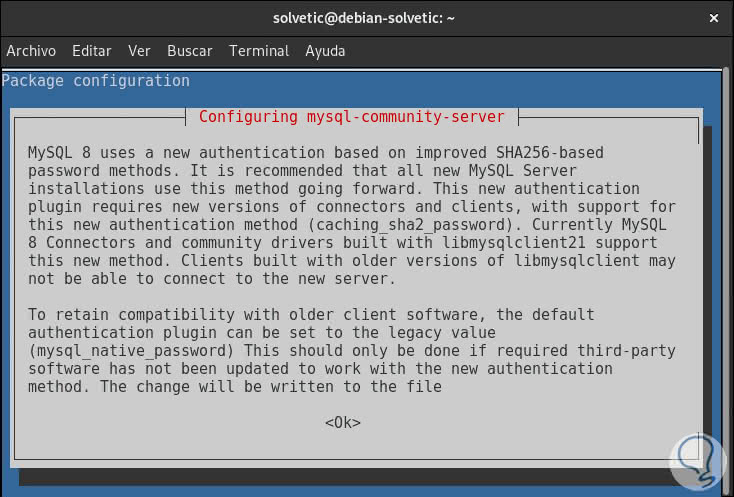
Step 12
There we can define the MySQL authentication mechanism, by clicking on OK we will see the following where we will define this aspect:
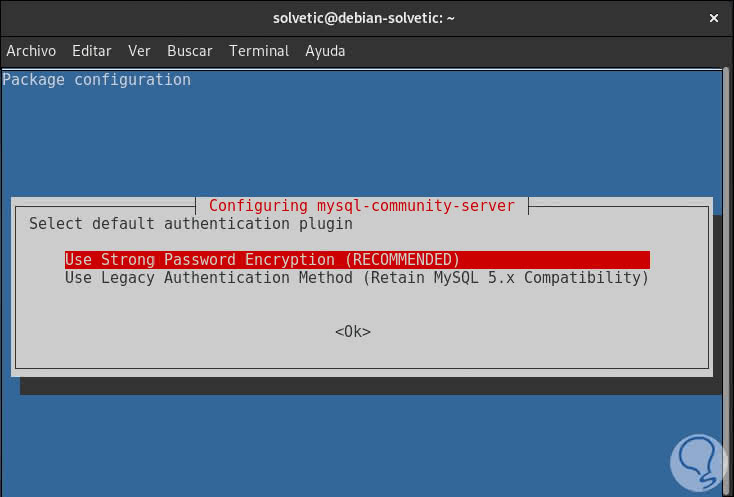
Step 13
This will end the MySQL installation process on Debian 10:
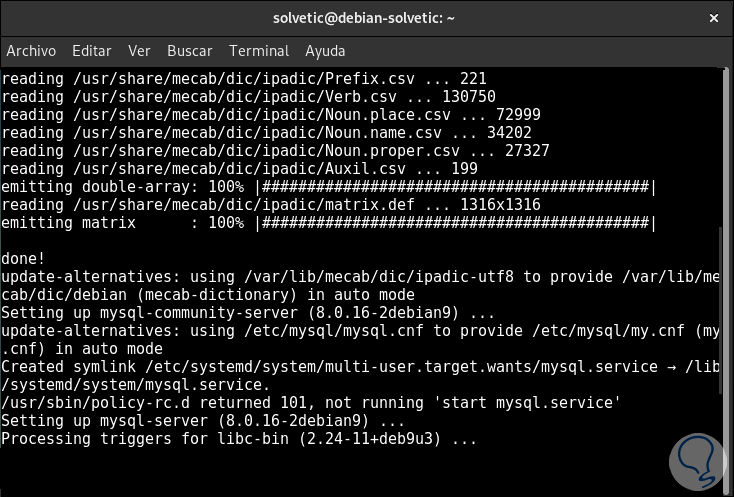
Step 14
Finally, we will start the MySQL service by running:
sudo systemctl restart mysql
Step 15
Then we ensure the installation of MySQL with the following order:
sudo mysql_secure_installation
Step 16
There, first, we will enter the root password defined before:
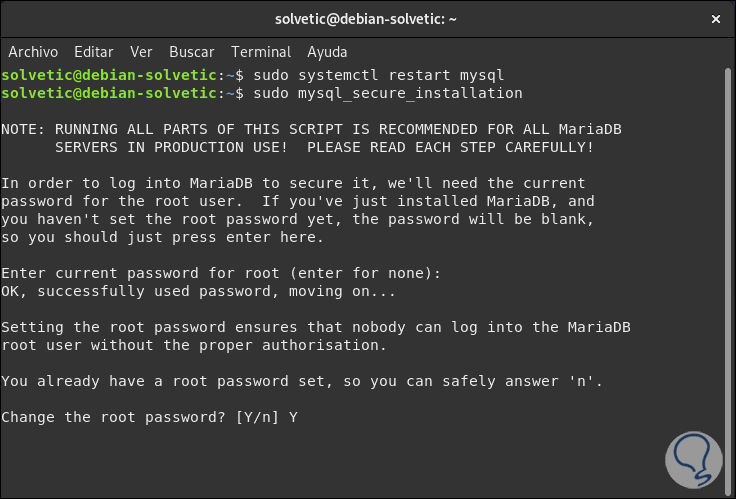
Step 17
There will be displayed a series of questions associated with aspects such as:
- Configure a new password for the root account.
