SFC (System File Checker - System File Checker) is a command integrated into Windows operating systems whose mission is to thoroughly examine Windows and restore corrupt files found in this process, this works directly with the NTFS file system which allows all operations in Windows 10 or 11 (especially read and write) to be executed accurately, an error in NTFS can be reflected in various ways in the behavior of the system or applications, basically SFC performs a scan and verification of the integrity of all protected system files and then replaces the incorrect versions with correct versions, thereby optimizing usage..
In the event that SFC detects that a protected file has been overwritten, it will take care of recovering the correct version of the file directly from the systemroot\ folder in order to replace said file, allowing its integrity.
SFC Syntax
The general SFC syntax is as follows:
sfc [/scannow] [/verifyonly] [/scanfile=<file>] [/verifyfile=<file>] [/offwindir=<Windows offline directory> /offbootdir=<offline boot directory> /offlogfile=<path>
SFC parameters
The parameters used have been:
- /scannow: it is the most used parameter and is responsible for analyzing the integrity of all system files and repairs files with some type of error
- /verifyonly: this parameter allows you to scan the integrity of all protected system files but does not perform any type of correction
- /scanfile <file>: allows you to scan the integrity of the indicated file to repair the detected problems
- /verifyfile <file>: performs a verification of the integrity of the file that we indicate without making any repair
- /offwindir <offline Windows directory> - Specifies the location of the offline Windows directory to which offline repair will be done
- /offbootdir <offline boot directory> – Indicates the location of the offline boot directory to which the offline repair will be done
- /offlogfile=<log file path> – refers to the location where the log file will be stored
TechnoWikis will explain how to use SFC in various ways and for this we will use Windows 11.
To stay up to date, remember to subscribe to our YouTube channel!
