The hard disk is one of the most essential hardware elements in any type of equipment and with any operating system used since without it it would be impossible to use the base operating system. Today there are many technologies at the hard disk level, we have the new solid state disks which offer us a unique boot and shutdown speed , better security features, but its failure, criticized in many cases, is the issue of storage since these hard drives are in presentations of 128 or 256 GB which, in a digital world like today, are really scarce..
One issue that we sometimes overlook when using a computer is precisely the theme of space , we install applications and programs, download games, music or movies, create backups and gradually the space is reduced dramatically and have a disk Hard without storage space results in some errors like:
- Sudden disk shutdowns or crashes
- Inability to access information hosted on the hard disk
- Read or write file failures
- System and application reboots for no reason
That is why it is ideal and fundamental to constantly monitor what free space our hard disk has in order to take support measures such as adding new drives, freeing up space, uninstalling applications, etc. TechnoWikis will give a series of tips on how to verify space in real time on Linux.
1. How to use the DF command on Linux
Step 1
The DF command has been designed to display accurate information about the total, occupied and free space in our operating system in order to improve its administration. To start the deployment of the information we will execute the following:
df -H
The -H parameter allows the information to be displayed in readable format. We can see specific details such as size, used and available space, as well as this percentage value.
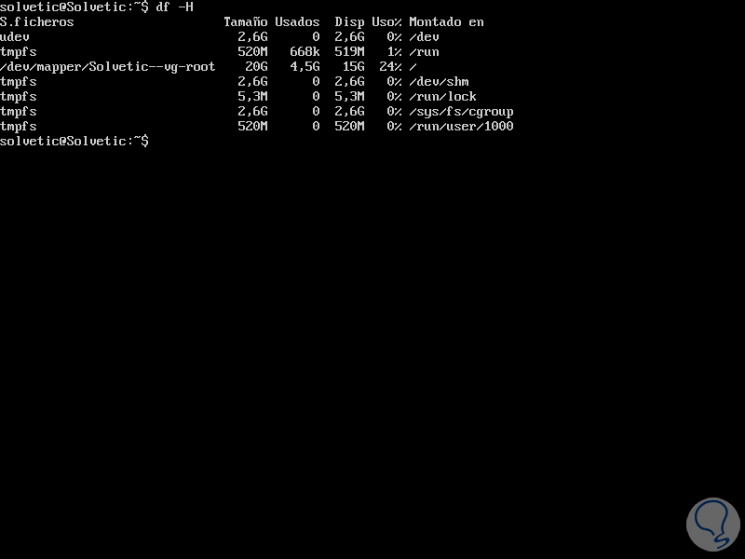
Step 2
In case a wide list of devices is displayed, there is the option to display the information of a single directory or path in particular, for example:
df -H / dev / sda1
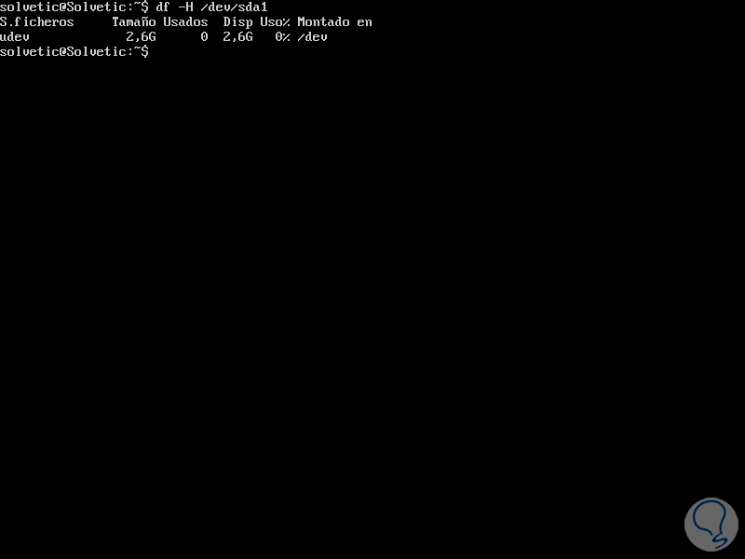
Step 3
The DF command has a general parameter called df output through which we can specify a series of attributes to display in the result, the available attributes are:
source
Indicates the source of the file system
size
Indicates the total number of blocks
used
Refers to the space used on the hard disk
avail
View the available space on the hard drive
pcent
Display the result of used space in%
target
Refers to the mounting point of a unit
Step 4
To use this option we will execute the following:
df -H --output = size, used, avail, pcent
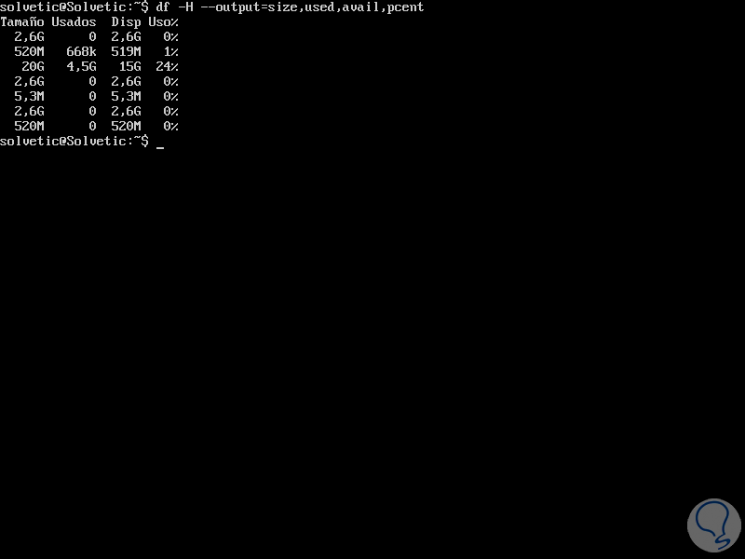
Other alternatives to use with the DF command are:
- To know the inodes that are free we will use the df -i command
- For the system to deploy the file systems, even if they have zero bytes, we execute -ao -all df -ao df -all
2. How to use the DU command in Linux
Step 1
Another of the most useful Linux commands to know everything related to storage is the DU (Disk Usage) command, which allows us to know what each of the folders and files weighs on the system.
The basic use of the DU command is:
du
This will be the result generated:
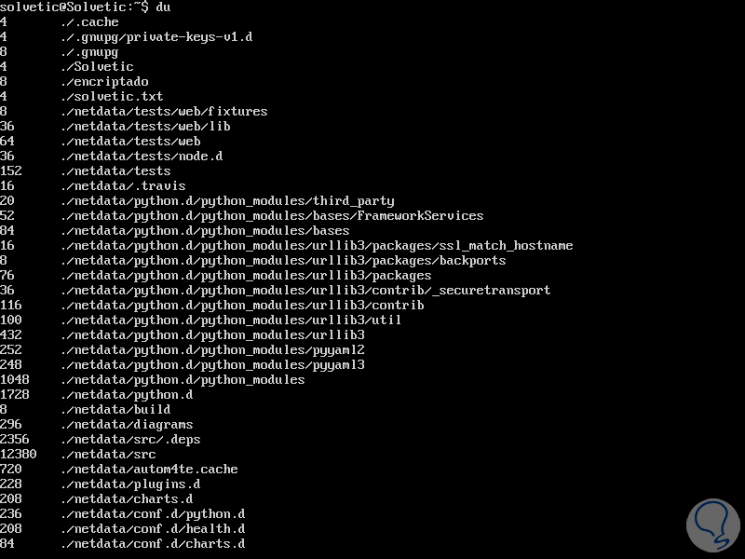
Step 2
With the basic du command, the space occupied by all directories from the current directory is shown, there it is distributed as follows:
- The number of the first column is the space occupied by the directory and is expressed in kb.