- Allow access only from localhost for the root account.
- Remove anonymous access to the database.
- Delete the test database to which all users have access.
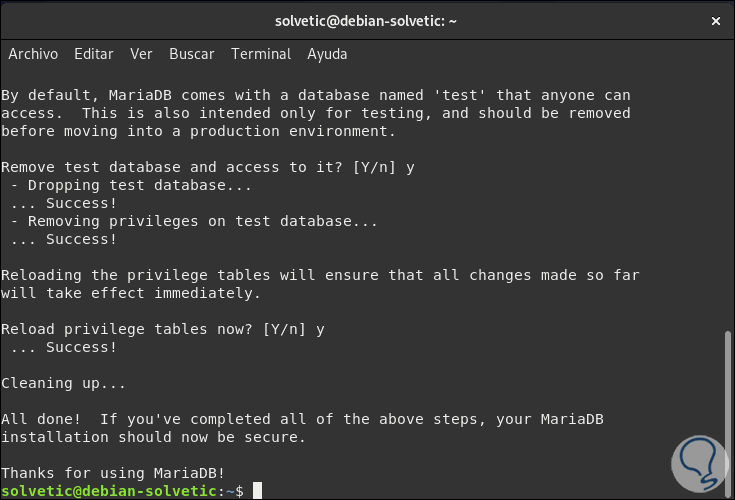
Step 18
Finally, we can connect to MySQL to see that it works correctly:
sudo mysql -u root -p
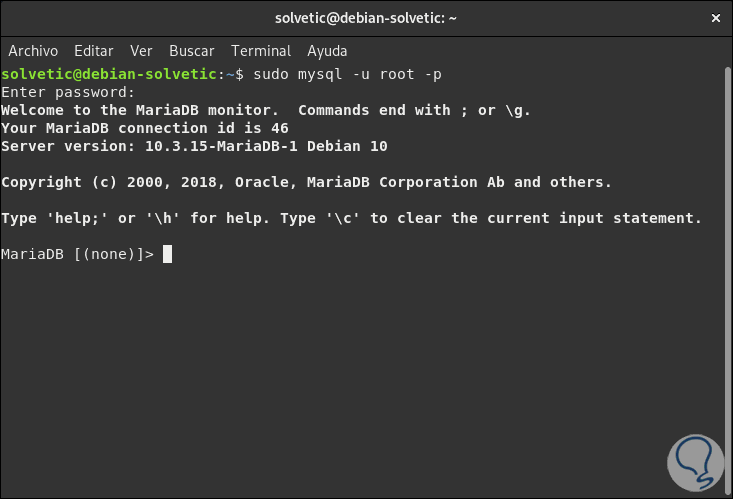
Note
There MariaDB indicates that as of Debian 10 MariaDB is the default Debian database, it has the same MySQL configuration.
