A memory expansion in the form of an SD card is always useful if you have little space left on your smartphone. However, Android and SD cards have a complicated relationship. Depending on which smartphone is used by which manufacturer or which Android version you are using, the whole thing can work or is prevented directly by the manufacturer. Samsung argues, for example, that outsourcing the internal storage poses a security risk, since it can be removed by the user at any time. You can find out what you can do with other manufacturers and what "adoptable storage" actually is in our tips + tricks.
Attention: All existing data on the SD card will be deleted in advance by formatting when it is set up as an internal memory card.
Adoptable Storage: Use SD card as internal storage
Compared to Apple's iOS, Android has always supported external storage and SD cards. Since Android 6.0 Marshmallow, there is also the option of merging the internal memory with the SD card. As a result, the card also functions as a non-removable memory, i.e. forms a common memory unit with the existing one. The name for this is " Adoptable Storage ".
Basically you need a smartphone with a microSD slot and Android version 6.0 or higher . In addition, the manufacturers of the different smartphones decide whether they allow this or not. Samsung, Sony, LG and Huawei generally reject the support of adoptable storage. Other manufacturers like However, HTC, Lenovo or Xiaomi allow the expansion. You can see whether your smartphone supports the function in the settings of the SD card. We will show you exactly how this works in our step-by-step instructions .
Note: If the memory card no longer works, all data is gone. For this reason, you should regularly back up your data elsewhere..
You should keep this in mind when expanding the memory
We recommend making a regular backup of your data, since your data will be gone if you have a defective microSD card or a broken smartphone. Also, as a precaution, make a backup before moving your data to the SD card in case something goes wrong with the process.
The SD card set up as internal storage should also not be removed from the smartphone during operation. There may be important functions on the card, which could cause the smartphone to malfunction. That is why the expansion is also being prevented by many manufacturers..
How to choose the right SD card for your smartphone
You can find lots of numbers, symbols, and letters on a microSD card. Knowing what they mean is important because it will make it a lot easier to choose the right option for you. There are many different specifications used to classify microSD card speed and performance, and most cards have at least two of these classifications in addition to the read / write-only speeds reported for the card. Here is an overview of these formats and which of them are better than others:
- Video Speed Class: This class, indicated by a stylized V followed by numbers from 6 to 90 , is one of the newer classification systems and is specially designed for recording ultra high definition video. V30 starts at a write speed of 30 MB / s, V60 at 60 MB / s and V90 at 90 MB / s. However, unless your phone is recording 8K video, you probably don't need a V90 card.
- UHS Speed Class: This class, denoted by a 1, 2, or 3 in a U , is still used on most maps today. U1 starts at a write speed of 10MB / s , U3 starts at a write speed of 30MB / s , and both are perfectly adequate for most Android phones.
- Speed Class : This was the original SD card classification system and is indicated by a number with a C. The highest class was Class 10 with a write speed of 10 MB / s. Virtually every card worth buying today is well above this speed , so it's no longer as helpful as an indicator of performance / quality these days.
- App performance class : The app performance class identifies the microSD cards that are best suited for smartphones and tablets. The A1 and A2 ratings mean that the card can open apps and process them quickly. The A2 rating means more than twice the minimum read and write speeds possible with A1 rating cards .
- Read speeds : The read speeds of a microSD card are indicated in different ways. Some simply state the theoretical maximum speed in Mbit / s on the card. On some cards an XXXX scheme is shown instead , e.g. B. 633x or 1000x. This dates back to the days of CD-ROM drives, where 1x equals 150kbps. 633x means a theoretical reading speed of 95Mbps and 1000x means a maximum of 150Mbps. This scheme is not widely used today, but can be found on Lexar microSD cards.
- Storage capacity : The most noticeable information on a microSD card is the storage capacity. The big font with the number is hard to miss and tells you what you need to know. Keep in mind that a 256GB card wo n't have as much storage space as the file system takes up some space.
- Card Type : MicroSD cards all look the same, but there are a few different types you should be aware of. MicroSDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity) cards are low capacity cards (4 GB to 32 GB). MicroSDXC cards (Secure Digital Extra Capacity), on the other hand, offer everything that goes beyond that, in a range from 64 GB to 1 TB. A very inexpensive cell phone or a much older device might only support microSDHC cards, but in most cases you don't need to worry about the card type.
