Maintaining a constant analysis of the system and users that we manage will undoubtedly be one of the best practices that we can perform as administrators because we have the opportunity to know in real time the behavior and state of the system and each of its components..
In this area we have the option of using the Guider tool thanks to which the administration and performance analysis options will be much more complete and we will have the possibility to know in detail if any component has any animalia to act before failures occur .
In this tutorial we will see how to install and use Guider in Linux environments..
What is Guider?
Guider is a Linux open source performance analyzer that was developed to measure the use of system resources and, taking these analyzes, give users advice to improve the performance of the operating system used.
Guider is able to track and analyze the use of thread, process and function resources in a detailed and complete way.
Guider is written in Python for Linux operating systems..
Guider features
Among the features that stand out in Guider we have:
- Easy to use: Its use is simple, just run the utility without installing or configuring anything additional
- Correct measurements: With Guider it is possible to measure the time in ms and the size in MB / KB
- Integrated functions: Using Guider it will be possible to deploy the use of CPU, memory or disk by thread, process or function (user / kernel).
Requirements to use Guider
Before using Guider we must have the following requirements:
- Kernel buffer size = 40960.
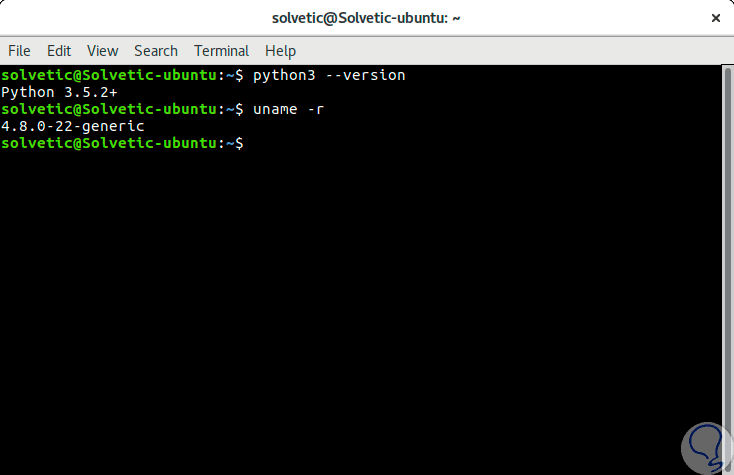
To know the version of Python in our system, in this case Ubuntu 17 Server, we will execute the following:
python3 –version
To know the version of Kernel we execute:
join me -r
In case of not having Python we can install it by executing the following command:
sudo apt-get install python3.4
sudo dnf install python3.4
sudo zypper install python3
1. Install Guider on Linux
Step 1
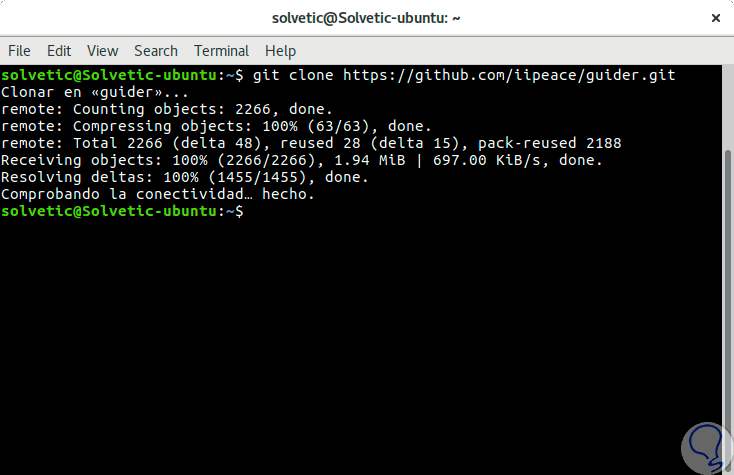
To install Guider correctly it will be necessary to clone the Guider repository located on GitHub by running the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/iipeace/guider.git
Step 2
Then we will access the directory of Guider by running:
cd guider
Step 3
Once there we have the following options:
- If we want to run Guider without installation we must execute the following:
guider.py
- If we want to install it we proceed to execute the following:
make sudo make install
- If we use PIP in the distribution we can execute the following:
sudo pip install --pre guider
Step 4
For this example we will use the
guide.py option to not install the utility on the system, for its startup we will execute the following:
sudo /guider.py
2. Configure the Guider buffer in Linux
By default, guider must configure the buffer size for the operations performed on the system, however, in case this does not happen, an error will be generated at the time of execution.