SUBSCRIBE ON YOUTUBE
1 How to use SFC Scannow Online command
Step 1
This is one of the most common methods of using SFC, we open the Terminal as administrators:

Step 2
We accept the UAC permission:
Step 3
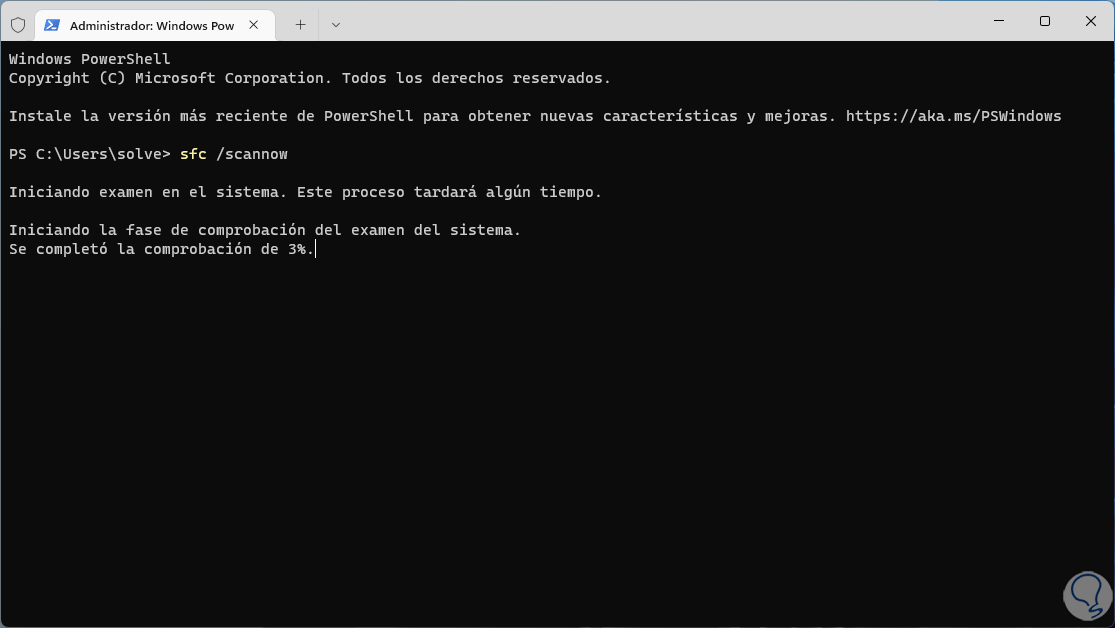
We execute:
sfc /scannow
Step 4
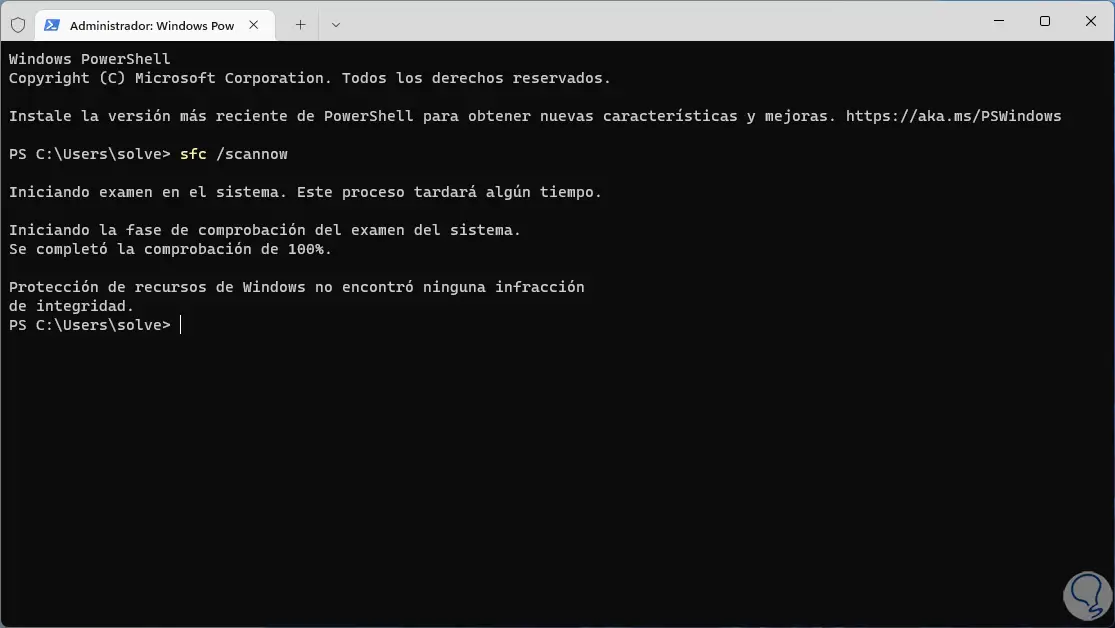
We wait for the process to finish:
step 5
In this case we can see that no error is detected, the message options that we can see will be the following:
- Windows Resource Protection found no integrity violations: This message indicates that there is no missing or corrupted system file
- Windows resource protection could not perform the requested operation: this message indicates an execution error, for its solution we run SFC again and additionally we check that the PendingDeletes and PendingRenames folders are created within %WinDir%\WinSxS\Temp
- Windows Resource Protection found corrupted files and successfully repaired them: refers to some errors have been fixed and are located in the CBS.Log file in the path %WinDir%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log
