The use of Linux systems is ideal for security and scalability of applications, but when it comes from another operating system we can find ourselves in various situations that can take us by surprise and one of them is to create a file, in Linux it is It is possible to use various alternatives to create a file and it can be empty to later record information in it or to enter the text from the moment this file is created..
Linux distributions make use of plain text files where key configurations in the behavior of the system are stored and we speak for example of /etc/hosts where searches are stored in static tables for host names and in this way many paths of administrative tasks, so with that in mind we are going to see some methods to create files from the terminal in Linux and in this case we will use Ubuntu.
To stay up to date, remember to subscribe to our YouTube channel!
SUBSCRIBE ON YOUTUBE
1 Create empty Linux file using >
Linux gives us the possibility of making use of redirection operators, for this example the ">" operator can be used to redirect the output of a command to a file but not show its result in the console, apart from redirecting the output as well will give us the opportunity to create a new file.
Step 1
To use this operator we are going to open the terminal and in the console we will use the following syntax:
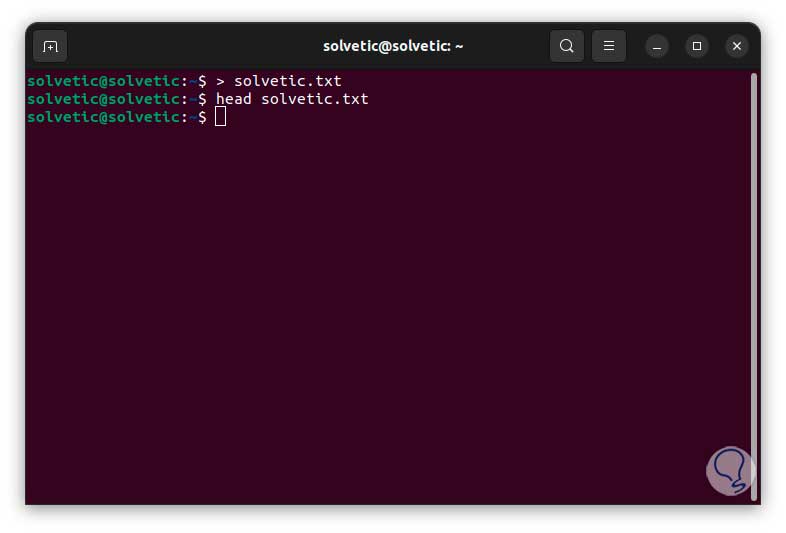
> name.txt
Step 2
We are going to check that it is a blank file, without content, we will use the head command and the file name to see that it does not have any text:
head file.txt
2 Create empty linux file using touch
The touch command in Linux allows us to create an empty file or update the access and modification timestamps of a file that is already available in the system, the global options for using touch are:
- -a: allows to change only the access time
- -c: if the file does not exist, it will not be created
- -d: is responsible for updating access and modification times
- -m: makes the change of the modification time
- -r: makes use of file access and modification times
- -t: create a file using a specified time
Step 1
To use this command we open the terminal and execute the following:
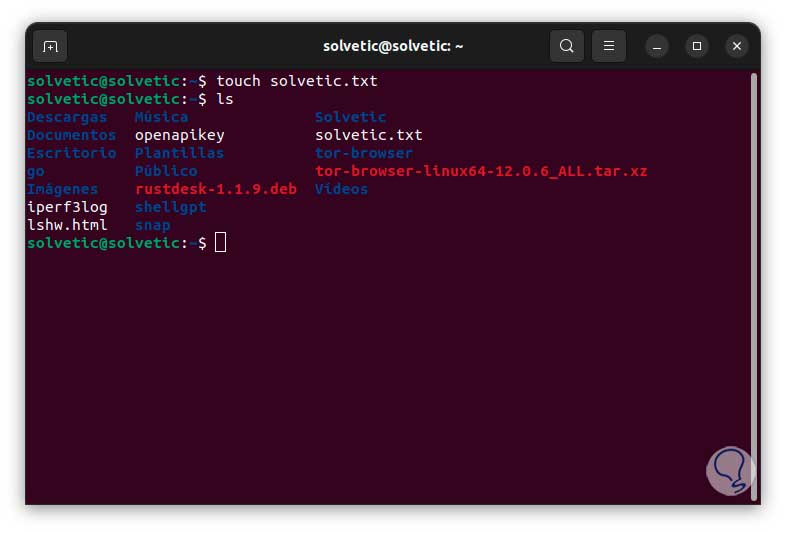
touch name.txt
Step 2
We can use the ls command to verify that the file has been created correctly:
3 Create empty Linux file using > with text
Step 1
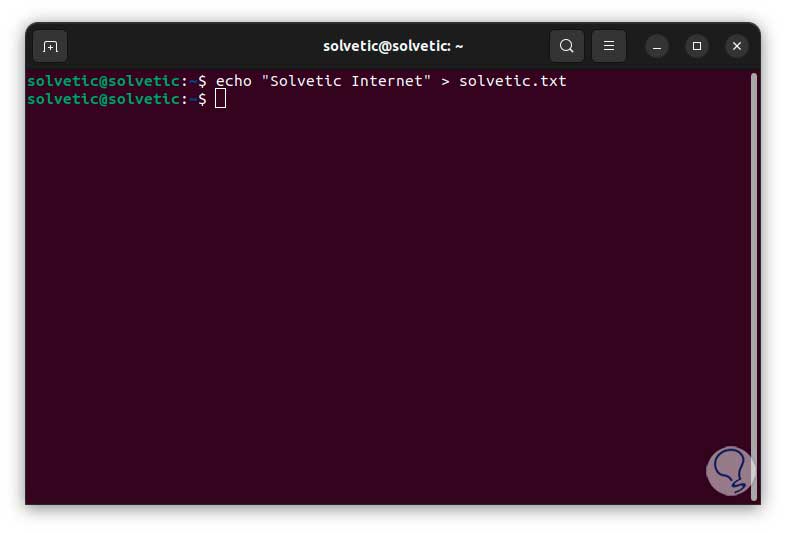
Now we can make use of the aforementioned operator to add text to our file, that is, we create and add at the same time, to achieve this we will use the following syntax:
echo “text” > file.txt
Step 2
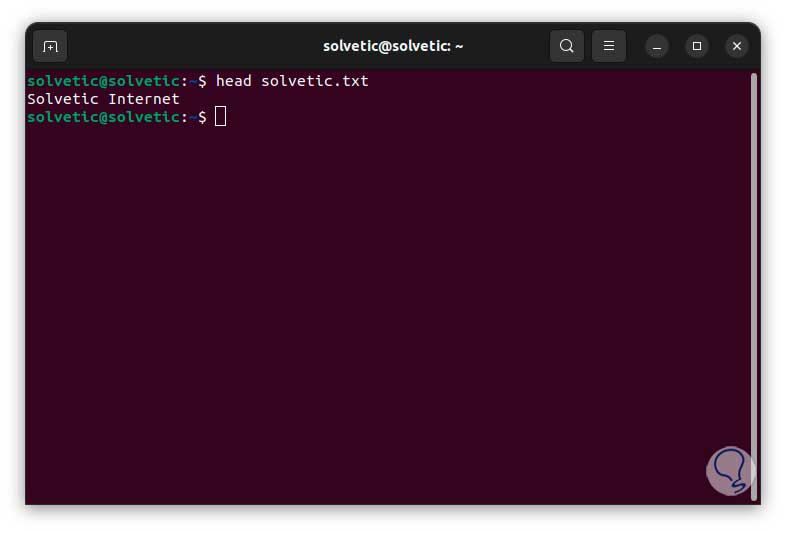
