One of the great vulnerabilities that exist today in the world is impersonation and not only because of the theft of our identification documents but because both organized gangs and solitary attackers have reached the point of creating strategies so well done that at some point we can fall into their traps even if we are more careful..
Internet has become one of the obligatory daily uses of the whole world since without it it would not be possible to access our emails, listen to music or watch movies via streaming , make videoconferences of business or access any of the social networks To talk and stay up to date with our friends. But behind all this, there is a more than potential danger where attackers look for a small gap or clue that we give to obtain sensitive information such as bank details, social security, travel and more.
Frequent internet scams
The chances of falling into scams of this type have increased over time, since the strategies of the attackers are getting better and better.
Scam applications
SMS scam
Fake antivirus
There are various ways of supplanting the identity of users and one of the most traditional ways is phishing. We have heard it again and again, it is important to keep in mind that it is and understand that its penetration and attack tactics have gradually evolved..
What is phishing
Phishing is popular as it is the way in which attackers create media (websites, ads, SMS messages, etc.) so that as users we provide sensitive personal information such as:
This task is carried out through the sending of fraudulent emails or doing that as a user, when we click, being redirected to a fake website.
What is considered an advantage of being able to access our banks and make purchases either from our PC or from our mobile phone, has become a headache for millions of people since there you need to enter credit card details or debit, including CVC and expiration date, bank account numbers with your access, which we do not know for sure if behind this there is a malignant force that can leave us the account at zero.
A clear example of this is the following email received from “PayPalâ€:
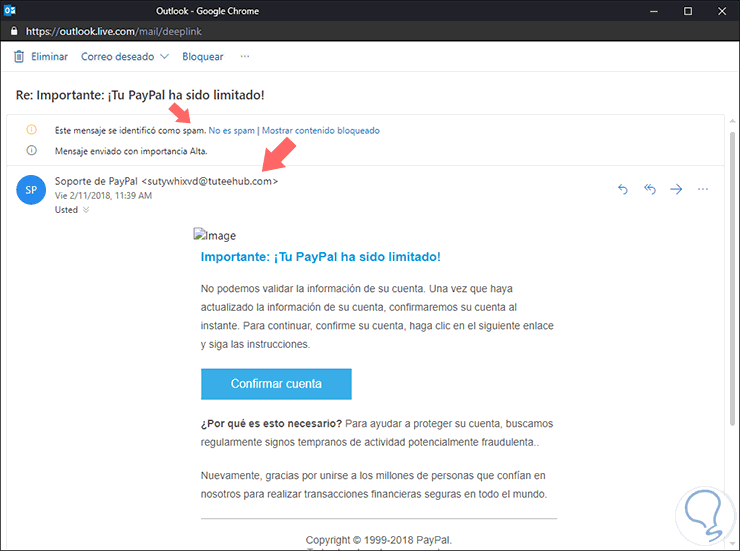
We can see that apparently the mail comes from a secure sender, it is more, we can see that the message has been sent with high priority requesting the confirmation of our PayPal account, worse, is it really PayPal who sent this? We must not have certifications in white hacking or systems penetration to verify details that make this email a fraud, let's just see the following that betrays this received email:
- First, it went directly to spam (Not always the safest, but it is a first step).
- Second, the message is with a Re (Forwarded), from whom or because, we do not know, it should be a unique message but not a forwarding.
- Third, and perhaps most importantly, if the mail comes from PayPal it should have a syntax more or less like [email protected], but we clearly see a domain tuteehub.com and a user sutywhixvd which by nowhere can give us the security That is something reliable.
Now, if we click on the Confirm Account button, two situations can happen:
- The first is to be redirected to a fake site where we must enter users and passwords so that the attacker then accesses without any problems and plays with our resources.
- As a second option, we can download malicious software on the system to capture all the actions performed there.
Phishing always gives the impression of coming from legitimate and reliable organizations such as PayPal, UPS, a government agency or the bank where we have our account registered. We recommend that entities often send messages indicating that neither by email nor by phone they request personal data, which is something to take into account the next time we receive this type of message..
Unfortunately there are more alternatives that attackers are using to access our personal information , not just emails, some of these new options are:
Injection of third-party software content
These can be represented by pop-ups or advertisements on various websites especially when we are connected to a public network and the reason for this is that being a public network we do not have the protection of the SSL secure protocol, so that the network can inject this content on the visited website
Call access
It is another technique used, not only in military intelligence, with which the attacker can listen to any connection and from there any information that is transmitted by this means.
