The Linux operating systems we offer a number of special commands for everything related to work and file management, processes and services and one of these commands is special for cloning tasks and Rsync. Rsync has been developed as a versatile, remote file copy utility that can be used locally..
Rsync can be used to make copies locally , to or from another using a remote shell or to or from a remote rsync daemon, one of the advantages of Rsync is that it makes use of a delta transfer algorithm, with which it seeks to reduce the amount of data that is transferred in the network, with this it is sought to send only the existing differences between the source files and the files that are already created in the destination, this allows changes in the preserved attributes to be executed directly in the destination file.
Advantage
Among the advantages of using Rsync we find:
- It integrates a CVS exclude mode that allows you to ignore files that CVS ignores.
- It has support to copy links, devices, owners, groups and file permissions.
- Lets you exclude options similar to GNU tar.
- Compatible with remote shell like ssh or rsh.
- It has a file transfer pipeline which minimizes latency costs.
- Provides support for anonymous or authenticated rsync daemons.
Now let's see how to clone one CentOS 8 server to another with Rsync..
1. How to clone one CentOS 8 server to another with Rsync
Step 1
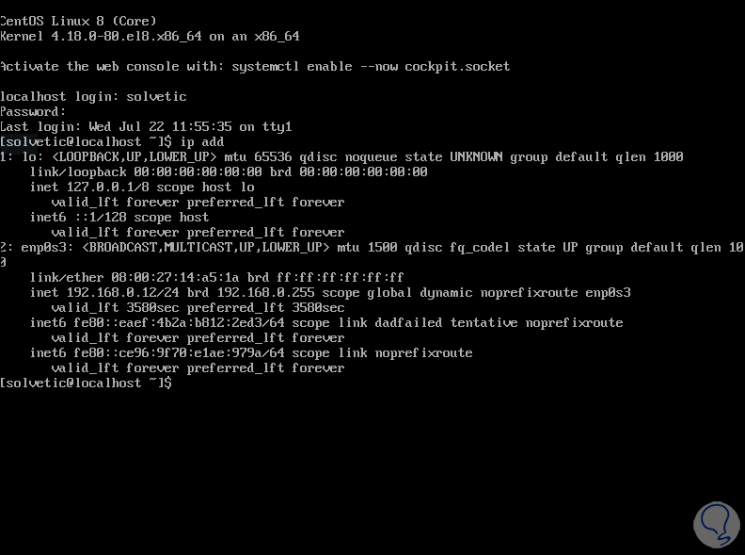
The destination server has the IP 192.168.0.12:
Step 2
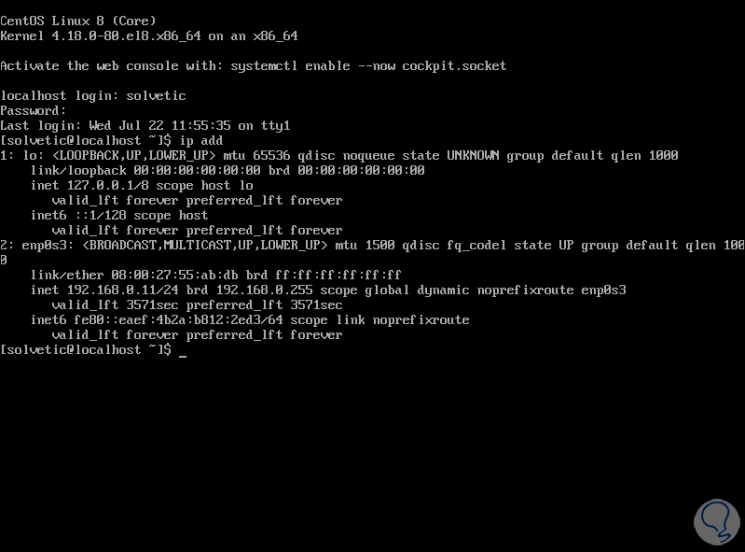
The origin server has the IP 192.168.0.11:
