
Who does not remember VHS video tapes or DVDs (which are still valid)? Enjoying audiovisual content or personal recordings in the comfort of our home has always been as simple as having a video player adapted to these formats..
Of course, if we think about the different types of computer video, things change, and the progressive disappearance of physical formats makes us depend, increasingly, on all existing video formats and codecs as the only alternative. What will all your secrets be?
Codecs, the basis of a video file

Right now, any device we have at home is capable of playing multimedia content such as videos or music. Televisions, music equipment, tablets, smartphones, game consoles, none are spared.
If we record our son's first steps, possibly we will do it with the camera of our smartphone or with a digital video camera, and both generate multimedia files encoded in a specific format..
The codecs are the basis for all these current devices are able to capture or play a file containing images and sound inside. All of them require a physical chip that is capable of translating the images and sounds into bits, but the key is hidden in the software.

The codecs by software (encoder-decoder) compress both the audio and the video, that is, they cause loss of information with respect to the original captures, to get files of measured sizes. There are also lossless codecs that allow you to take videos with the highest quality, but require immense sizes..
Multimedia files, which generally include video and audio, are usually stored in so-called “ containers, †which store video, audio, subtitle, and other data under one file.
Currently the most popular containers are .mp4 (MPEG-4), .mov (Apple Quicktime file), .avi (Microsoft Audio Video Interleave) and the popular .mkv (Matroska). All these containers can make use, in turn, of different video and audio codecs inside.
H.264, the current standard in the world of codecs
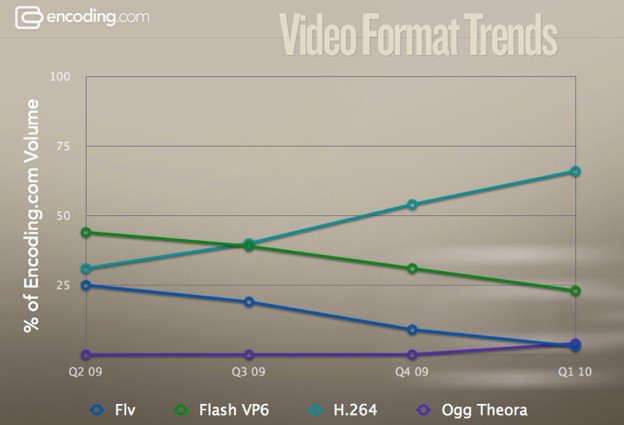
H.264 has become the most popular video codec in recent years thanks to its size / quality ratio, ideal for using content in HD quality. It is also used on televisions, smartphones, Blu-ray players or YouTube videos.
Its success has been such that, in a few years, it has superseded other popular codecs such as Divx or Xvid in the world of multimedia files, or FLV, Flash VP6 and Ogg Theora in the world of streaming videos.
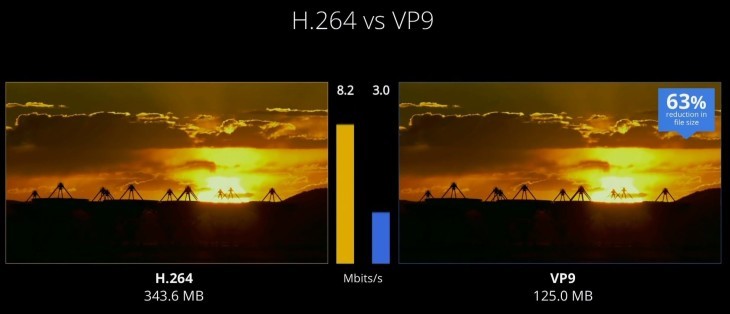
The biggest “problem†of this codec for many content developers is that it is a non-free codec , that is, if an application wants to use it natively, it will have to pay for it.
There are already free alternatives very focused on the web that "fight" against these proprietary codecs such as the VP9 codec , or the WebM container, promoted mainly by companies like Google.
H.265 or HEVC, the future of video codecs
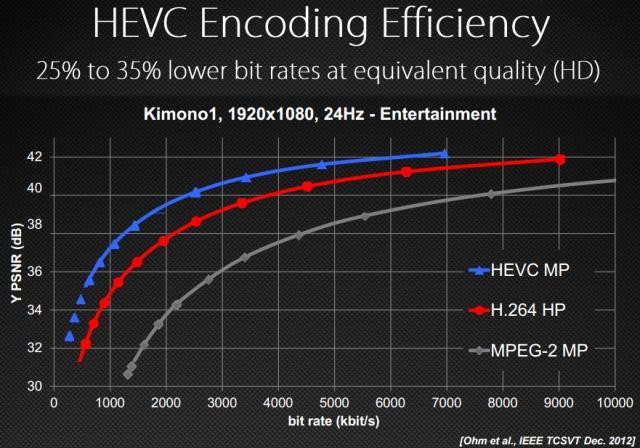
Given the success of H.264 within the codec world, the arrival of new times requires improvements that follow the same line. H.265 , also known as HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding), is the new version of this codec.