- In the second column the route of this space is indicated
If we want to know only the total space used, we will execute the following:
du -s

Step 3
To know what the files occupy in addition to the directories we will use the following line:
du -a
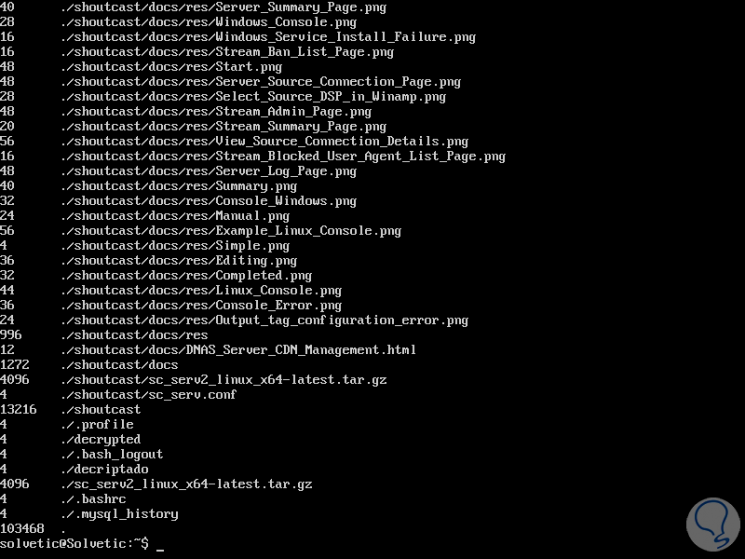
Step 4
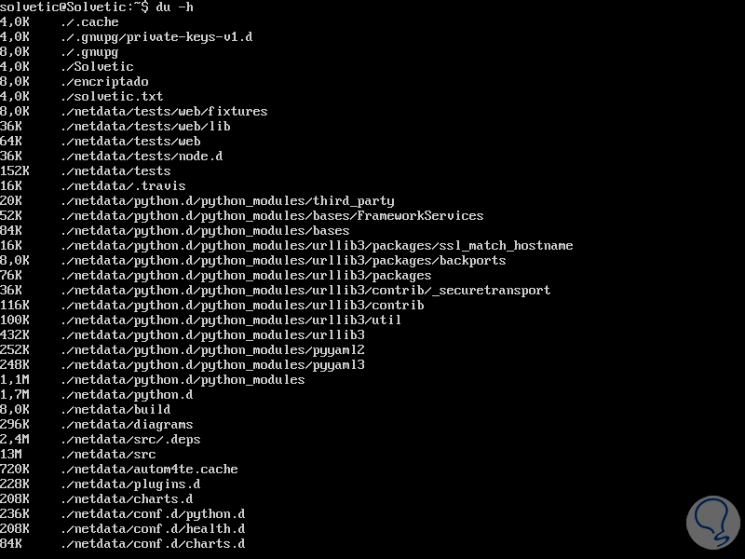
If we want to obtain the results in human or readable language, just execute:
du -h
Step 5
We can know in detail the weight of a specific directory, for this we use the following syntax:
du -sh (Route)
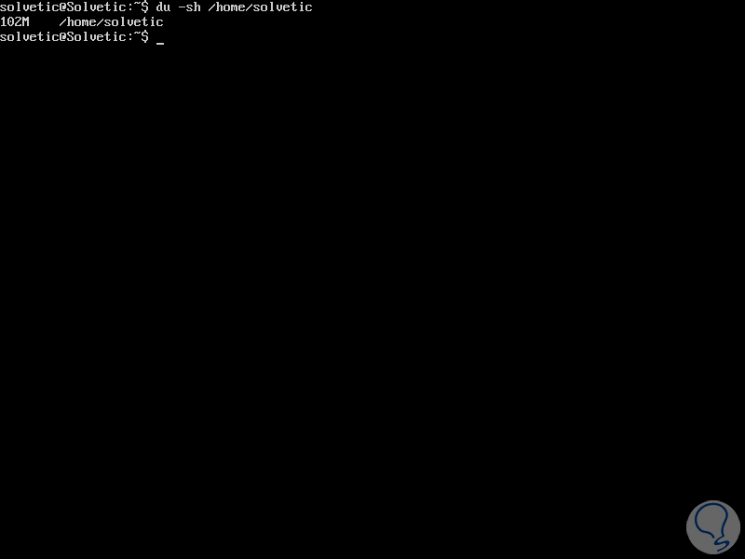
Step 6
These are two of the most useful commands to know in detail the space on the hard disk, but in Linux we can use some additional commands such as:
lsblk
This command displays the size of each disk and partitions in MB, GB, etc.