- UHS-I or UHS-II : Another speed specification is the UHS-BUS speed . Most microSD cards are marked with the Roman numerals I or II . You can usually find this identification on U1 or U3 cards . UHS-II theoretically offers much higher speeds and has a different pin layout on the back of the card. Note that backward compatibility is not an issue. If you add a UHS-II card to a device that only supports UHS-I , it will also work without the speed benefits.
So if you see a card with a transfer speed of 100MB / s but only a U3 class, it is likely that this card has a read speed of 100MB / s and a write speed of 30MB / s. For most users who only want to use a microSD card to store app data, music and movies for offline playback, a U1 or U3 card like the Samsung EVO Select will do just fine . However, if you plan to use a microSD card as internal storage and for large amounts of data, you should opt for a U3 / V30 (30 MB / s) or V60 card , such as B. the Lexar Professional 1000x.
Perhaps the most important question is whether choosing a microSD card will improve your phone's performance . The short answer is "yes". When you store apps and photos on your microSD card, a higher-speed microSD card saves photos faster, improves data transfer speeds when moving files between devices, and opens apps stored on your microSD card faster. Note that opening apps on microSD card can be a little slower than saving them on your phone's internal storage, as it requires an additional layer of communication between your phone and the microSD card.
As you can see, there are many things to consider when purchasing a microSD card. It is also worth going for well-known brands like SanDisk, Samsung and Kingston for microSD cards . Also, orientate yourself on the prices of these brands - if you see another company's microSD card that is five times cheaper than this one, you should be careful about its quality.
How to set up the SD card as internal storage
Note: Formatting the SD card to internal storage may not work on newer versions of Android such as Android 11. Whether it works also depends on the smartphone manufacturer. More and more manufacturers are deciding against this option.
Follow our step-by-step instructions or take a look at the quick start guide .
1st step:
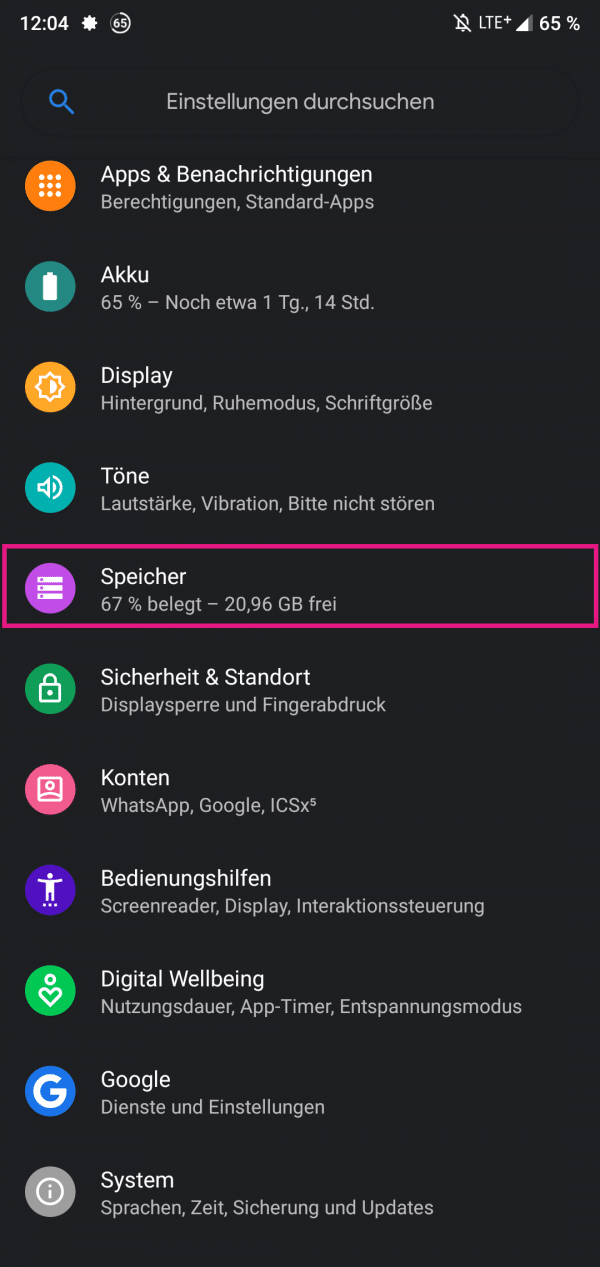 Open the settings and select " Storage ". Depending on the manufacturer and operating system, this entry can also be called " Storage and USB ", for example .
Open the settings and select " Storage ". Depending on the manufacturer and operating system, this entry can also be called " Storage and USB ", for example .