Are you of what when you hear the word "command" you want the earth to swallow it? Or maybe you think that the commands are an almost impossible mission to carry out. Well, it's not like that, TechnoWikis assures you that every command in Linux , although it seems complex and extremely difficult to assimilate, is actually very practical and supports the tasks of support to be performed. Just understand its structure and purpose to realize that they will be our friends and with them many, we would say hundreds of tasks, will be executed more simply and completely..
Well, one of these "dark" commands is the pwd command which we will discuss in detail and with examples in this tutorial.
What is the PWD command?
The command PWD (Present Working Directory), we already understood clearly what it does, has as task to print the name of the current working directory in which we are, this helps to understand more about what we are working on without making mistakes.
The pwd command prints the name of the current directory, integrating the complete path with the root (/) as its origin. When using this command, it is important to know that it is integrated in the shell command and is available in most shell: bash, Bourne shell, ksh, zsh and more..
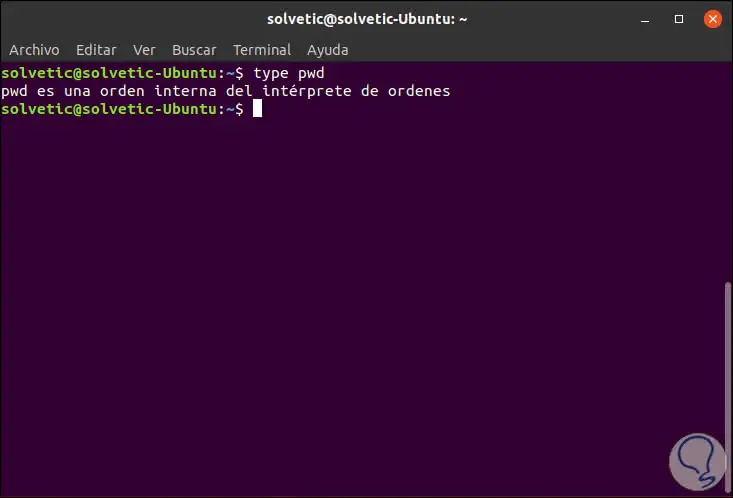
To determine which pwd is the default in our system, we must execute the following:
type pwd
The basic syntax of use of pwd is the following:
pwd [OPTION] ...
Now, the options that Linux offers us for the pwd command are:
-L, - logical
This option states that if the PWD environment variable has an absolute name of the current directory without "." or the components "..", we can be sure that this content will be generated, even if it contains symbolic links.
-PAG, --physical
With this option, we will obtain in response the printing of the name of the current directory, understanding that all the components of the name are real directory names but not symbolic links.
--help
Display command help
--version
Display the used version of pwd
TechnoWikis will explain some ways in which we can use this practical command in Linux and thus have one more ally in each task of support to execute.
1. How to print the current directory pwd Linux command
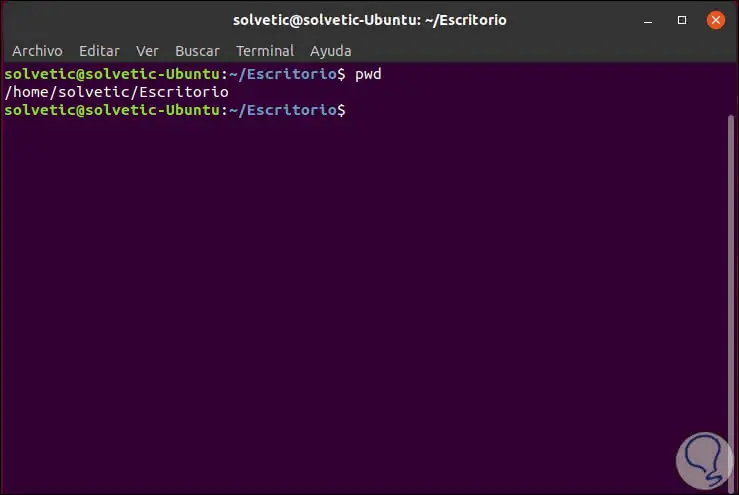
To visualize in which directory we are currently going to execute the following:
pwd
This option prints the name of the current working directory, in case any subdirectory in the path is a symbolic link, those symbolic link names will be printed.