Fraudulent ads
These are represented by advertisements where products are offered, which normally do not need to have pop-up ads, for really low costs, so, in theory we can buy a mobile device for USD 15 when it is really worth more than USD 1,000, the reason is for small defects. Which is not true.
We can see how it is a complete world everything related to phishing and for this reason TechnoWikis will give some essential guidelines to learn to identify fraudulent sites and avoid being a victim of them.
1. How to check the URL and detect fake web pages
It is the most important step that we must verify when we receive an email where our personal or financial information is involved, they are small details but they make a difference.
For this we must understand a technical detail that browsers use on their websites. This is called the line of death or Line of Death and arises when creating applications that display unreliable content which allows an attacker to be in full control of a pixel block, so that the browser controls totally the top of the window, while the pixels under the top are under the control of the site itself.
This allows that if a user trusts the pixels above the death line, it means that the navigation will be safe, but if you trust the pixels that are below the line, we may have problems, hence its direct name ( Death).
To represent this we take the following public image:
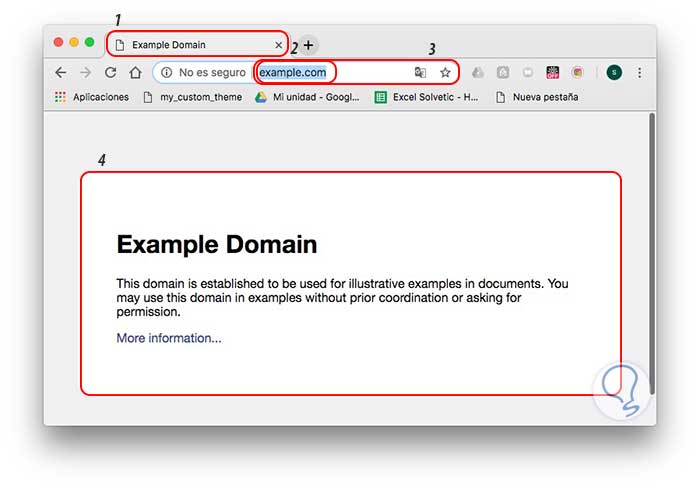
We can see that it is divided into four zones that are:
Zone 1
The attacker's icon and website title are displayed, this information is controlled by the attacker so that it can be a fraudulent site.
Zone 2
We can see the domain name of the attacker and there we can face an argument since we have seen that the HTTPS (Secure HTTP) protocol indicates that the site is reliable, but the attacker can upload something like
https://citibank-account.com / more is not related to the site
https://citibank.com which is legal.
Zone 3
We see the component of the URL path which can be totally false.
Zone 4
It is the area of ​​web content where we can run the risk of being violated with catastrophic results.
As users we cannot rely only on HTTPS, we must go one step further than it takes only a minute. In the previous example of PayPal, the site should redirect us to https: paypal.com, but no, it really addresses a site with URL http: //tabere.discov...inistersuj.html which is far from the reality of Be a reliable site.
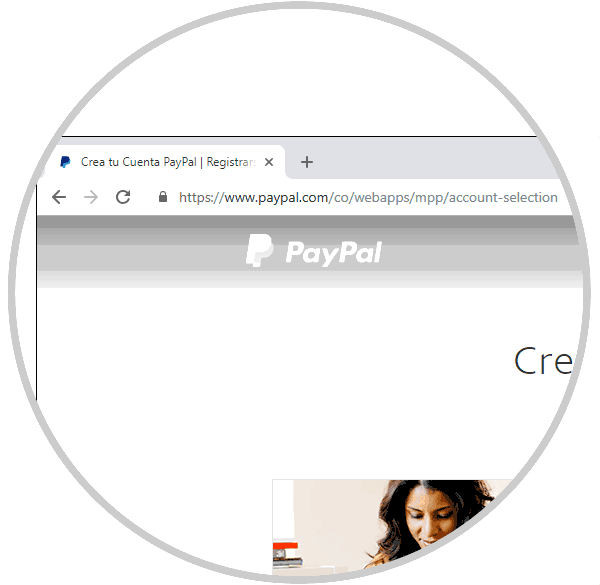
2. How to check security indicators and detect fake website
Undoubtedly, the address bar is a central point from which we can begin to validate the integrity of a website or not. We can see that in the address bar we have several connection indicators through which it will be possible to know if the connection to this website is private or not.
