Red Hat is one of the operating systems at the organization level that attracts the most attention in thousands of users for all that it has to offer in terms of scalability , security and above all performance for all types of corporate approach. We can see below a series of Red Hat options within the system itself..
Red Hat options
When we talk about scalability it is important that we keep in mind that Red Hat offers us system options such as:
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server for High-Performance Computing (HPC).
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux for Power.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux for IBM z Systems.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux for SAP Applications and more
Each of them has a structure for a special area of ​​the public, so it is one of the most common and known Linux distros, but you must also understand that to use Red Hat requires the use of an ID which you can create in a way Free on the official Red Hat website, once registered we can download Red Hat 8 at the following link:
Red hat 8
Red Hat functionalities
Just to understand a little everything that Red Hat gives us these are some of its features:
- Integration of the update-crypto-policy command with which it will be possible to switch between the default, inherited, future and fips modes.
- The LUKS version 2 (LUKS2) format has been added to replace the LUKS format (LUKS1).
- Now the GNOME Shell has been updated to version 3.28.
- Python 3.6 is the default Red Hat 8 version.
- It has kernel support for eBPF tracking
The purpose of TechnoWikis on this day is to explain in detail how you can install Red Hat 8 in VirtualBox which you find available for free at the following link:
Virtualbox