4. How to install MariaDB on Debian 10
Step 1
To install MariaDB first we will update the system packages by running:
sudo apt update && sudo apt -y upgrade
Step 2
The next step will be to install the MariaDB components (client / server) with the following command:
sudo apt -y install mariadb-server mariadb-client
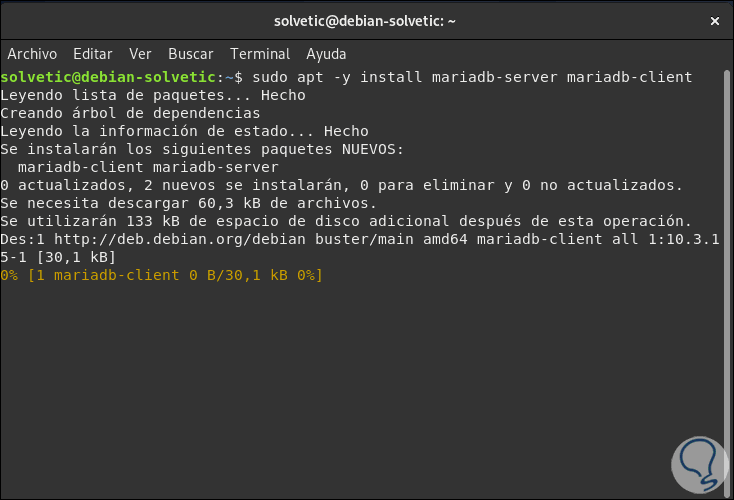
Step 3
We can validate the installed version by running:
apt policy mariadb-server
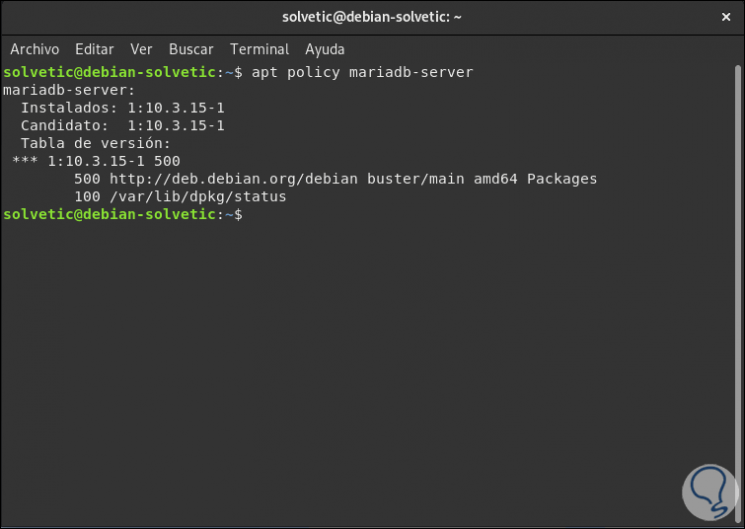
Step 4
Now we are going to check the status of the MariaDB service, for this we execute the following order:
systemctl status mariadb
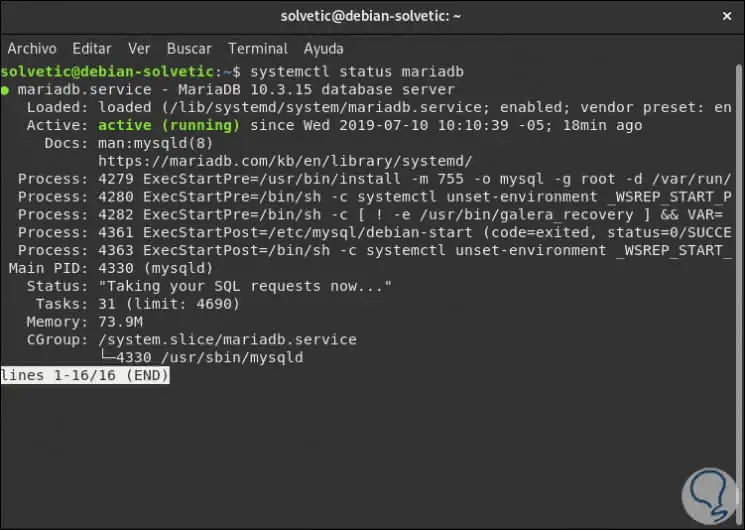
5. How to configure the MariaDB installation on Debian 10
Step 1