The Internet was originally based on HTTP, hypertext transfer protocol. This means that any type of data sent over HTTP was sent in plain text so that it could be easily intercepted and stolen, this because the Internet did not have such a giant use as it is today.
Step 1
With the passage of time, and with the constant problems generated, the SSL or Secure Sockets Layer protocol was developed and after SSL, TLS or Transport Layer Security has been introduced to give better connection security. For this reason, when we click on the lock icon located on the side of the address bar, we can see the status of that site:
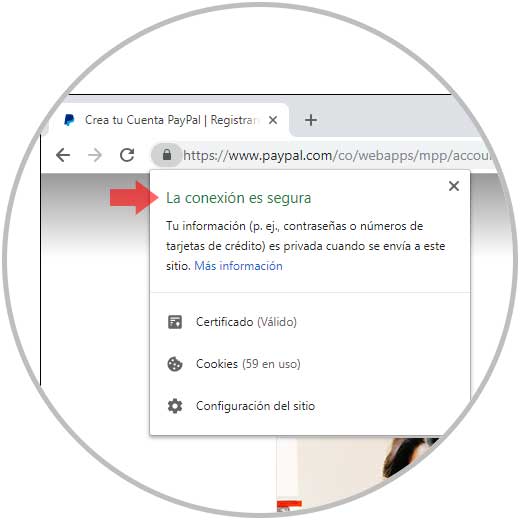
Thus, HTTP + TLS gives rise to HTTPS, we can see that today most websites use this protocol and this will tell us if we can be in a dangerous website and it is best to avoid entering personal information there as much as possible.
Step 2
The browsers also give the guidelines to identify the security of the site, we see in the previous image how Google Chrome sets a lock icon. In the case of Microsoft Edge we will see the name of the domain in green and by clicking on it we will know if it is safe or not. In the case of Firefox Quantum we will also see the domain in green with its respective security test.
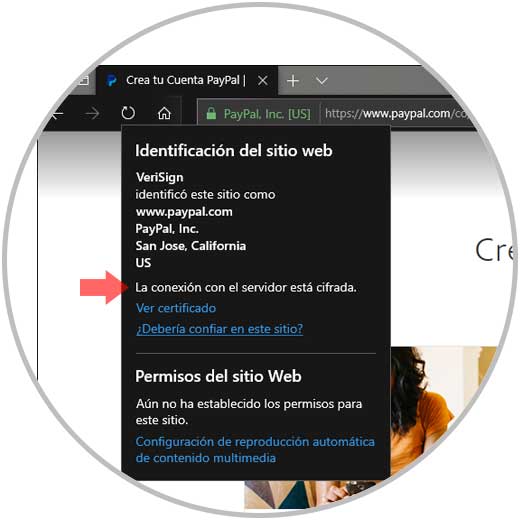
Step 3
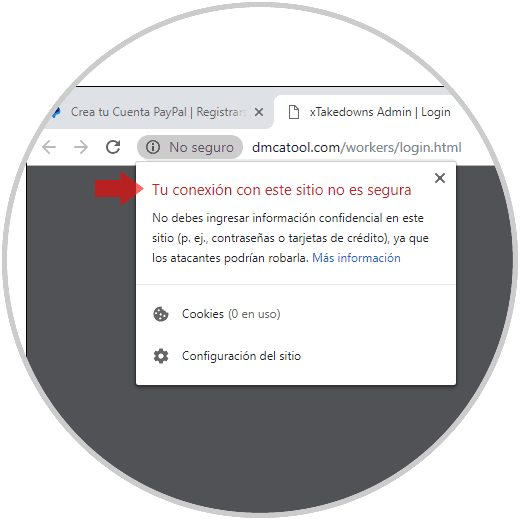
In the event that a website does not pass the security tests, we will see the respective legend and when clicking on it we will receive advice on not entering private information:
3. How to check the details of the certificates of the websites and detect fraudulent websites
This is an essential element in all websites since they must have security certificates which are implemented as an additional security measure focused on the users who make transactions on that website. These certificates allow you to encrypt the data between the client computer and the server where the website is hosted.
Currently, we have SSL security certificates which have been implemented with the best security measures so that searches, navigation and data exchange in a reliable and secure environment since these certificates can have 128 or 256 bit encryption for greater data security
If we want to validate the certificates in the respective browsers, TechnoWikis will explain how to achieve it.
