
Intel® is a leading manufacturer in the world of processors and chipsets for desktops, laptops and other computing devices. Lenovo trusts in quality above all other aspects, and for this reason all its computers mount this type of processors..
Of course, knowing the category of the processors themselves is important to obtain adequate results. The new Intel® processors are divided into several different series ranging from the Intel® Core ™ M , perfect for ultrabooks, to the Intel® Core ™ i7, Intel® Core ™ i5, Intel® Core ™ i3, the best choice in terms of to performance.
The Evolution of Intel® Processors
For the past seven years, all of the common Intel® processors have been named Intel® Core ™ i X , subdivided into three categories, i3, i5, and i7, which specify their power and end use by name.
In seven years we have known six generations of Intel® Core ™ processors, counting on each relay with a different CPU microarchitecture that collected the best of the previous one, boosted it and compressed it even more in terms of size in a progressive way..
With this in mind, each year we have seen new microarchitectures and evolutions of each , following the Intel® Tick-Tock model, called Nehalem, Sandy Bridge, Ivy Bridge, Haswell, Broadwell and the recent Skylake, as well as manufacturing sizes that They range from 45 nanometers in the Nehalem to 14 nanometers in the Skylake.

It is truly admirable to have much smaller processors, but with an incredibly greater power than the namesakes of years ago, the problem arises when we want to apply these processors to new generation computers and demanding design: ultrabooks..
Intel® Core ™ M, full stop in the efficiency race

The demands of the new times have brought with them much more portable products than we are used to seeing normally in computing. Smartphones and tablets are a good example, but it is interesting to have equipment that provides a higher level of power, offering precisely the advantages of designing a smartphone or tablet.
Intel® thought it was time to expand its product line and introduced the new category called Intel® Core ™ M, processors designed to balance power and efficiency and be able to integrate into small devices.
Manufacturing processors using 14nm in size has been the great “excuse†to bring us the Intel® Core ™ M from the 5th generation of Intel® Core ™ processors (called Haswell) onwards.
Plus, it can be used even on ultrabooks that are no thicker than 9mm and even lack fans.

But let's not forget that the great asset of these processors is their efficiency: An Intel® Core ™ M processor is up to 50% more efficient than an Intel® Core ™ i5 processor from its same microarchitecture.
To make it clearer, the Thermal Design Power , which indicates the final consumption of a processor, goes from 15W minimum in an Intel® Core ™ processor to only 4.5W minimum and maximum in an Intel® Core ™ M The battery will last up to twice as long as a device that uses a conventional processor.
Skylake, improving thanks to the 6th generation
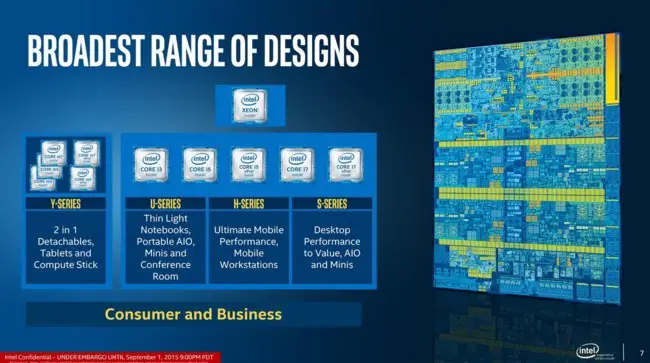
The new generation of Intel® Core ™ processors, the sixth, is already with us. The new Skylake microarchitecture is organized into categories in a much more precise way, according to the final task that we want to give to each processor, so we are going to know one by one what they are and what we could use the Skylake series of processors for:
Y Series Intel® Core ™ Processors (Skylake) Here we find the Intel® Core ™ M processors , which can be found under the names Core ™ m3, Core ™ m5 and Core ™ m7, depending on their power. The new Intel® Core ™ increases autonomy up to 10 hours and performance by 40% more than seen in the previous generation. Its Thermal Design Power does not move from 4.5W. These processors will be included in ultrabooks, tablets or micro-computers, such as those in the Lenovo Yoga Pro range.
Intel® Core ™ Processor U Series (Skylake) If we move to this series, we will find Intel® Core ™ processors with names Intel® Core ™ i3 and Intel® Core ™ i5 . Here we will have integrated GPUs Intel HD Graphics 520 or Iris HD Graphics 540 and a Thermal Design Power of 15W. Advanced models with 28W of Thermal Design Power, Iris Graphics 550 graphics and support for DDR4 memories are added, designed to be equipped in ultralight high-performance notebooks. These processors will be included in ultrabooks or laptops, such as the Lenovo ThinkPad E550.

H Series Intel® Core ™ Processors (Skylake) In the H series we have Intel® Core ™ i5 and Intel® Core ™ i7 as maximum exponents. These processors are intended primarily for gamers as they include Intel Graphics 530 GPUs, more special instructions, higher processing frequencies, and a 45W cap from Thermal Design Power. These processors will be included in laptops or desktops, such as the Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 SFF Pro.
Intel® Core ™ Processor S Series (Skylake) Here we will find processors that are generally designed to be used in desktop computers with maximum power. The Intel® Core ™ i7 are the only “inhabitants†of this series, as we can see in the Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Carbon Ultrabook that have unlocked overclocking functions and, in addition, reach 91W of Thermal Design Power. These processors are designed for very high-end desktops and laptops.