2. How to print the real names pwd Linux command
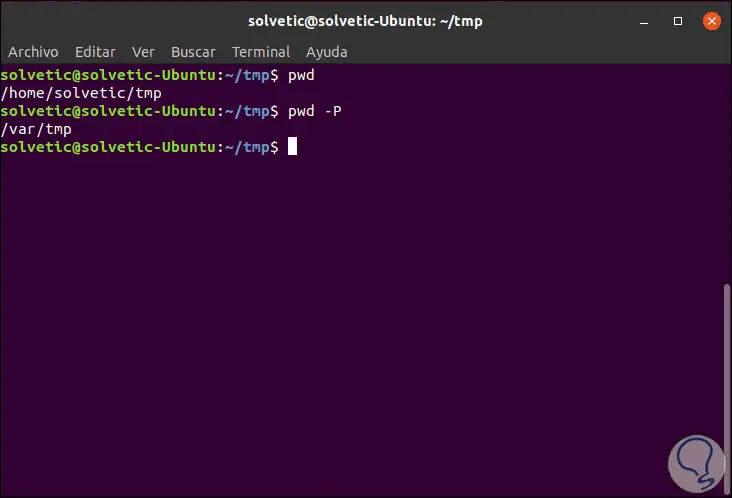
In the previous command, the symbolic names of the current work path will be printed, but if we want the real names of the directory components printed, we must use the following line:
pwd -P
For this example we have created a symbol link to / tmp and we can notice the difference between both commands:
3. How to use / bin / pwd Linux pwd command
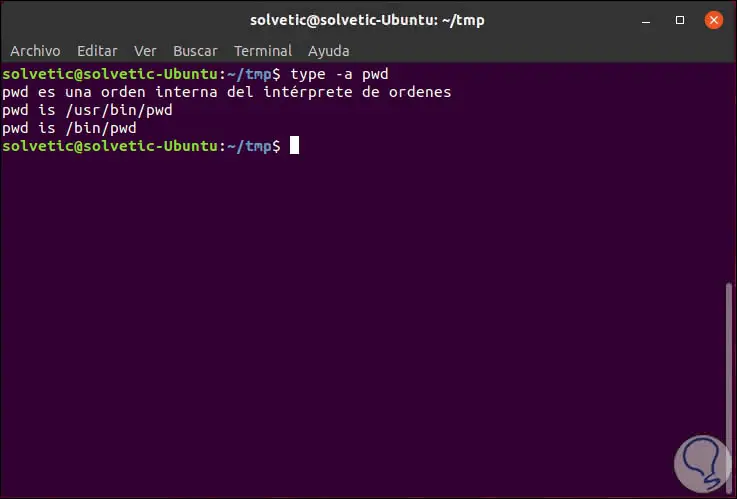
While pwd is integrated in the shell, / bin / pwd is the tool that is available in the Linux distribution used, we can verify this by executing:
type -a pwd
We can visualize the current directory by executing:
/ bin / pwd
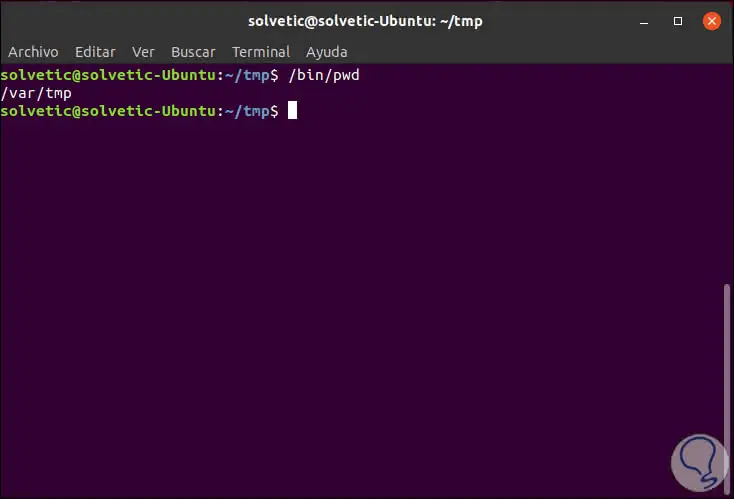
4. How to print symbolic links pwd Linux command
If we want to print the current working directory even if it contains symbolic links, we will execute:
/ bin / pwd -L
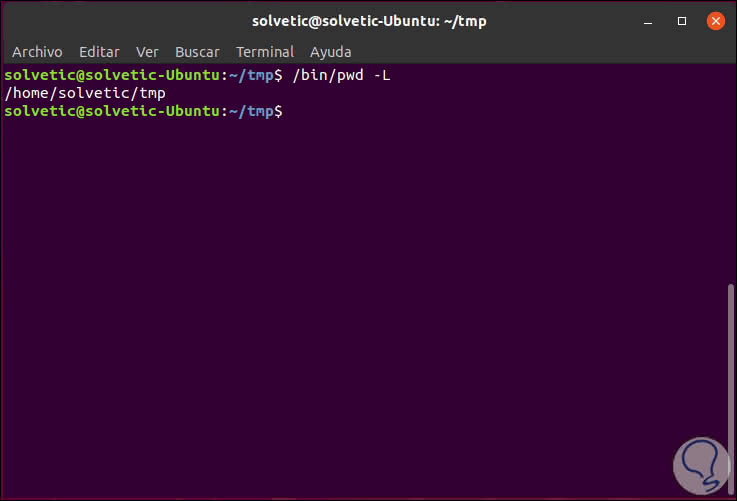
5. How to view the used version of pwd Linux
To check which version we are using, we must execute the following:
/ bin / pwd -version
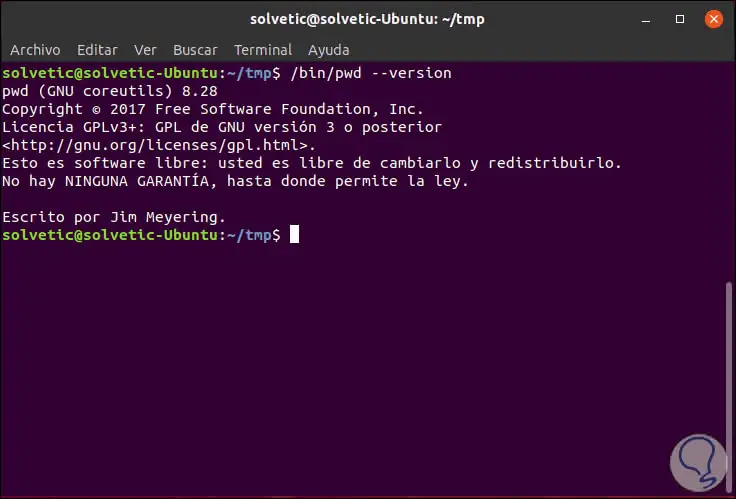
We have seen how the use of commands in Linux is not a mystery of another universe, but it is clear that it will be very practical to carry out more management tasks in Linux..