How to view certificates in Google Chrome
For Google Chrome, click on the Customize and control Google Chrome button and then go to the More tools / Developer tools route, alternatively we can use the Ctrl + Shift + I keys:
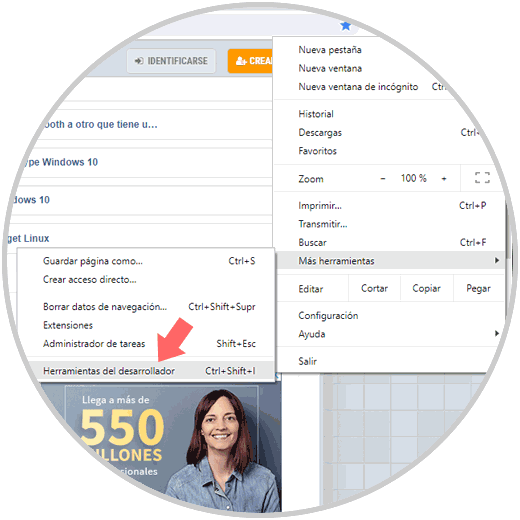
In the developer window we will go to the Security tab and there we click on the View Certificate button:
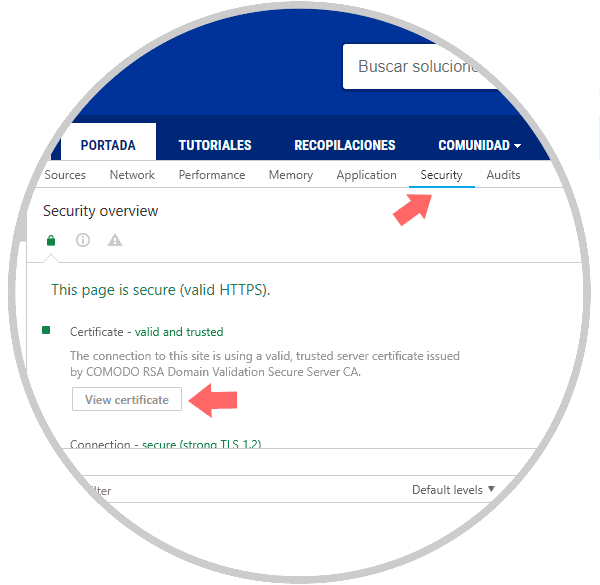
This will be the certificate we will see:
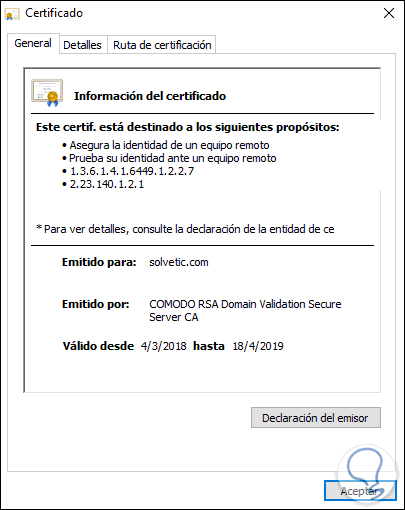
View certificates in Firefox Quantum
In the case of Quantum, we must click on the information balloon in the address bar and there select the option More information:
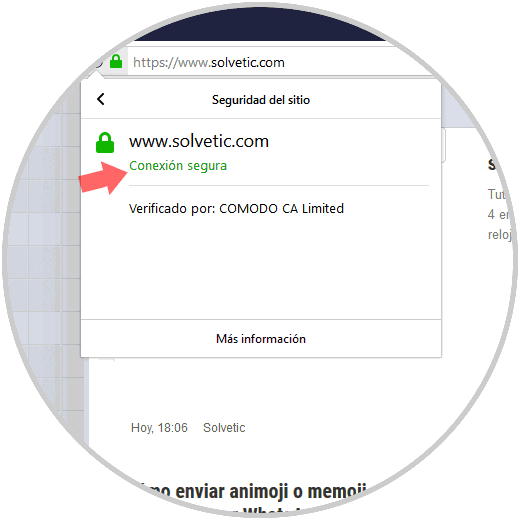
Clicking there will display the respective site certificate:
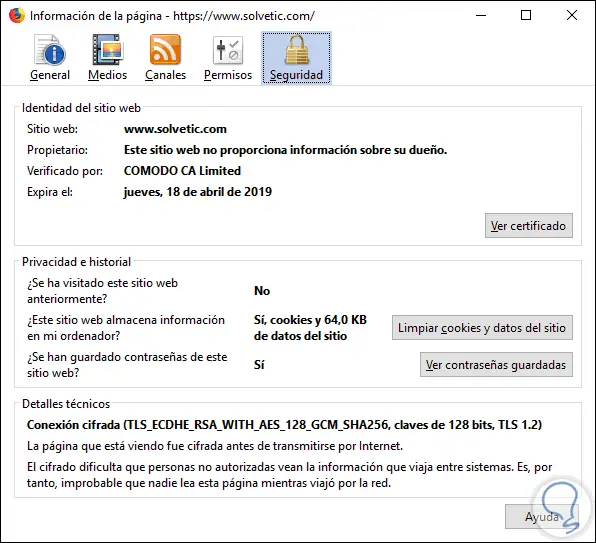
