One of the components present in all operating systems and through which administrative or management tasks can be performed is the BIOS or UEFI which we have all heard at some point..
What is BIOS?
BIOS has long been the predominant level of boot management and hardware and system parameters, but we know that UEFI is setting the trend in new equipment and offers much more advanced functions both at the level of parameters and security.
BIOS (Basic Input Output System) has as its main function, to start the hardware components and allow the operating system to boot with all its services and processes.
BIOS features
When we use BIOS we have certain features such as:
- It is capable of executing codes in order to verify the integrity of all firmware components before they are executed and the operating system starts up.
- It performs a validation of the main hardware components in the equipment in order to ensure that all stored information loads correctly and does not generate problems during this process.
- BIOS can control additional modules such as video card or network card.
- Through the BIOS, it is possible to select the boot device, such as CD or USB, this for administration purposes.
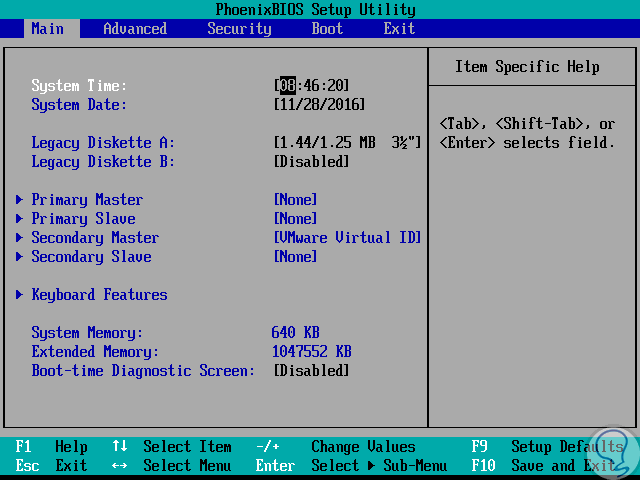
What is UEFI?
UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is the new boot management technology which is written in the C language and although it does the same as the BIOS, when our computer uses UEFI, it will have many more options highlighting a modern graphical interface, a safer boot system, better boot speed and support for hard drives larger than 2TB which is a limitation in BIOS.
UEFI Advantages
Some of the advantages of UEFI are:
- Start much faster and safer.
- It can be executed in 32 or 64 bits while BIOS is in 16 bits.
- It can support disks with capacities of up to 9.4 zettabytes while BIOS only supports 4 disks with a maximum 2.2 TB capacity.
- UEFI improves security by including the Secure Boot function.
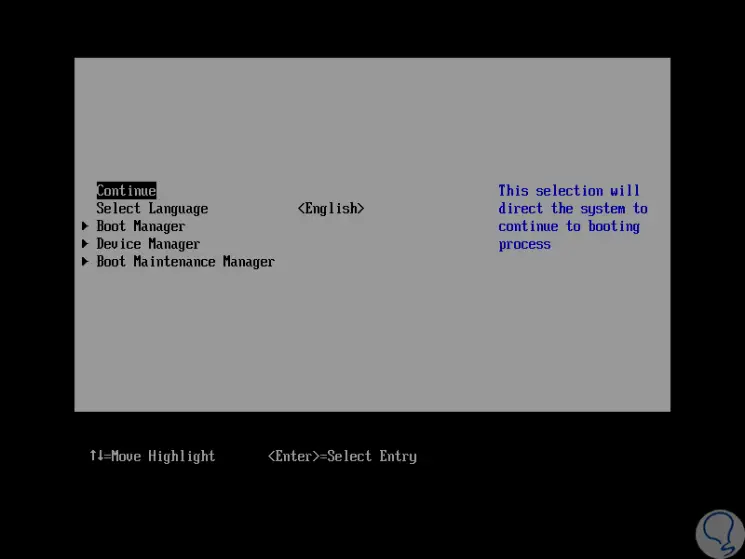
Now we will see how to check what type of manager we have in Windows or Linux..
