Information security is one of the most important bastions that every user or system administrator must take care of and implement in their own equipment as well as those under their responsibility, and although there are hundreds of options to increase security in an operating system , both software and hardware, we must select the one that best suits the needs of each environment and those of the system are the most appropriate..
In the case of Linux, the ideal integrated option to improve security is the firewall, based on the distribution used, it will fulfill certain special functions but a common objective that is to protect both the system and its services and the information hosted of all kinds of attacks
The firewall has the task of protecting all the information of the packets that enter and leave through the system ports, remember that each port has a clear mission, so, port 80 is used for insecure web browsing while port 443 It is used for secure web browsing.
With the firewall it will be possible to allow certain types of network traffic to enter and exit the system or we can also configure rules to allow or restrict access to specific IP addresses or domains thereby increasing overall security. We will talk a little about the firewall in two of the most known and used Linux distributions: CentOS and Ubuntu..
Ubuntu Firewall
Ubuntu distributions integrate a firewall called UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) which has been developed as a front-end for iptables and its use is practical for host-based firewalls.
UFW was added as of Ubuntu 8.04 LTS and as such it is available in all Ubuntu distributions as of this version.
Some of the features of UFW are:
- It has default entry policies (allow / deny)
- Allow or deny incoming rules
- It can be integrated into applications
- Deletion capacity per rule number
CentOS 7 firewall
In the case of CentOS, this makes use of firewalld as its integrated firewall, this is a firewall that dynamically manages the network areas which in turn define the level of trust of the network connections or interfaces available on the computer .