The goal of virtualization is to allow us to create a secure environment where we can test new operating systems, compilations and applications to see their behavior without ever affecting the real environment. In addition to this, virtualization helps us in economic matters since when mounting a virtual machine we should not acquire additional hardware. Without further ado let's see how to create our Red Hat 8 virtual machine in VirtualBox .
1. Create the Red Hat 8 virtual machine in VirtualBox
Step 1
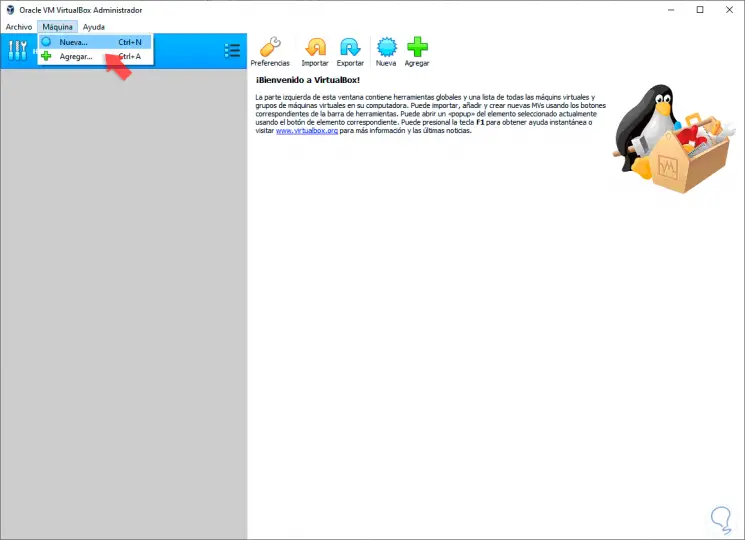
Once we install VirtualBox and download the Red Hat 8 ISO image, we access VirtualBox and proceed to create the virtual machine using one of the following options:
- By clicking on the New button from the central panel
- Go to the Machine / New menu
- Use the following key combination:
+ N Ctrl + N
Step 2
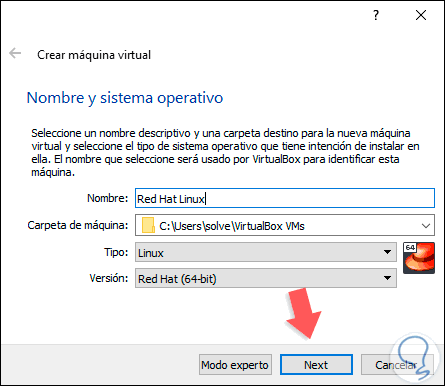
Once we click there, the following wizard will be displayed where we define the following:
- Route where the virtual machine will be hosted
- System type, in this case Linux
- System version which in this case is Red Hat (64 bit)
Step 3
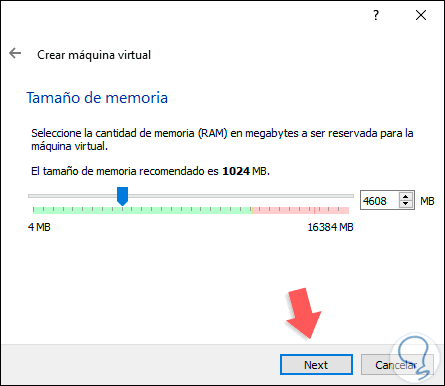
We click Next and now define the amount of RAM to allocate to the Red Hat 8 virtual machine:
Step 4
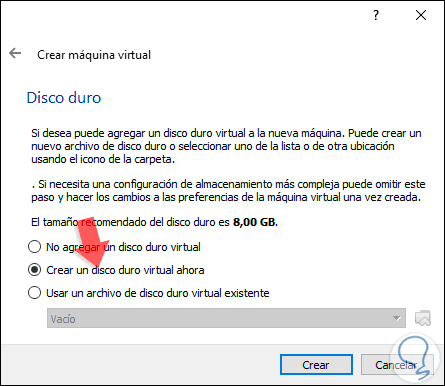
In the next window we will see the option of the hard disk and there we can create a new virtual hard disk (default option) or use an existing disk:
Step 5
In this case we will create a new virtual hard disk and click on Create and then define the type of hard disk to create:
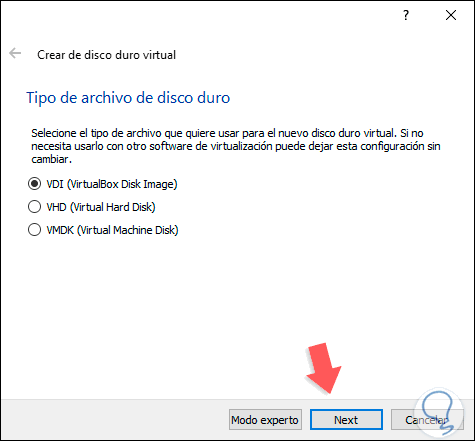
Step 6
In the following window we will define the way in which the space on the hard disk will be stored, in a fixed or dynamic way:
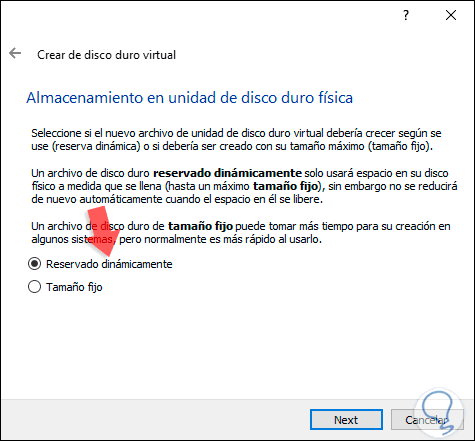
Step 7
Click on Next or Next and now we will define the path where the hard drive will be, as well as its size:
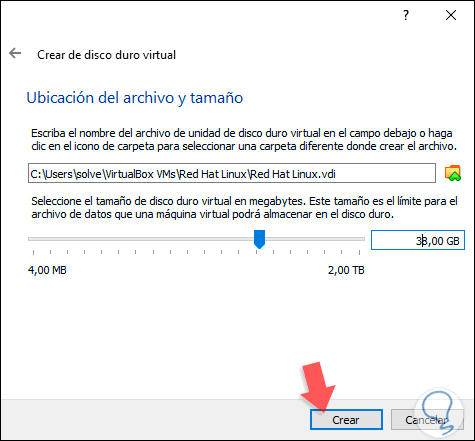
Step 8
Again click on Create and we will have the structure of the Red Hat 8 virtual machine:
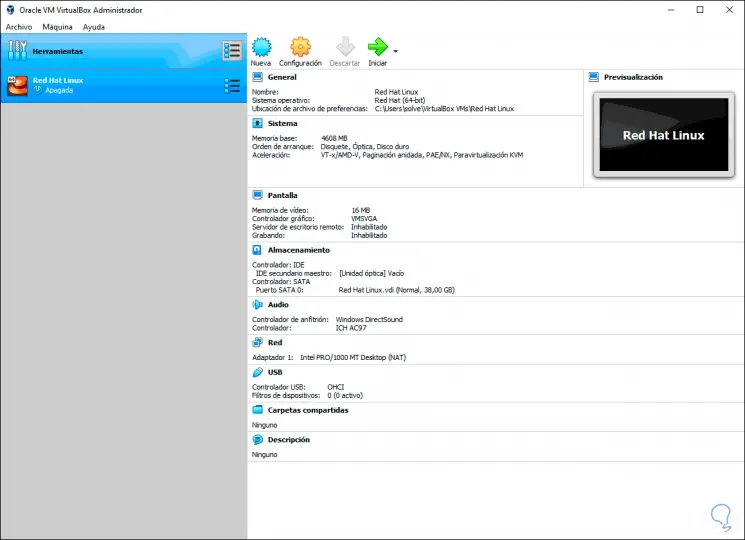

Login Join up!