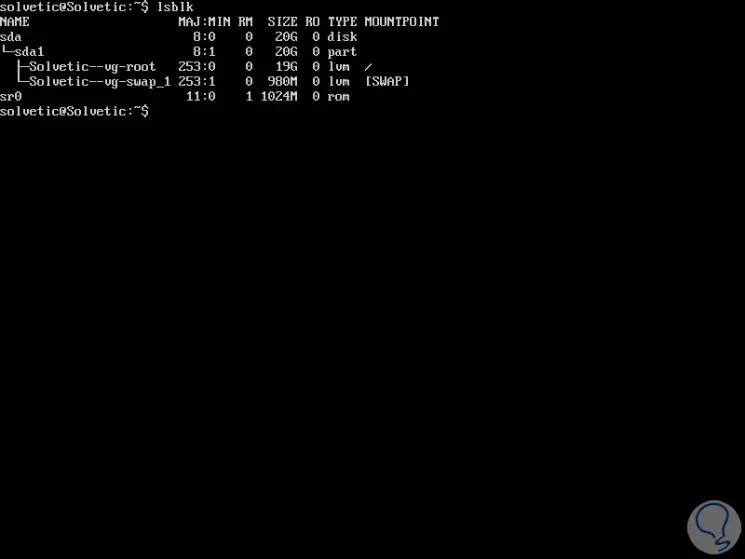
Tree
This command displays the results in tree format with each subdirectory which gives us a more global scope of information.
Step 7
For its installation we execute:
sudo apt install tree
The use options are:
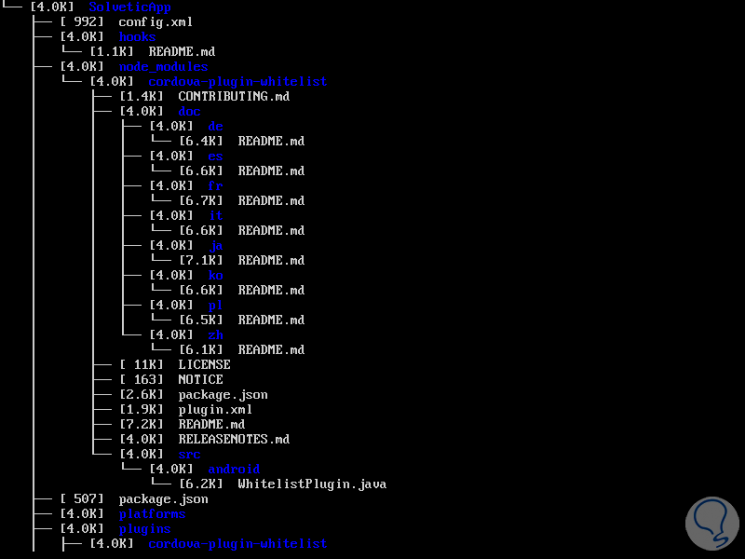
With any of these options it will be possible to know exactly the free space used in Linux..