- Windows Resource Protection found damaged files, but could not fix some of them: indicates that not all the task was successful and we can see details in CBS.Log in the path %WinDir%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log
step 6
Now we open CMD as administrator.
step 7
We execute the following:
findstr /c:"[SR]" %windir%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log > C:\sfclogs.txt"
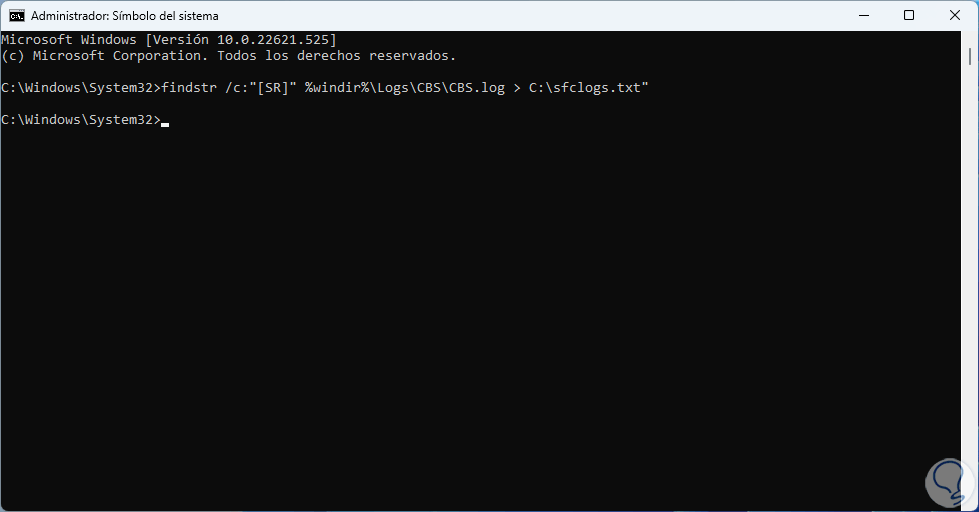
step 8
With this we have created a text file to see the details of the CBS.Log file, we open the File Explorer and in the C drive we will see the file created:
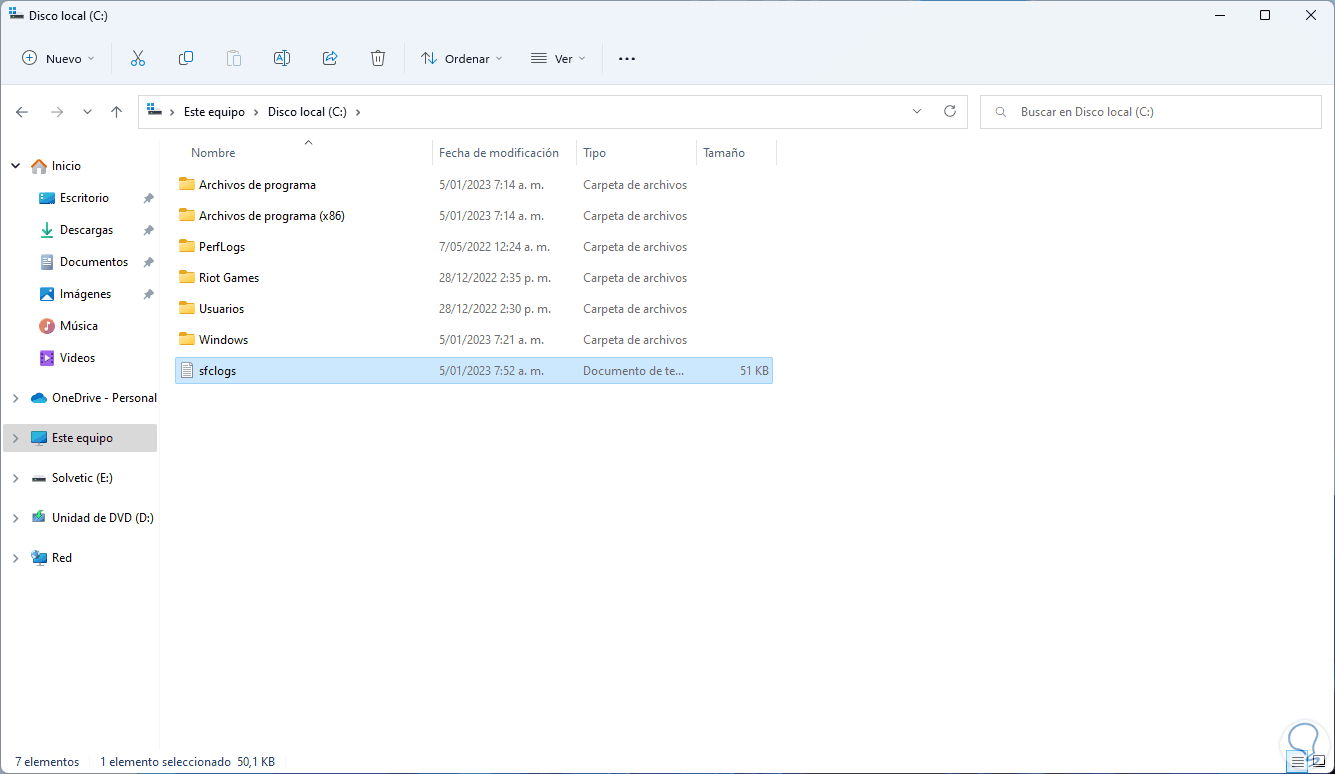
step 9
It is possible to open it to see the SFC process:
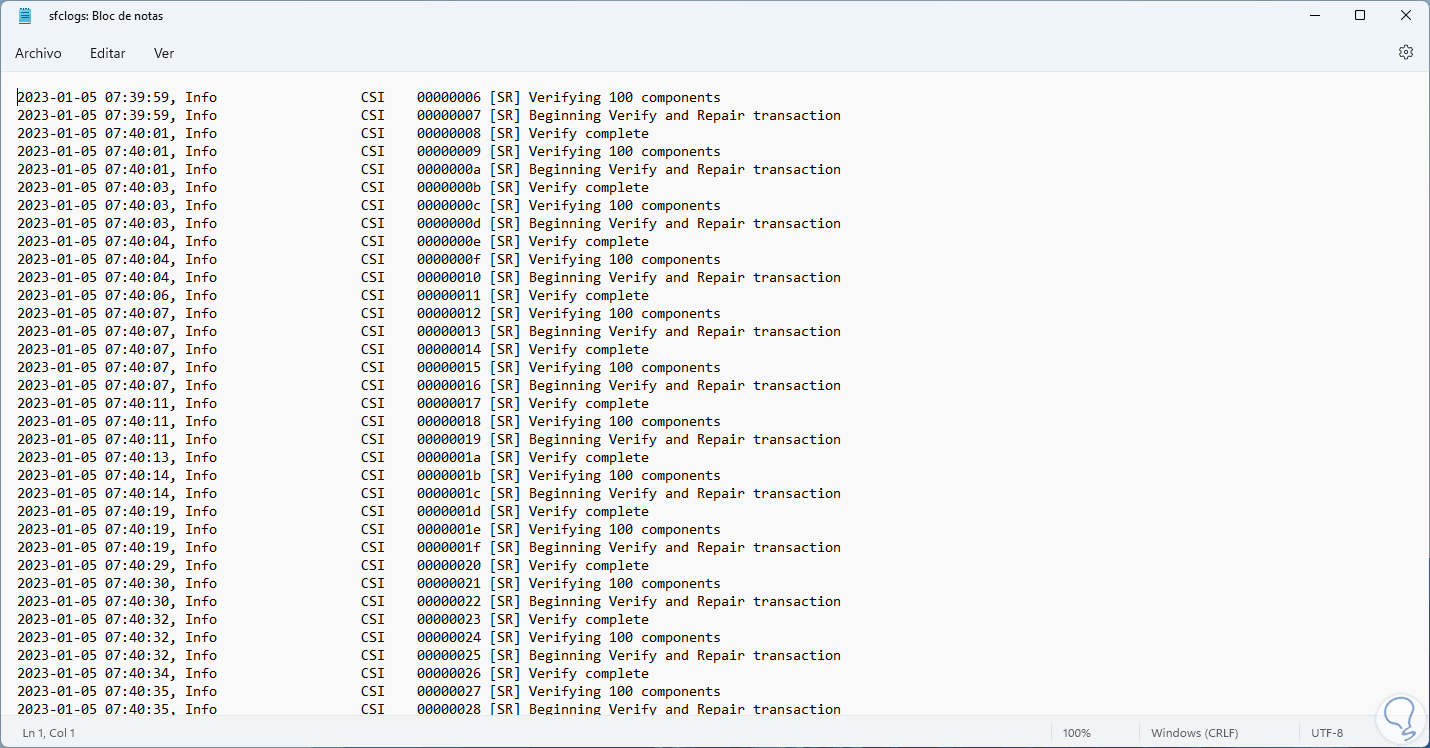
step 10
There we find the following syntax:
- Date and time of SFC execution
2 How to use SFC Scannow Offline command
It is now possible to use SFC in offline mode which allows a full scan to be performed without interfering with active processes..