To keep up, remember to subscribe to our YouTube channel! SUBSCRIBE
1. Check BIOS or UEFI from msinfo in Windows 10
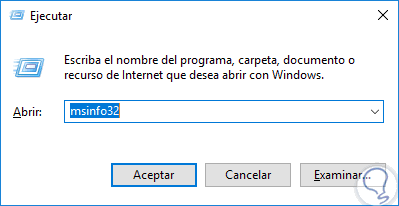
Step 1
The most practical method in Windows operating systems is to go to the System Information utility which can be accessed using the following key combination and execute the "msinfo32" command:
+ R
msinfo32
Step 2
Press Enter or Accept. We will be redirected to the next window and there we must locate the “BIOS Mode†line.
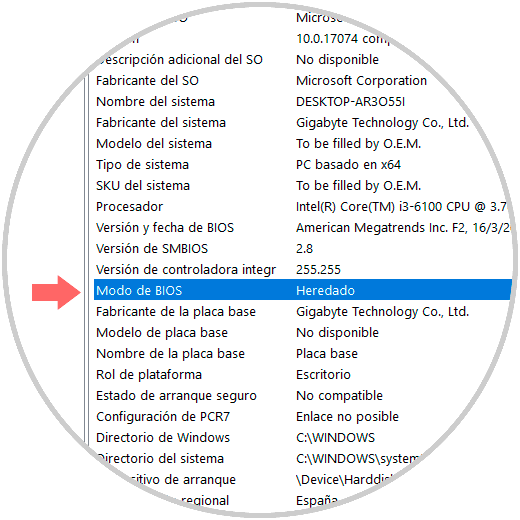
Step 2
There we can see two options:
Inherited
It indicates that we handle BIOS.
UEFI
As the name implies we will be using UEFI.
2. Check BIOS or UEFI from file in Windows 10
Step 1
Another option that Windows offers us to verify this information is to go to the following route:
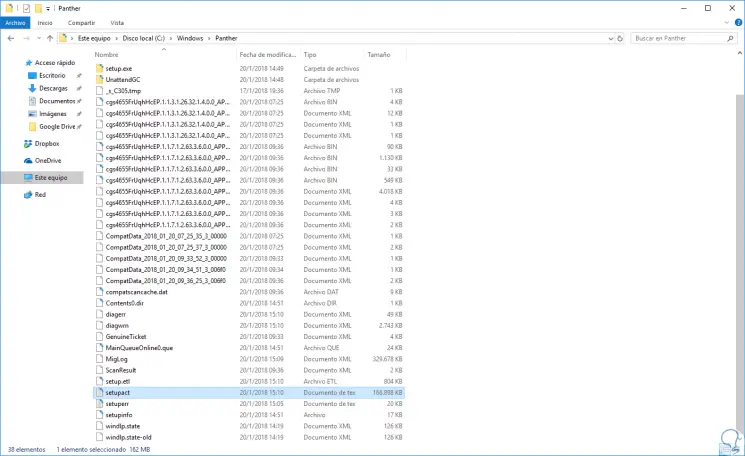
C: \ Windows \ Panther
Step 2
There we will locate the following line:
setupact.log
Step 3
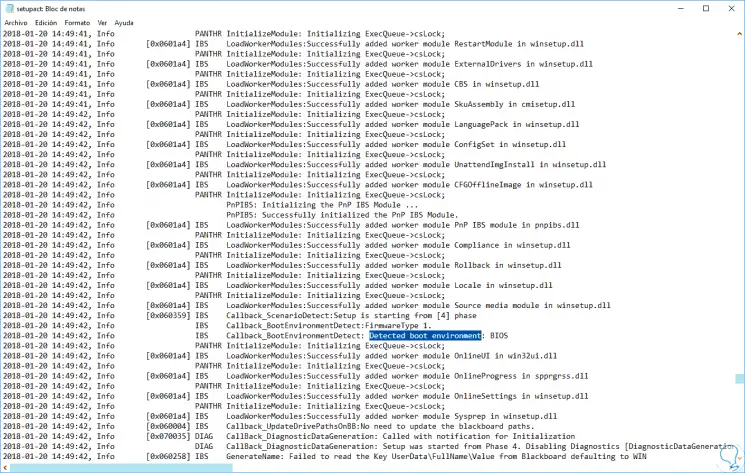
We proceed to open this file with some text editor and there we must locate the following line. There, we will see that the type of manager used is indicated.
Detected boot environment
Note
This action must be run as administrator.
3. Check BIOS or UEFI on Linux
The process in Linux is simple and it is enough to do UEFI checks.