Now we will use the head command to check that the text has been added:
Step 3
In case it is necessary to add more text, we are going to use the echo command together with the >> operator, this allows us to attach text to the selected file:
echo “text” >> file.txt
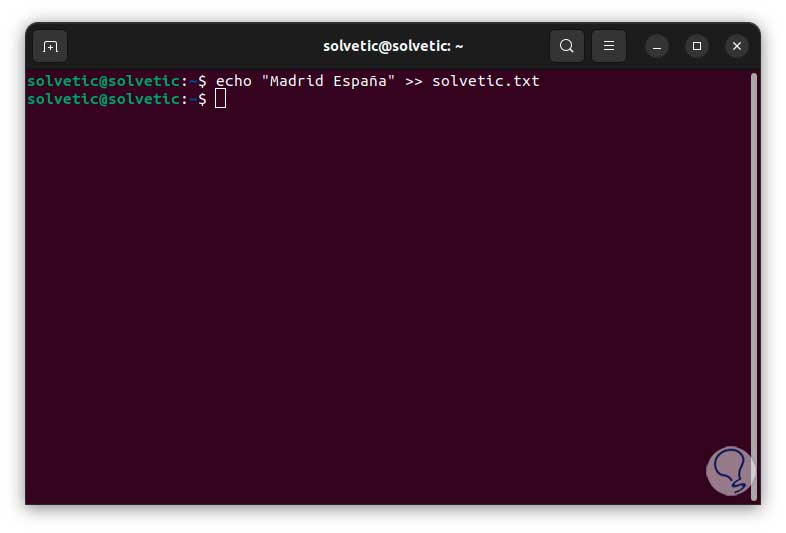
Step 4
After this we will see that the text was correctly added to the file using head:
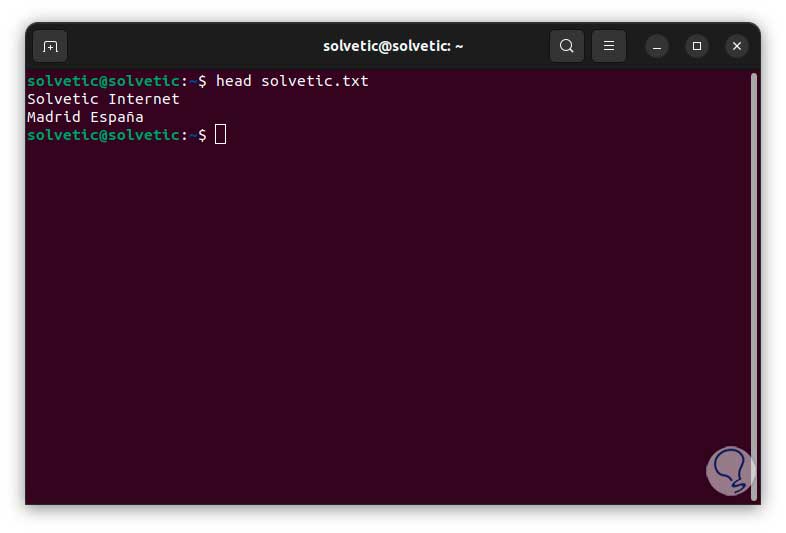
4 Create empty linux file using cat
The cat command, short for concatenate, allows us to display the content of one or more files and can also be used to create and concatenate files, the basic usage options are:
- -n : list all lines of output
- -b : takes care of listing only the lines of output that are not blank
- -s : suppress repeated empty lines of output
- -E: displays a dollar sign ($) at the end of each line
Step 1
For its use we will execute the following syntax:
cat > file.txt
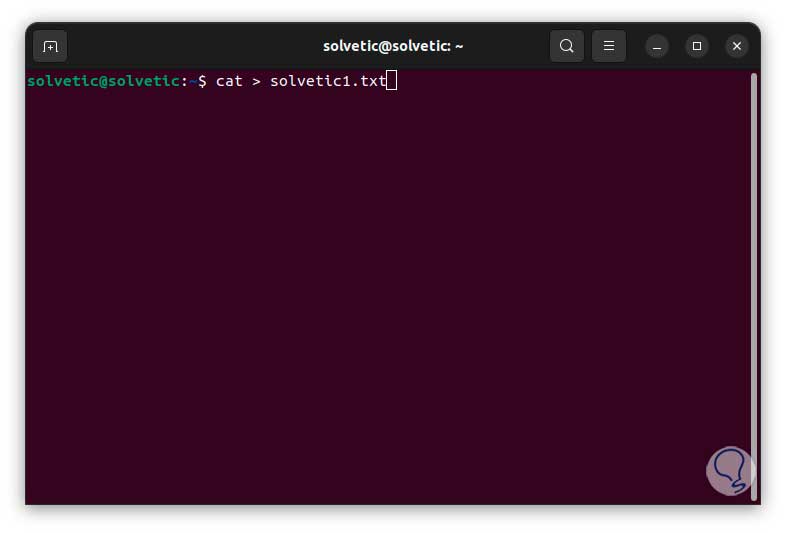
Step 2
We press Enter to enter the text directly in the terminal, we save the changes with the following keys:
Ctrl + D
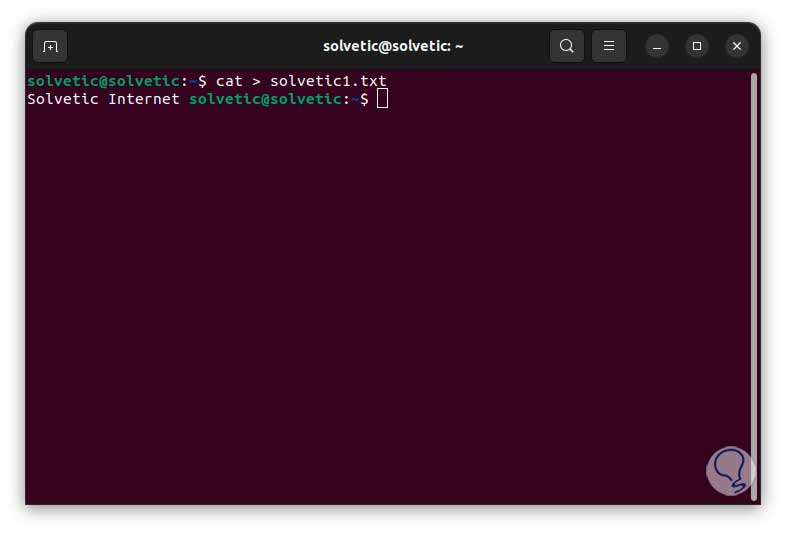
Step 3
With the head command we are going to check that the text was added correctly:
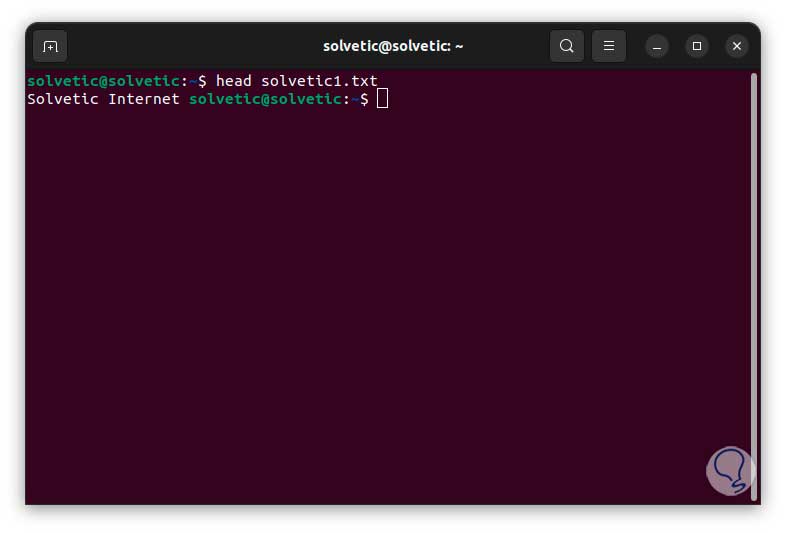
Step 4
In case we need to add text to this file we will use the following syntax:
cat >> file.txt
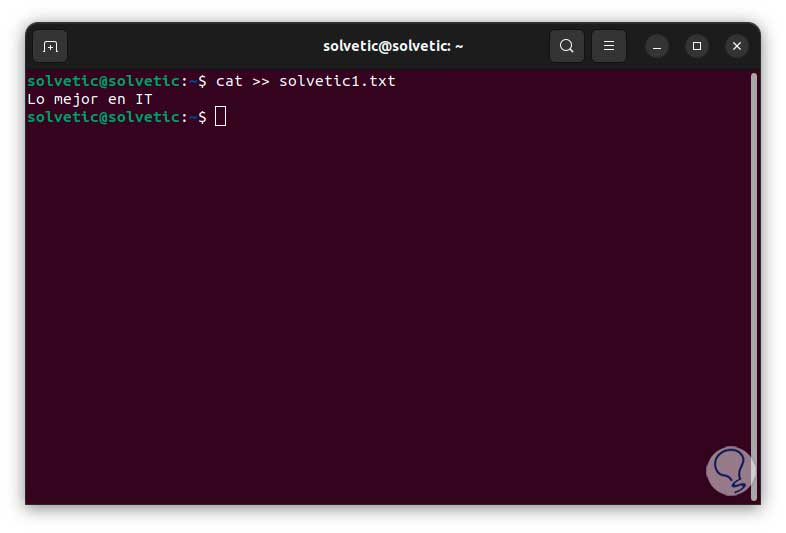
Note
save the changes with the keys:
Ctrl + D
step 5
With head it validates that the text has been entered:
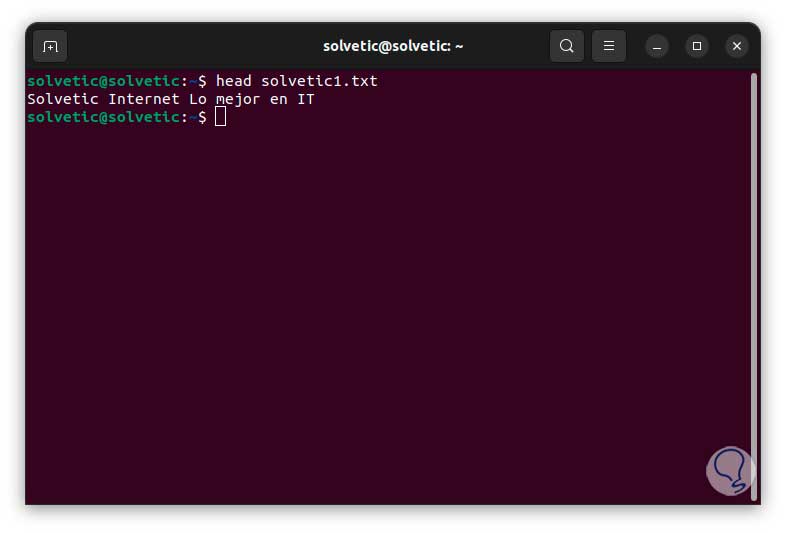
5 Create empty linux file using tee
Another option to use to create a file in Linux is using tee, this command is responsible for reading the standard input (stdin) and redirecting it to the standard output (stdout) of one or more files.