View certificates in Microsoft Edge
In this case, click on the site information icon and click on the View certificate line:
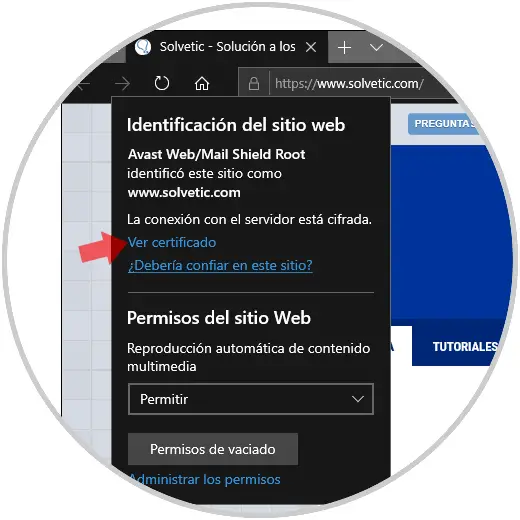
In Edge we will see the result on the right side of the browser:
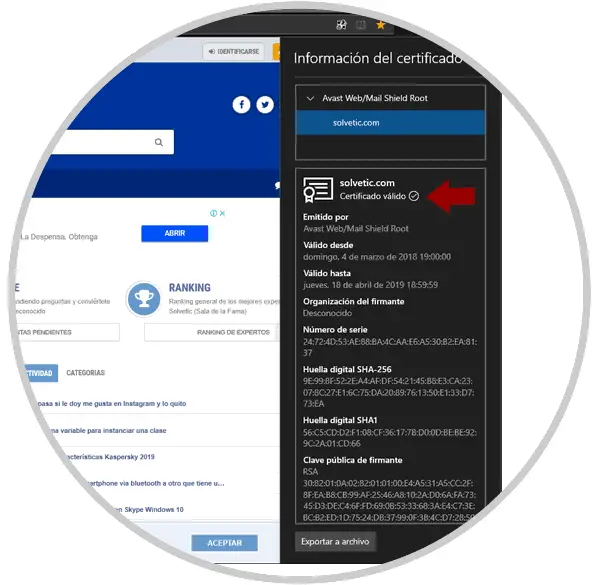
See certificates in Safari
For the macOS Mojave browser, click on the lock icon right next to the site and click on the Show certificate line:
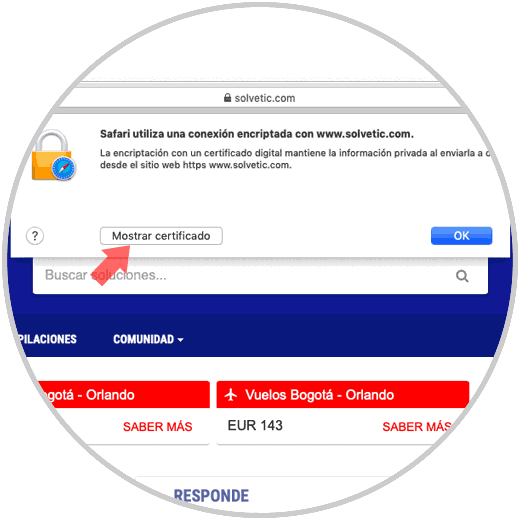
Then we can click on the Details line to access more complete certificate information:

The certificates of a secure website contain the following information:
- Serial Number: It is unique for the certificate.
- Subject: Identifies both the owner of the certificate and the organization that owns it.
- Issuer: Identifies the entity that issued the certificate for the website.