Like MySQL, we must ensure the installation of MariaDB with parameters such as password change, elimination of test bases and others, for this we execute:
sudo mysql_secure_installation
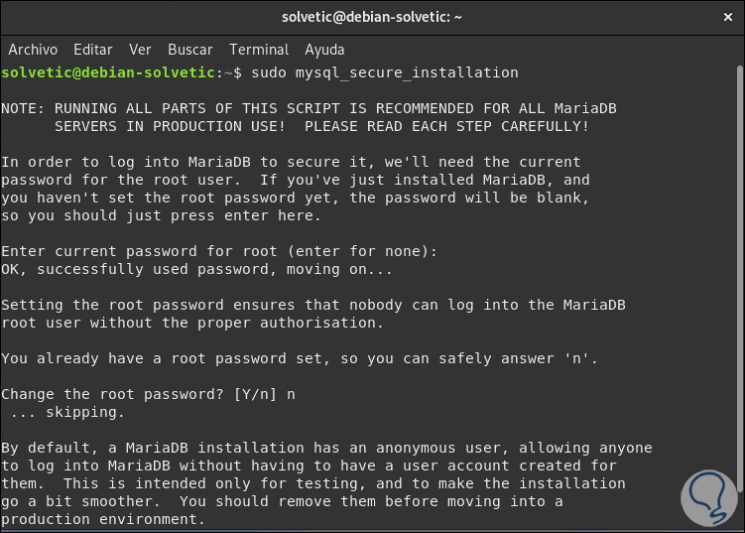
]
Step 2
Once configured this we will see the following:
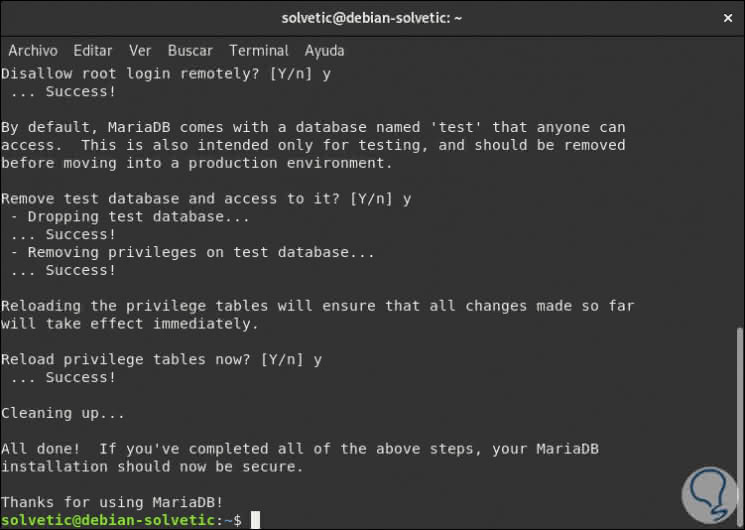
Step 3
Finally, we will access the MariaDB database with the following line:
sudo mysql -u root -p
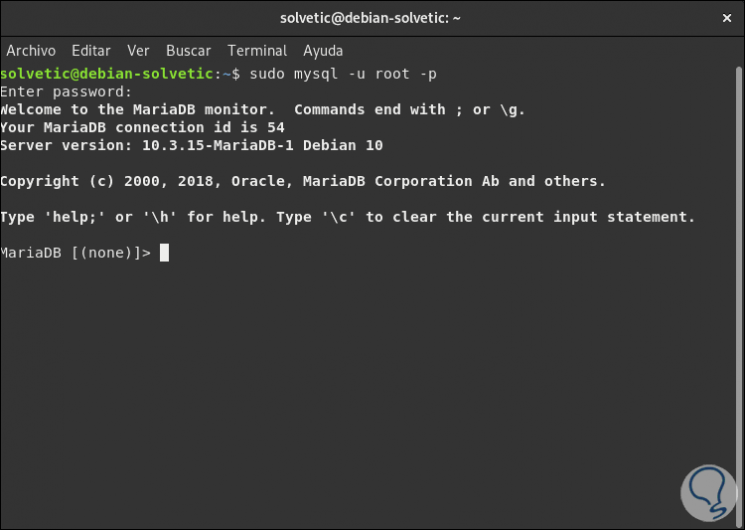
Step 4
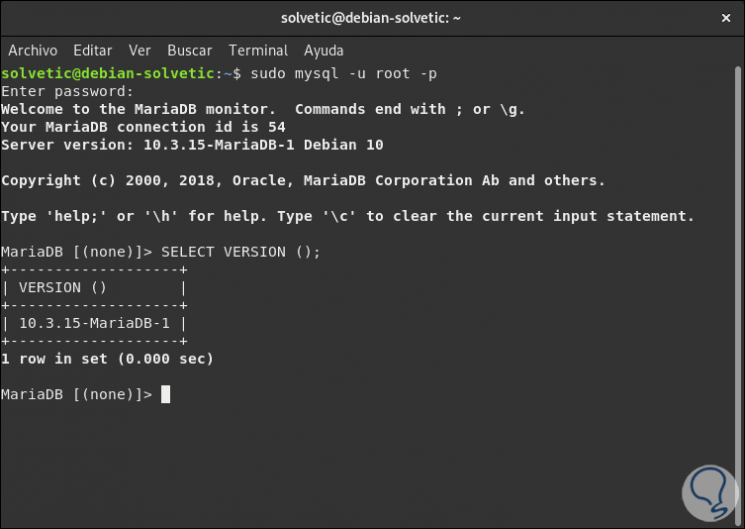
To check the version used we must enter the following order:
SELECT VERSION ();
With any of these two database engines it will be possible to manage all the data registered on our servers globally and completely with ease of control over them.