Step 1
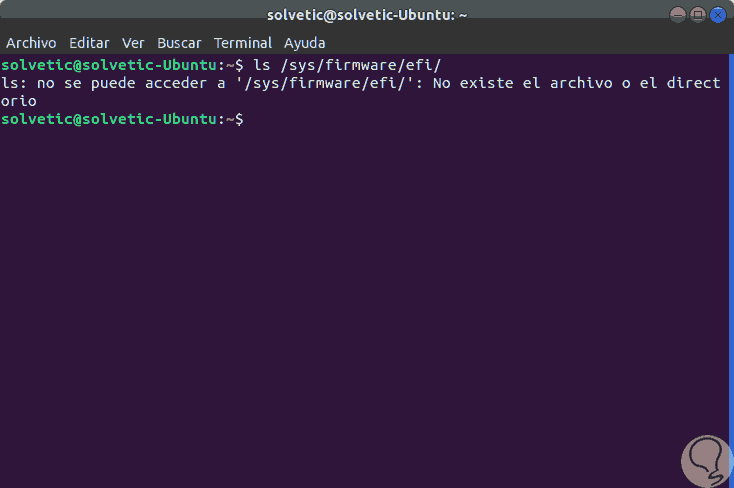
The first option to use is to go to the following directory:
/ sys / firmware / efi
Step 2
If there is any result, it means that we will have UEFI, but if the result is an error, it indicates that we use BIOS:
4. Check BIOS or UEFI on Deibian and Ubuntu Linux
Step 3
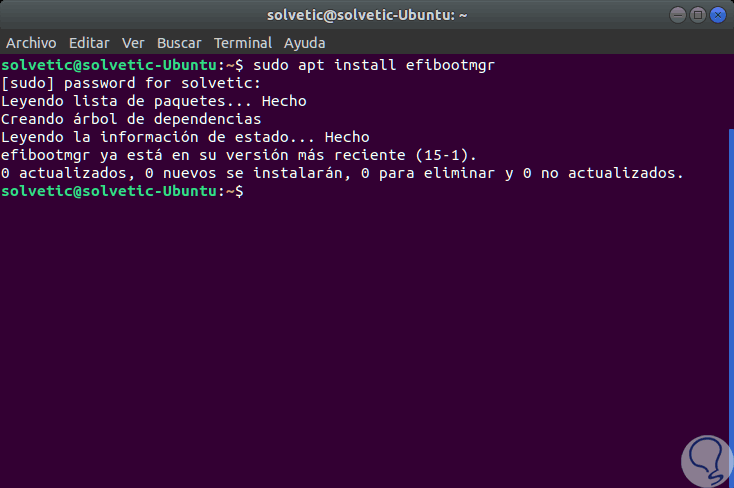
The second alternative, in Debian and Ubuntu, is to run the following command:
sudo apt install efibootmgr
Step 4
Once installed, we will execute the following:
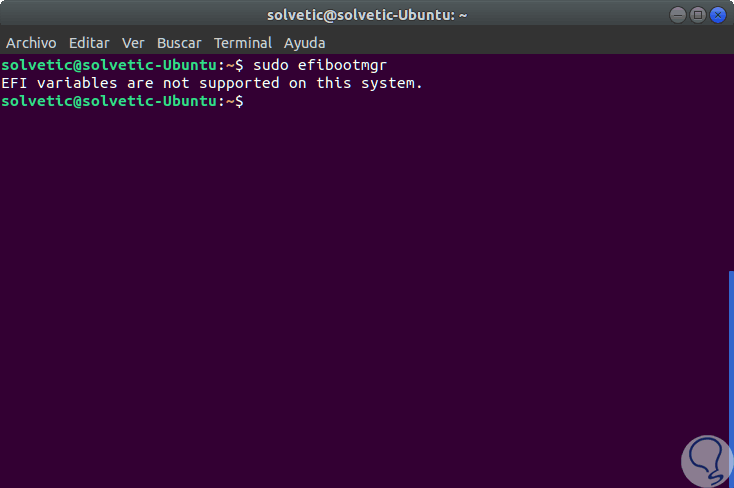
sudo efibootmgr
Step 5
Because UEFI makes use of variables, we should see them, otherwise this will be the result:
Thus we have checked UEFI or BIOS in Windows or Linux environments.