- Alternative extension: These are the list of website addresses that can use the certificate to identify themselves.
- Signature: These are the data that confirm that the certificate comes from a reliable issuer.
- Algorithmic signature: It is the algorithm that was used in the signature creation process.
- Valid from: Indicates the date from which the certificate is valid.
- Valid until: It is the expiration date of the certificate.
- Use (extended) of the key: Indicates how the certificate can be used, for example, to confirm ownership of a website (Web Server Authentication)
- Public key: Refers to the public part of the data that contains the public / private key pair, both public and private keys are mathematically linked, so the data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the key corresponding private which significantly increases your security.
- Private algorithmic key: It is an algorithm used to create the public key.
- Fingerprint: It is the abbreviated form of the public key.
- Fingerprint algorithm: It is another algorithm for creating the fingerprint.
4. How to access secure websites
Reliable websites, especially those where users' information and their money are at risk, create commercial links with security entities, those that develop products to prevent phishing, seeking to achieve a common goal of privacy and integrity of the User information.
That is why today many companies add in their logos the information that is protected by a third party:
It is natural that this would not be a fraudulent website because its malicious algorithms would be detected and could carry all the weight that the laws of each country have for this type of crime. When we access a website that has a security seal, usually on its home page, we can click there to check the status of that certificate:
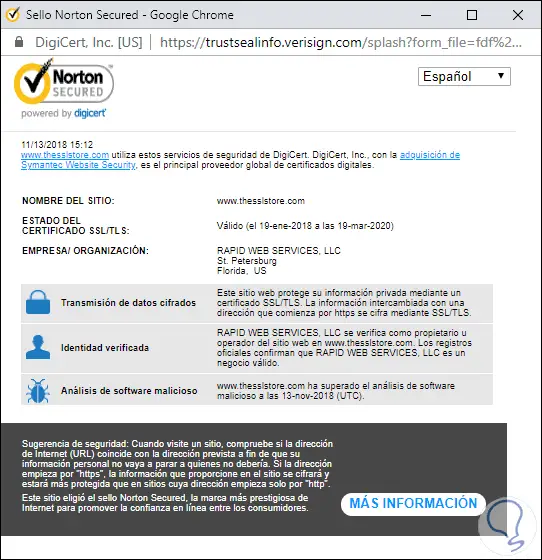
There we find specific details about everything related to the security of this site and so we will be certain that it is a suitable place to record our operations.
5. How to access the Google Safe Browsing Transparency Report and detect fraudulent websites
Google being the largest provider in the world at the internet level, offers us Safe Browsing which is a service developed by the Google security team and whose mission is to identify insecure websites on the web and notify users and Webmasters about possible failures or consequences that these sites can cause to users.
Within the Transparency Report, we can access details about the threats that are detected and the warnings that will be displayed to users. It is a central point to learn more about unsafe websites.