Firewalld supports IPv4, IPv6 firewall configuration, Ethernet bridges and IP sets and also provides us with an interface to manage services or applications in order to add firewall rules directly from there. Firewalld is available for CentOS and Red Hat distributions, some of its functions are:
- Compatibility with IPv4, IPv6, bridge and ipset
- Compatibility with IPv4 and IPv6 NAT
- Predefined list of zones, services and icmptypes
- Automatic loading of Linux kernel modules.
- Graphical configuration tool using gtk3
- Timed firewall rules in zones
- Simple registration of denied packages
- Simple service definition integrating ports, protocols, source ports, modules and destination address management
By default the firewall in both distributions is disabled and its activation is logically recommended, but for some type of administrative or support tasks it may be required that the firewall is temporarily disabled so that it does not interfere with the transfer of packets, so TechnoWikis will explain how to disable the firewall in these two distributions..
To keep up, remember to subscribe to our YouTube channel! SUBSCRIBE
1. How to disable the UFW firewall in Ubuntu
Step 1
For this case we will use Ubuntu 19.04 and first we must validate the status of the firewall by executing the following command.
sudo ufw status
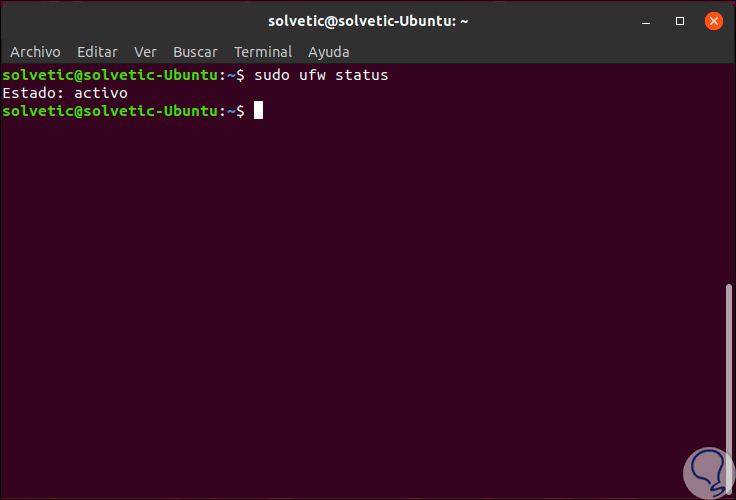
Step 2
As we see its status is active, now, to deactivate it, we will execute the following line:
sudo ufw disable
Step 3
We will enter our administrator password and we can verify that the firewall has been correctly disabled in Ubuntu:
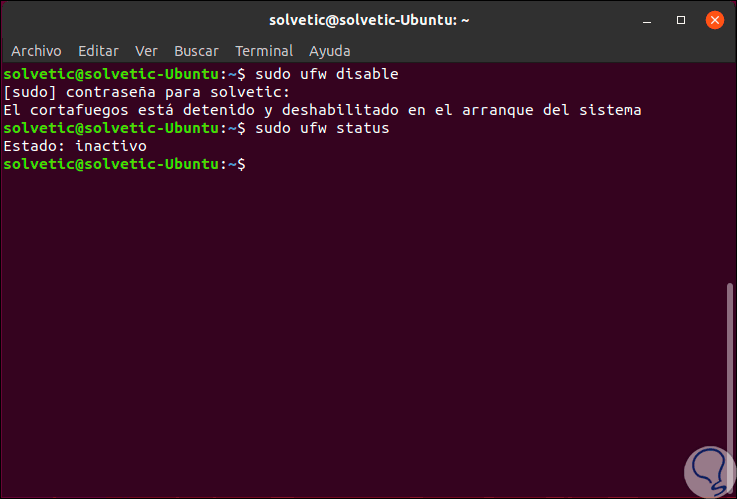
Step 4
Ubuntu gives us the option to administer the system firewall graphically thanks to a utility called GUFW which we install by running the following:
sudo apt install gufw
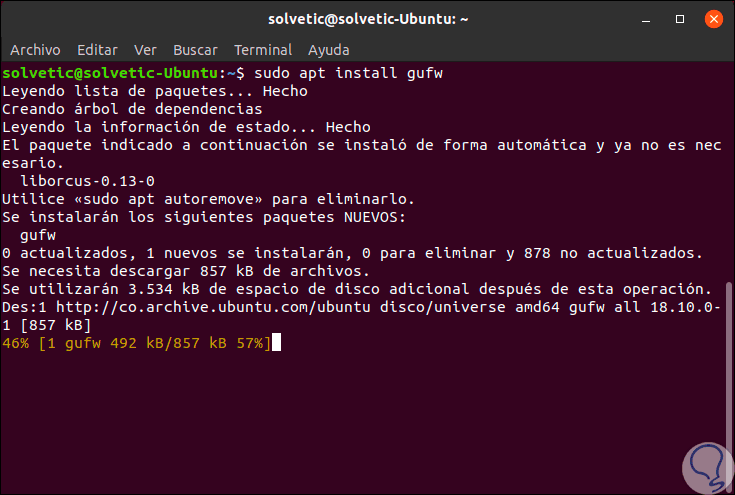
Step 5
Once installed, we can access it from the Ubuntu 19 search engine:

Step 6
Authentication will be requested:
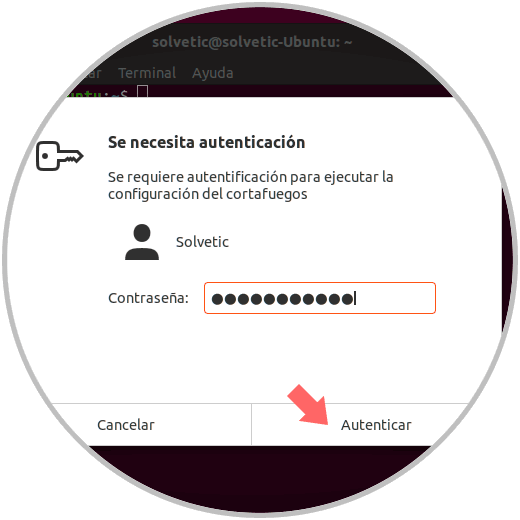
Step 7
Click on the "Authenticate" button and this will be the GUFW environment. There we can define the type of state for outgoing or incoming rules, as well as see the current rules, reports and so on.
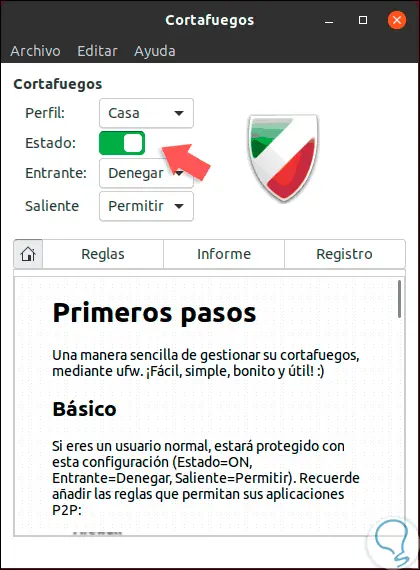
Step 8
To deactivate the firewall through this medium, we click on the "Status" switch. Thus, we can manage the firewall in Ubuntu.