Step 1
To create our file we execute:
tee name.txt
Step 2
We enter the text in the terminal and finish with the following keys:
Ctrl + C
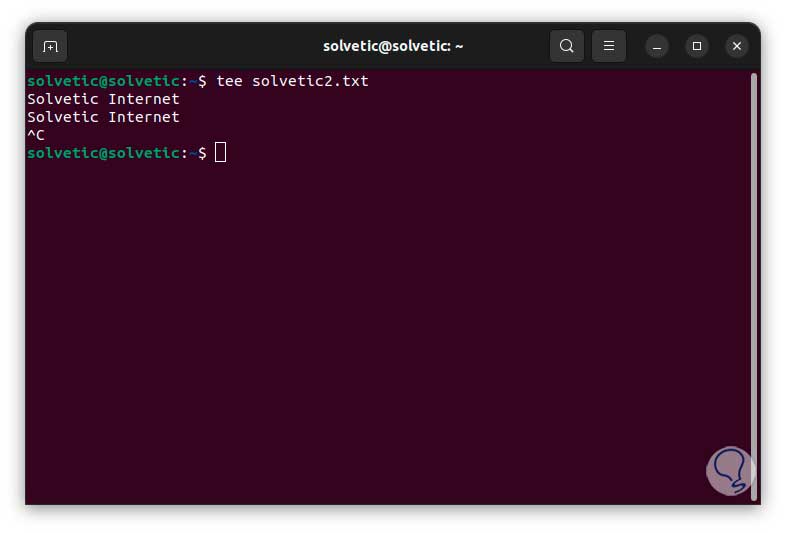
Step 3
We use head again to validate that the text has been entered correctly:
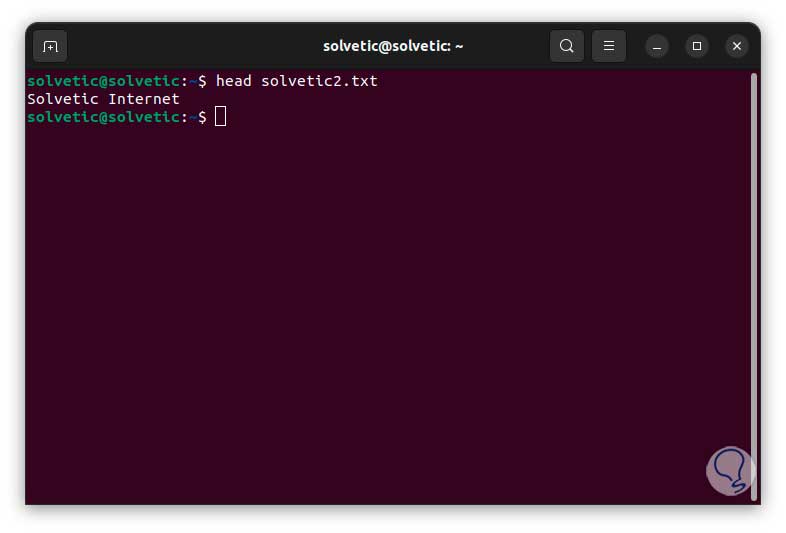
Step 4
If you need to replace the text of the file we will execute the following:
echo “text” | tee file.txt