We can access this site in the following link.
Google Safe Browsing Transparency Report
Step 1
On this site we can access a complete report on how threats, such as phishing, affect today's world:
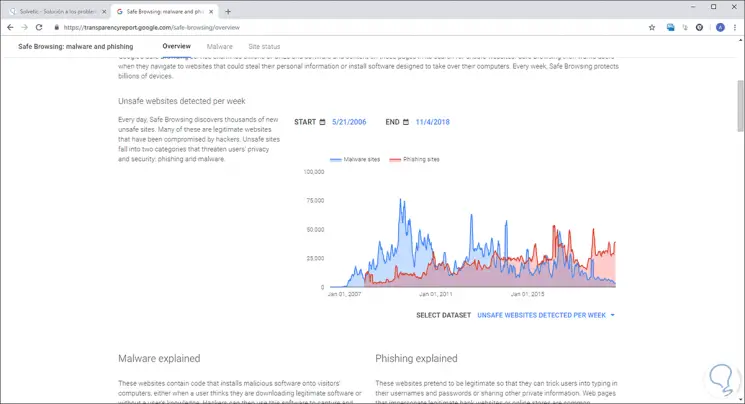
Step 2
We will also access a complete report on how malware is distributed worldwide:
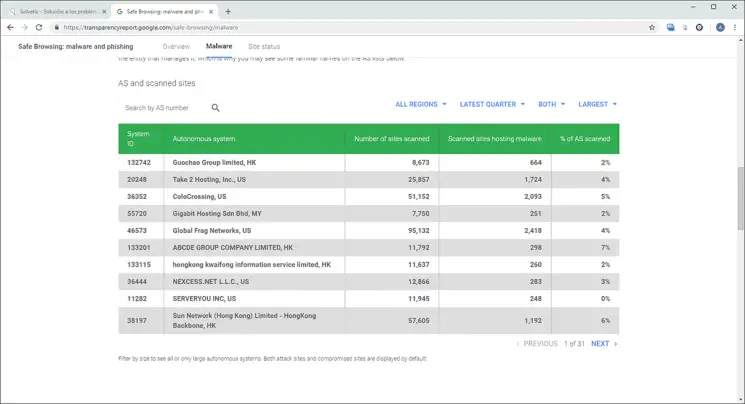
Step 3
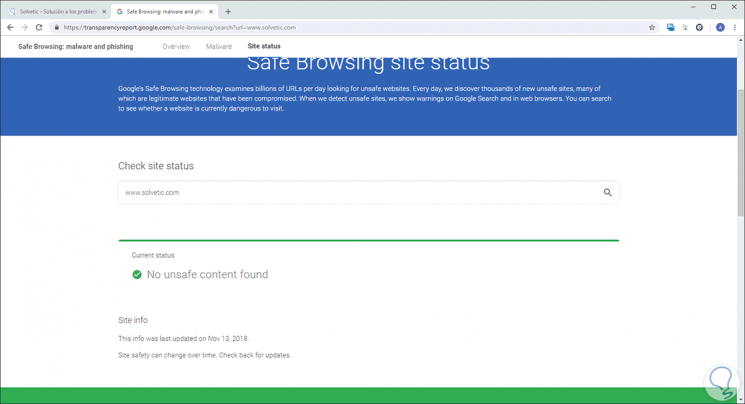
And there, in the Site status tab, we can enter the URL to analyze and thus determine whether or not it is an insecure site:
6. How to know information about a domain or IP address
Another method that we can use to detect if a website is fraudulent or not, is WHOIS. It is a public directory which shows us the information of a domain and in this way we can know who is the owner of this domain.
whois
Step 1
All you have to do is access the following website, and write the name of the page we want to analyze.
Step 2
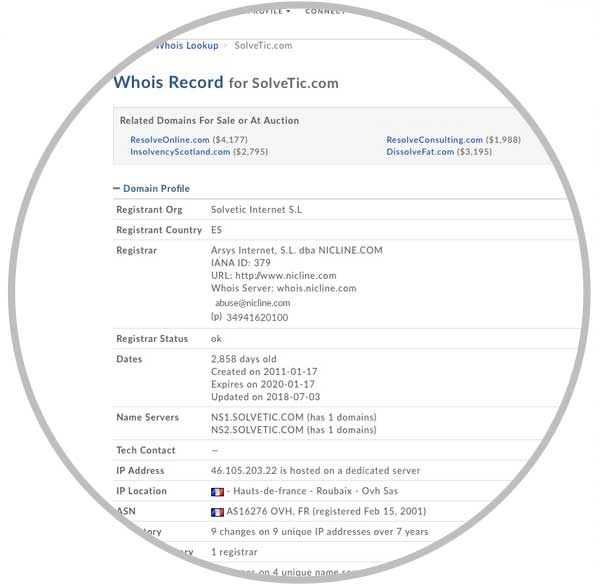
We will see that below is different information related to the page we are analyzing.
7. Tips on how to avoid being victims of phishing
Although phishing has taken a lot of boom, as users we can be aware of this and take some security measures such as:
- Be cautious and do not respond or click on links in unsolicited emails or on platforms such as Facebook.
- Do not open attachments from unsolicited emails.
- Protect passwords, if necessary modify them by strong passwords, and do not indicate them to anyone.
- Do not give any confidential information to another person by phone, in person or through an email.
- Check the URL of the site, remember that the web address may seem legitimate, but this URL may be misspelled or your domain may be different as .edu when it should be .gov.
- Periodically update both the browser and the operating system.
- To analyze in detail the text of the website since in many occasions the pages are made from other countries with a language different from ours and makes use of translators that do not have coherence in their content.
- If the site has contact numbers, try calling to validate that everything is real and request more information.
- Validate that the legal notice or company information is available on the website.
We have seen how phishing is growing rapidly and every day captures more unsuspecting in its trap to obtain confidential information and thus profit from the error or bad information of many users, TechnoWikis invites everyone to keep these guidelines in mind and avoid Be one more on this list.