Step 1
For this method we are going to:
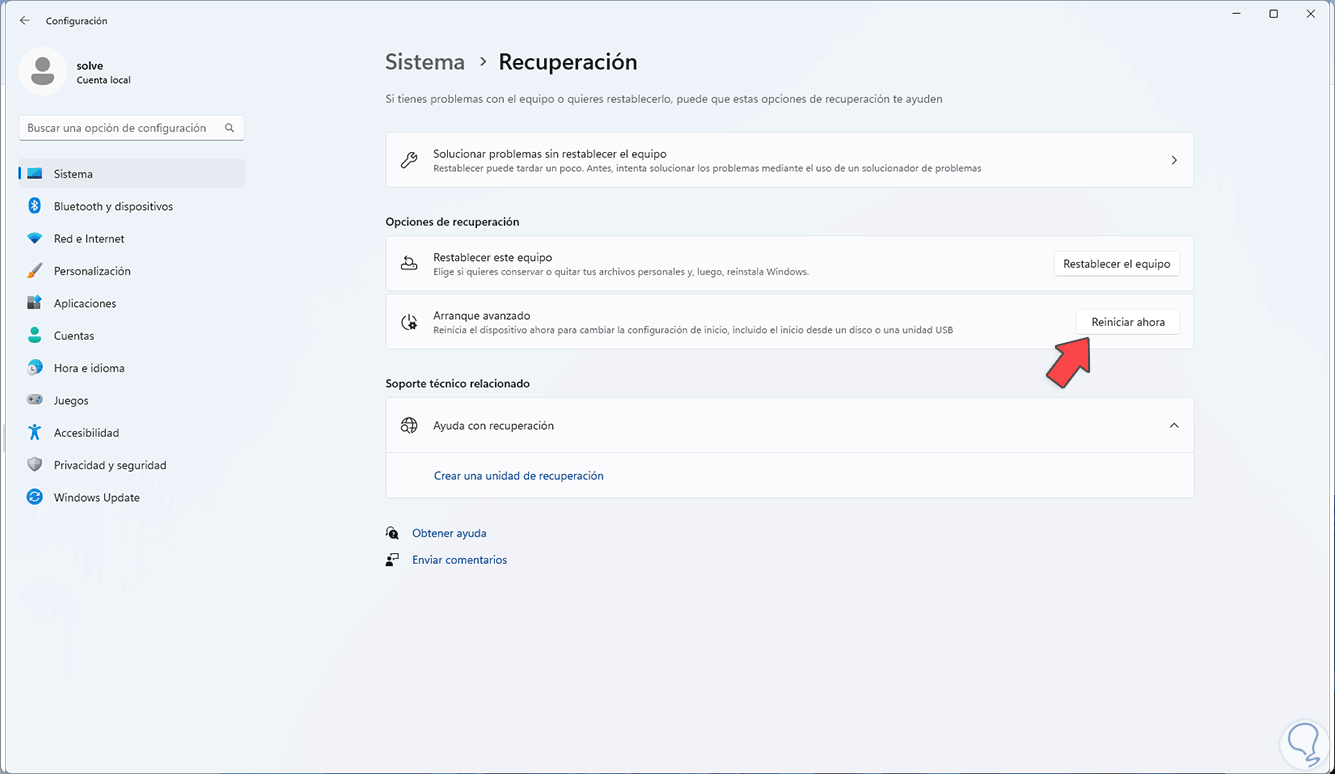
Step 2
There we will click on "Restart now":
Step 3
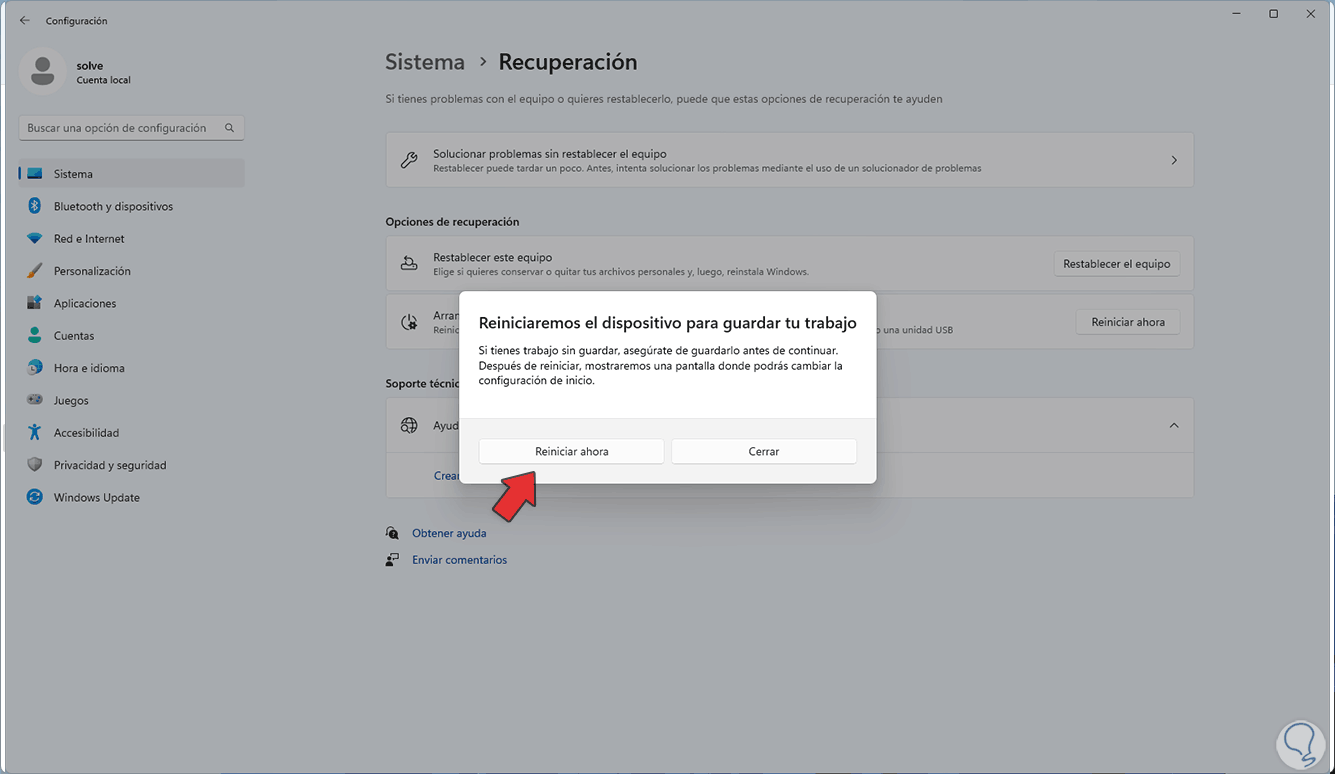
We will see the following message:
Step 4