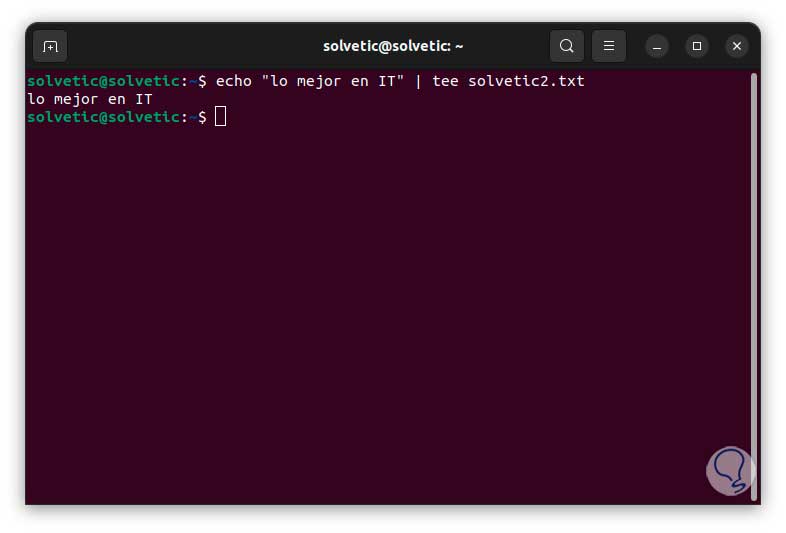
step 5
We verify that the change has been made:
head file.txt
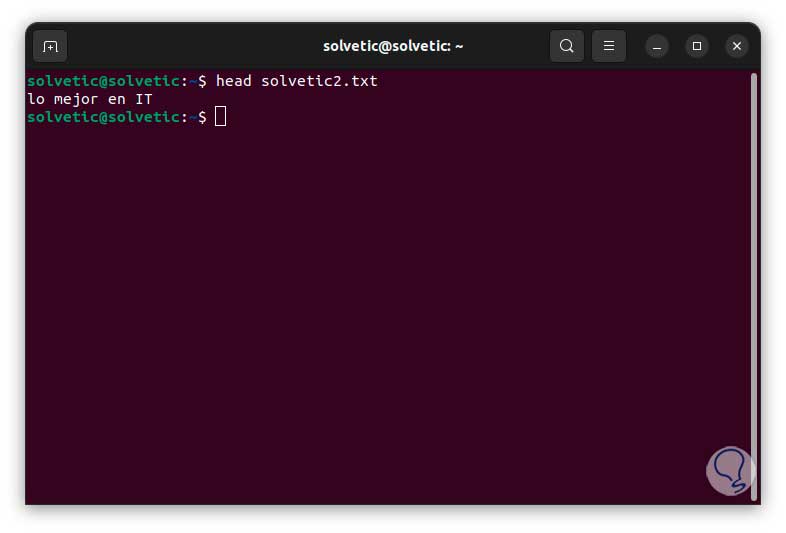
step 6
Now if you need to add more text we are going to use the syntax:
echo “text” | tee -a file.txt
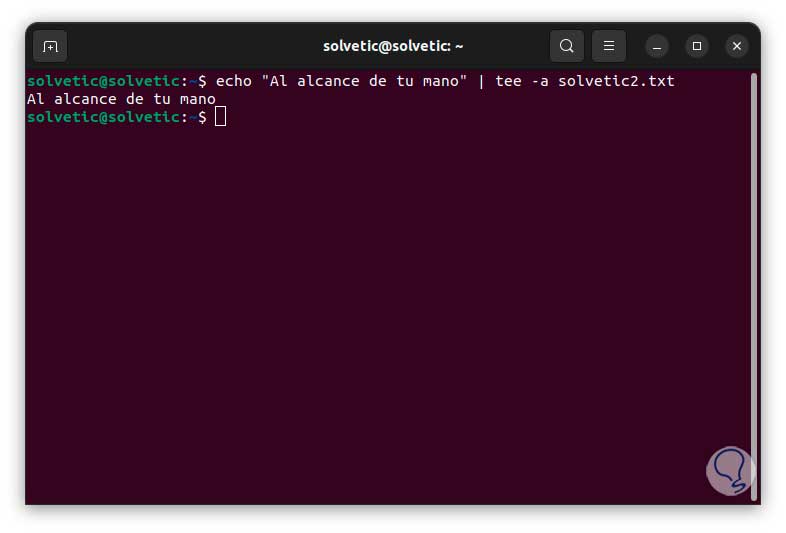
step 7
We validate:
So TechnoWikis has taught you various options to create a text in Linux and have it available at any time..