Step 1
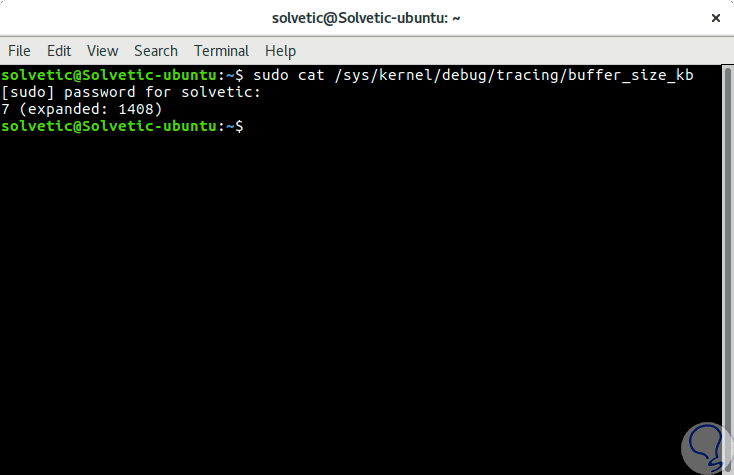
We can verify the size of the buffer with the following command:
sudo cat / sys / kernel / debug / tracing / buffer_size_kb
Step 2
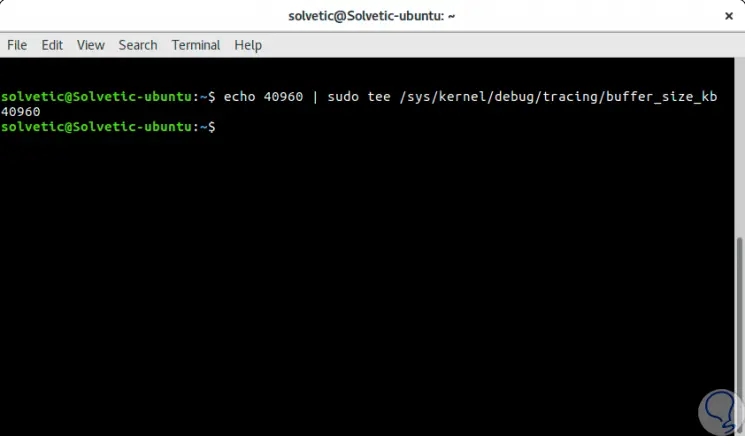
In case the value is less than 40960 we must execute the following line to establish this value:
echo 40960 | sudo tee / sys / kernel / debug / tracing / buffer_size_kb
Step 3
With this defined we can start Guider using the line mentioned above:
sudo /guider.py
Step 4
It will be possible to use guider in the thread, function, startup, file and system modes using the following syntax:
guider [mode | file] [options]
3. Perform CPU usage analysis in thread mode in Linux
Step 1
With the following command we will start the sequence tracking process which we can end by pressing the Ctrl + C keys, after this, the data will be saved and the analysis process will begin to finally display the analysis report.