H.265 allows videos to be compressed much more while maintaining excellent image quality even with low bitrates, something that comes "like a finger" to be able to compress content in 4K or UHD format , which quadruples the resolution of current Full HD content .
In addition to the enhancement in compression technology, the new H.265 codec also incorporates improvements in color depth, increased maximum resolution, and frame rate per second.
Codec packs, are they really necessary?
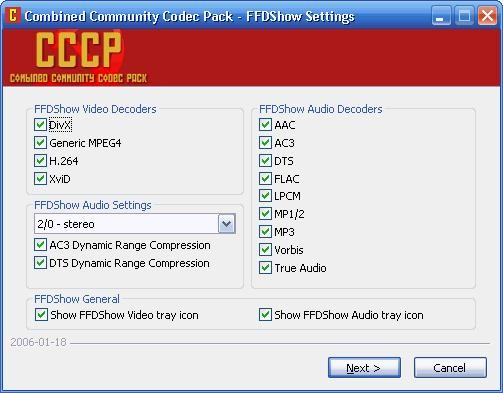
A few years ago it was essential to get a good pack of codecs for our computer if we were going to download and enjoy multimedia files of all kinds. At this time, this custom is also destined to disappear.
The current video players usually already have all the necessary codecs incorporated , to solve the problem of making us look for specific codecs. Only in the most isolated cases we will be forced to look for a specific codec to reproduce a file correctly.
Nowadays it is very common to enjoy movies or series on a computer in front of a conventional DVD player. A computer like the Lenovo Z51 is one of the best options when it comes to enjoying all kinds of multimedia content, since thanks to its Full HD IPS LED 1920 × 1080 screen and its integrated AMD Radeon R7 M360 2GB card, playback will be smooth whatever the resolution of the video. In addition, the use of a video player with integrated codecs makes a computer like this Lenovo Z51 an ideal multimedia center , powerful and very easy to use.
Of course, if we are professionals or enthusiasts of the audiovisual world and edit videos continuously, it may be necessary to install some codecs manually to be able to compress videos correctly in all the editing programs or applications that we install on our equipment.
The best video players currently available
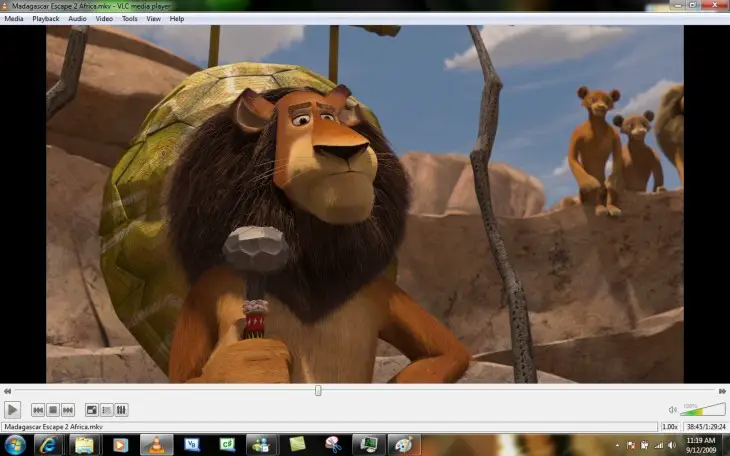
The golden age of Windows Media Player or Windows Media Player has passed to a better life. The program is still part of Windows, but today there are much more efficient and powerful solutions, as well as free, to play any type of multimedia content on a computer.
The undisputed king is VLC Media Player , the multimedia file player that plays practically everything, is free and free, and has various functions such as file compression, theme support, plug-ins or video playback from the network.
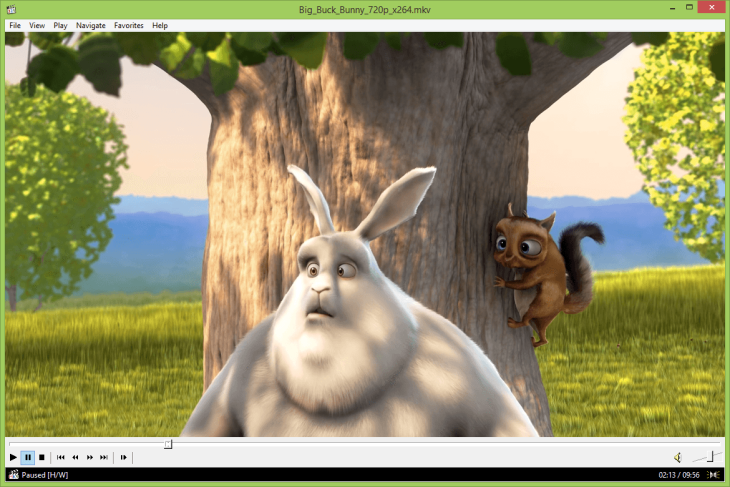
They are closely followed by other alternatives such as MPC-HC, previously known as Media Player Classic , another open and free player that is light and reads a large number of files, in addition to incorporating other multiple functions.
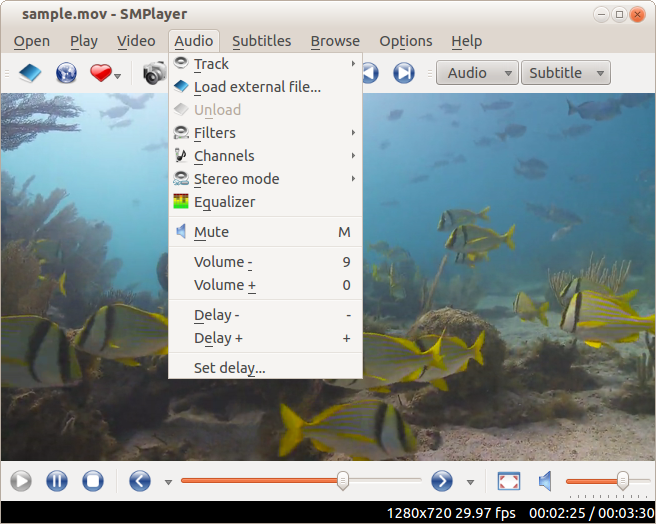
SMPlayer also boasts of being a lightweight player that plays almost all formats thanks to its built-in codecs, in this case it uses the MPlayer engine to ensure perfect video playback.

Another player to take into account is KMPlayer, which has a very careful design and the trick of integrating all the codecs in your installation, to avoid searching independently, although they can be downloaded and used separately if we wish.
Images | boilsoft | ubergizmo | extremetech | anymp4 | digital freedom