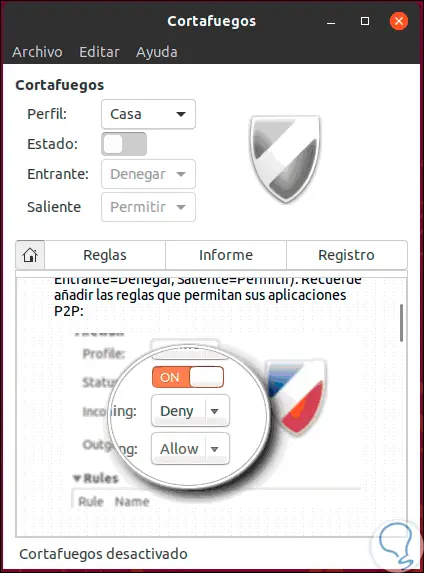
2. How to disable the UFW firewall in CentOS
Step 1
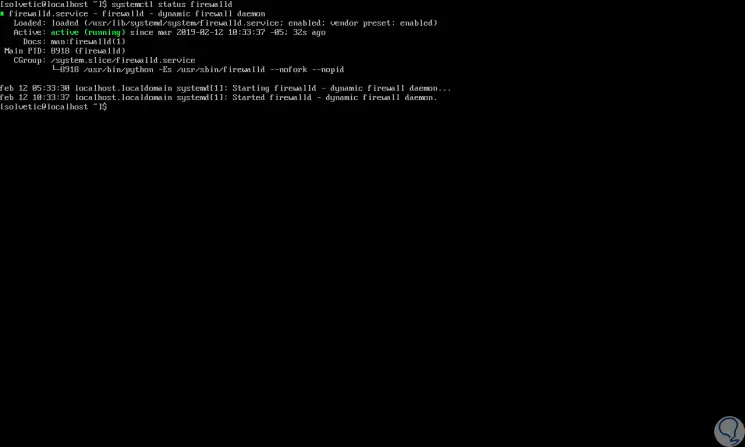
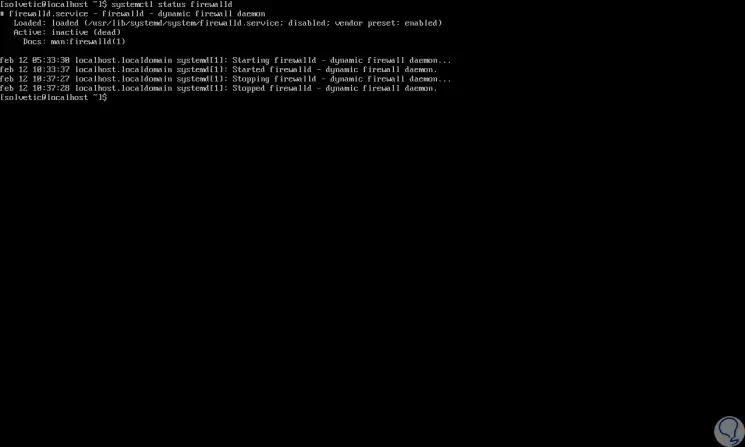
In the case of CentOS 7, the process is equally simple, first, we check the status of the firewall with the following command:
systemctl status firewalld
Step 2
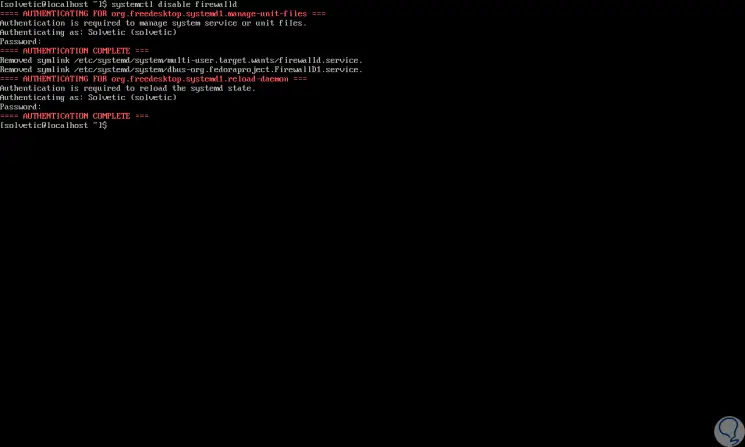
Once we validate this, we proceed to disable the CentOS 7 firewall with the following command. There we must enter and confirm our password to complete the process.
systemctl disable firewalld
Step 3
Finally, if we want to stop the firewall, we must execute the following line:
systemctl stop firewalld

Step 4
We can verify that the firewall has been disabled by running again:
systemctl status firewalld
With any of the options mentioned above, we can manage everything related to the disablement of the firewall in CentOS or Ubuntu and thus be able to execute the required tasks without problems but remember the importance of the firewall in the system.