sudo guider record
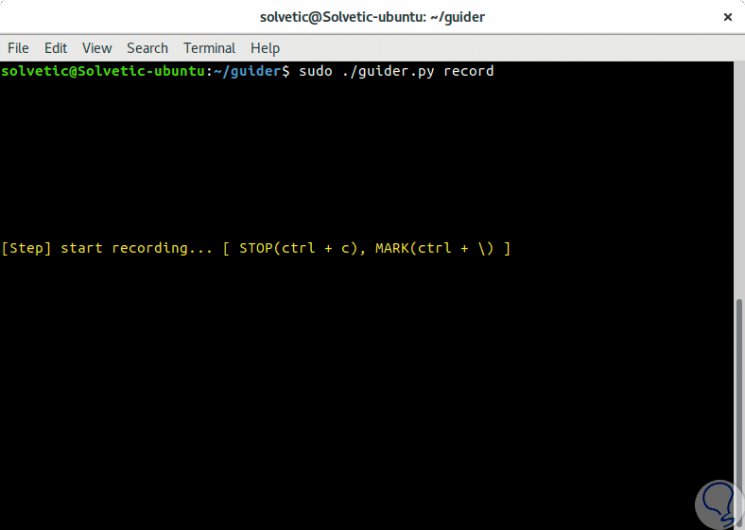
Step 2
By pressing Ctrl + C the data will be stored and we will automatically see the results:
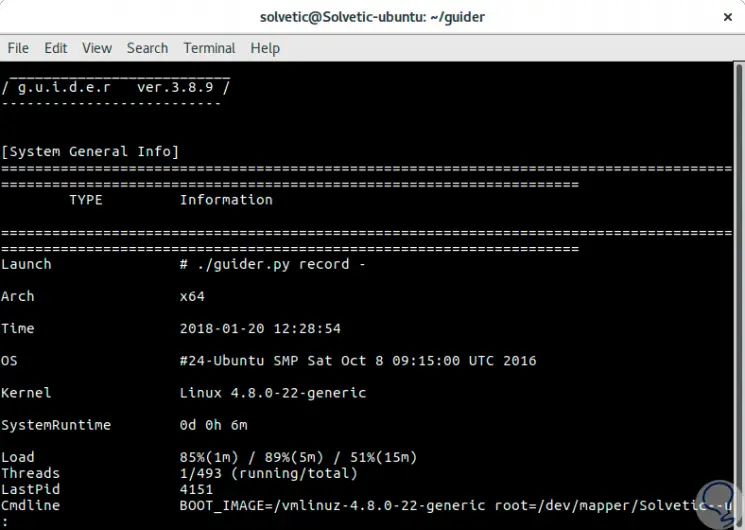
Step 3
We can see details such as date, kernel, system load time and many more parameters. We can go forward in the report with the AvPag keys or go back with RePag:
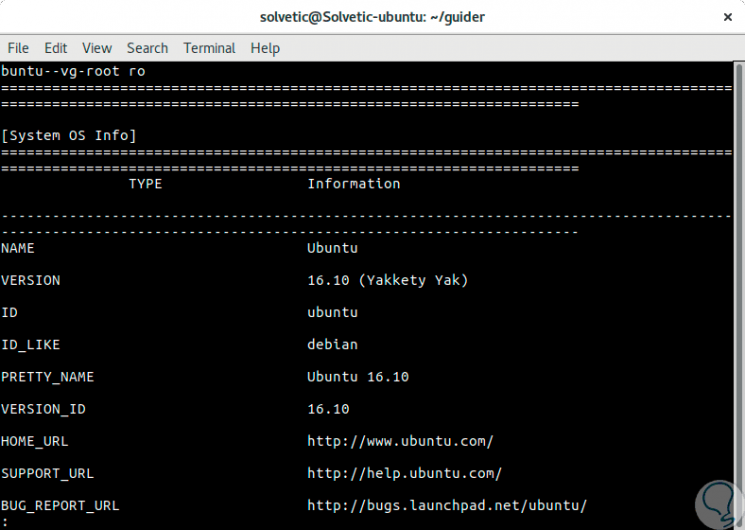
Step 4
As we move forward we will see new details of the system used.