Step 3
Rsync check
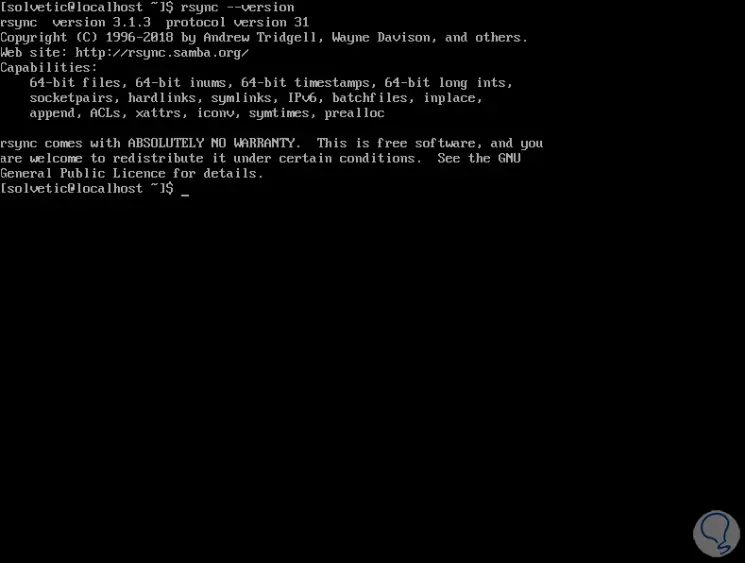
Rsync is integrated by default in the CentOS system and we can validate its version with the following command:
rsync –version
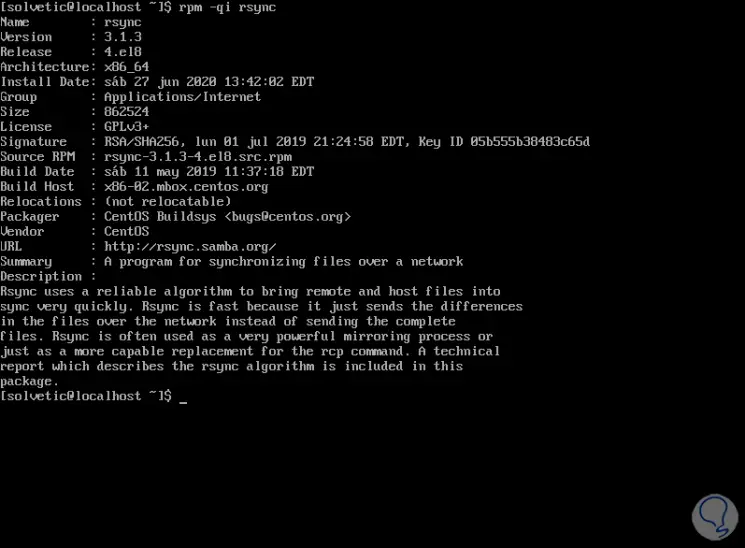
If we want additional Rsync details we must execute the following command:
rpm -qi rsync
In case Rsync is not installed on CentOS 8, we must install it with the following command:
sudo yum install rsync
Step 4
Resource settings
It is possible that some directories and files are excluded from the cloning process since they are available on the destination server, this includes files like / boot, / tmp or / dev, to exclude them, we must create a file in the path / root / exclude -files.txt, for this we will use the desired editor like this:
sudo nano /root/exclude-files.txt
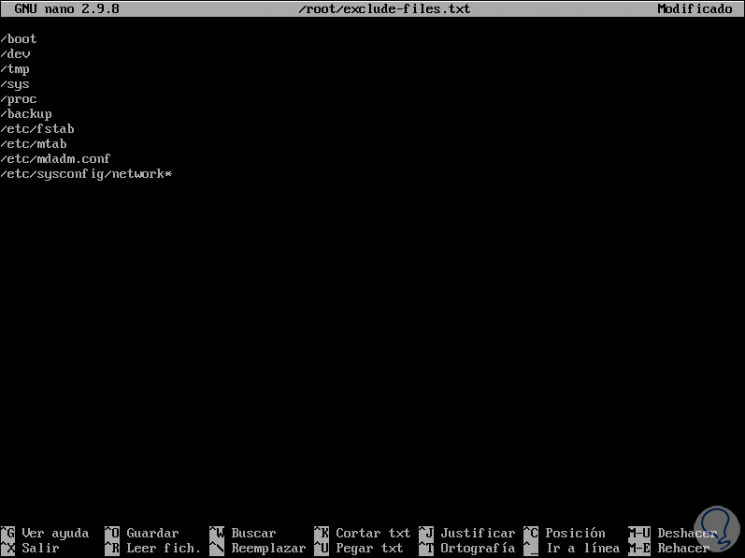
In this file we enter the following:
· / Boot · / Dev · / Tmp · / Sys · / Proc · / Backup · / Etc / fstab · / Etc / mtab · /Etc/mdadm.conf · / Etc / sysconfig / network *
We save the changes with the Ctrl + O keys and exit the editor with the Ctrl + X keys.
Step 5
Server cloning
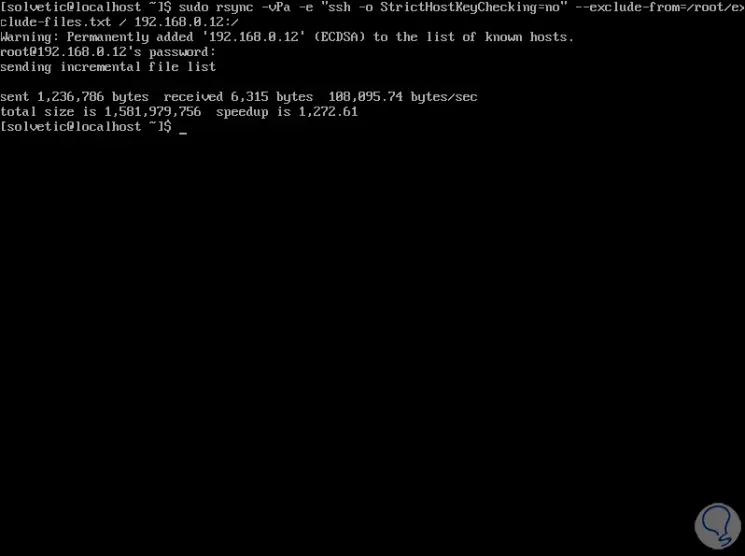
Now we are simply going to run the following command to clone the server with the following syntax:
sudo rsync -vPa -e "ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking = no" --exclude-from = / root / exclude-files.txt / IP_REMOTA: /
We can see that the files are copied to the IP of the remote computer.
With this simple but functional command we can clone our server in no time..