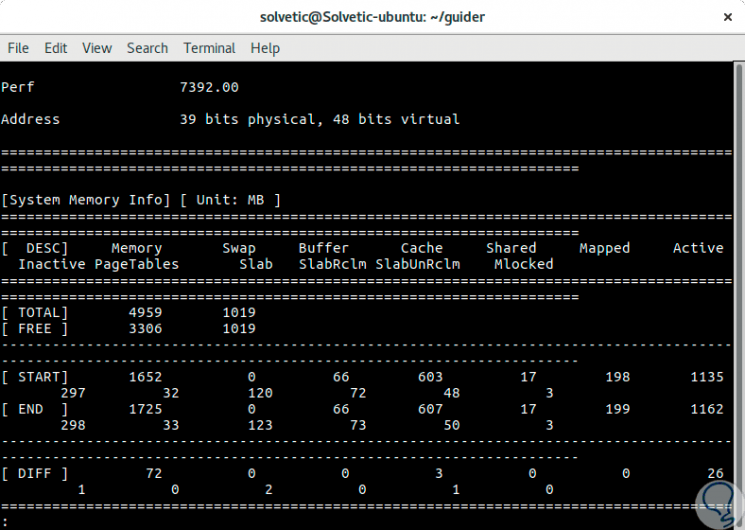
4. Perform real-time Linux monitoring in Top Linux mode
Step 1
With the following command we can see the use of Linux process resources in real time:
sudo guider.py top
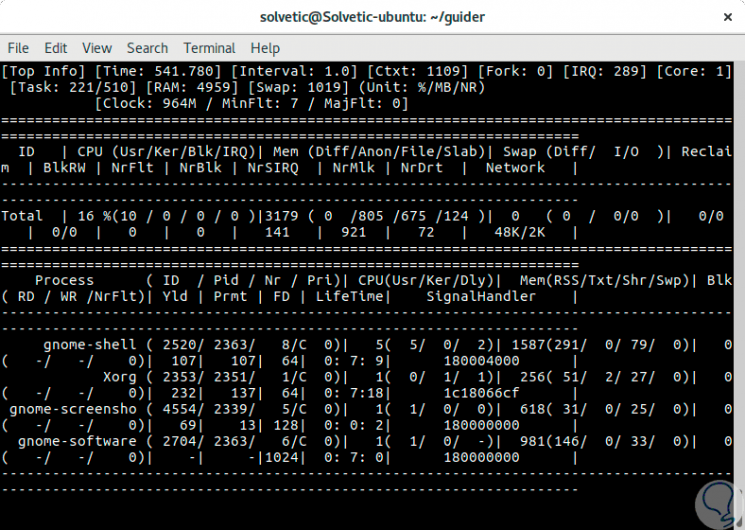
Step 2
It will be possible to set an interval to show the output using the
-i switch followed by the seconds:
sudo guider top -i 4
5. Analyze a simple Guider process using PID in Linux
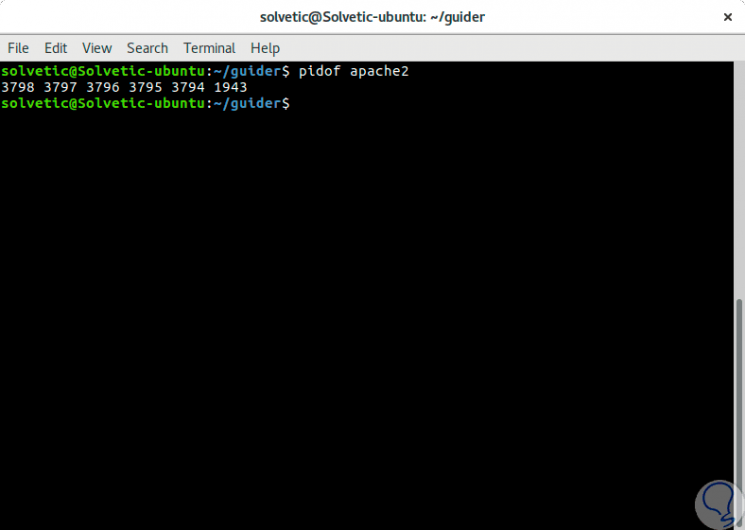
Step 1
To perform this process, we must first know the process PID, in this Apache example, for this we can execute any of the following options:
pidof apache2 ps -e | grep apache2
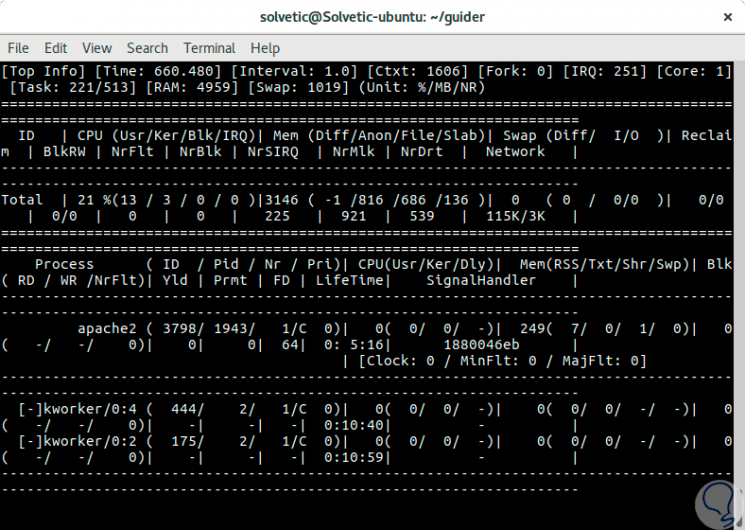
Step 2
We will see the list of associated processes, now, we can use the following line which generates the CPU cycle, the instruction number, the IPC, the failures, the lack of cache, the real-time branch failure:
sudo guider top -eP -g 1943
Step 3
The
-g parameter filters by the indicated process.
5. Save Guider results to a file in Linux
For administration tasks, it is possible to save the tracking data or any output in a file for its respective analysis.
Step 1
With the following command, we will save the trace data in a file called guider.dat, defined by default, in the current directory, but if we wish we can set a different path:
sudo guider -s.
Step 2
To save another output in a file called guider.out, by default, in the current directory we will use the following line:
sudo guider top -o.
Step 3
At the moment we want to see the contents of these files we can execute the following commands:
cat guider.dat cat guider.out
Step 4
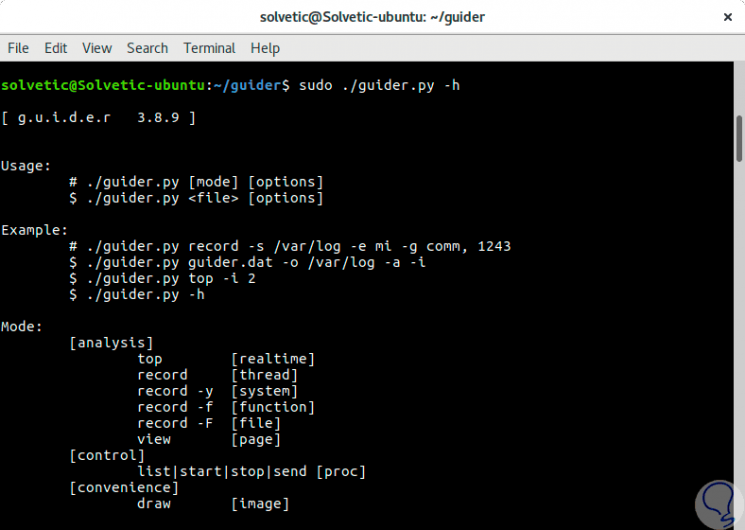
In many it will be possible that we want to get the help of Guider, this will be obtained with the following command:
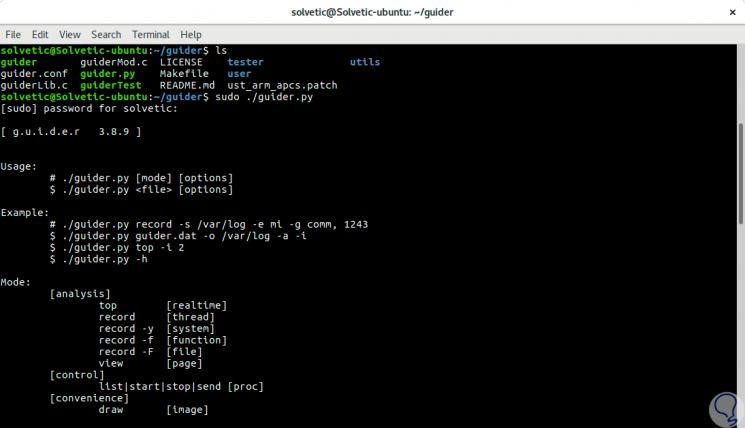
sudo ./guider.py -h
6. Ways to use Guider on Linux
Guider allows us to use various operating modes such as:
top [real time] record [thread] record -and [system] record -f [function] record -F [file] view [page]
7. General Guider options on Linux
-and
Enable options according to mode.
-d
Disable options according to mode.
-S
Sort the data output with values ​​such as .c (pu) / m (em) / b (lock) / w (fc) / p (id) / n (ew) / r (untime)
-
-or
It runs in the background.
-D
It generates a dependency on a thread.
-t
Analyze the Syscall values.
-j
Define the report path.
-OR
Generate user event values.
-K
Generate kernel event values.
-x
Define the address of the local server.
-L
Convert text to images.
-to
Show all information.
-i
Set intervals in seconds.
Thus, Guider is an additional help to the common administration tasks offering us possibilities to obtain global or real-time results of the elements of the system and thus manage them in a much more direct way.