Confirm the operation to start Windows in Advanced Mode:
step 5
We expect this mode to start:

step 6
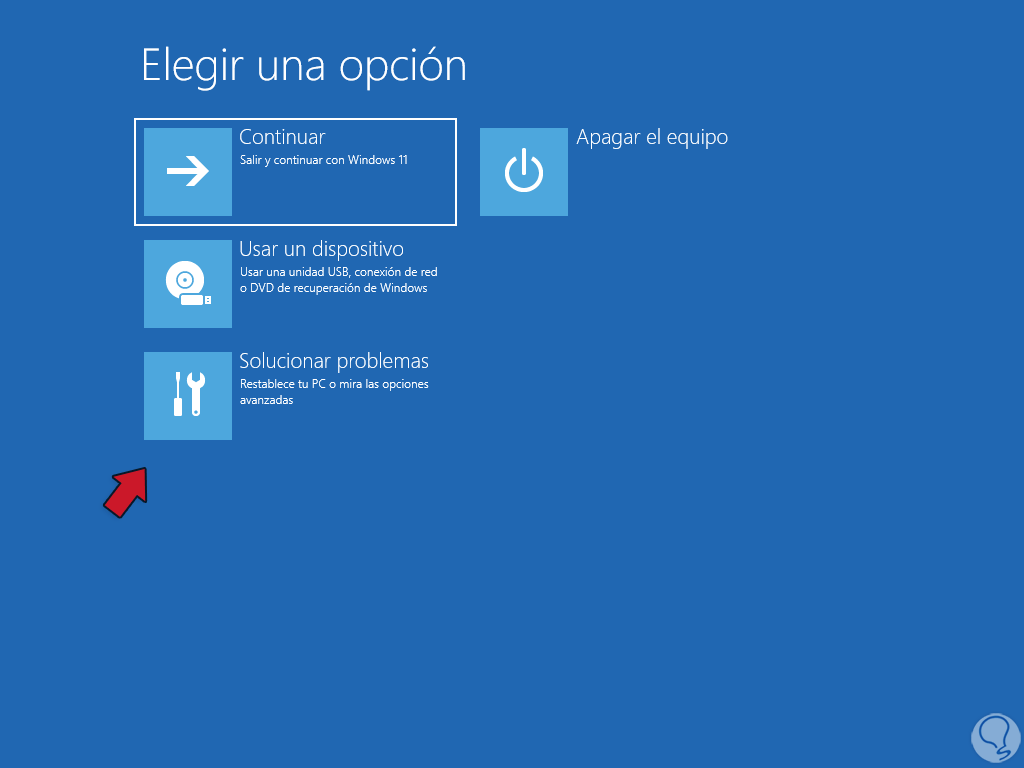
Now we click on "Troubleshoot":
step 7
Then we click on "Advanced options":
step 8
Now we click on "Command Prompt":
step 9
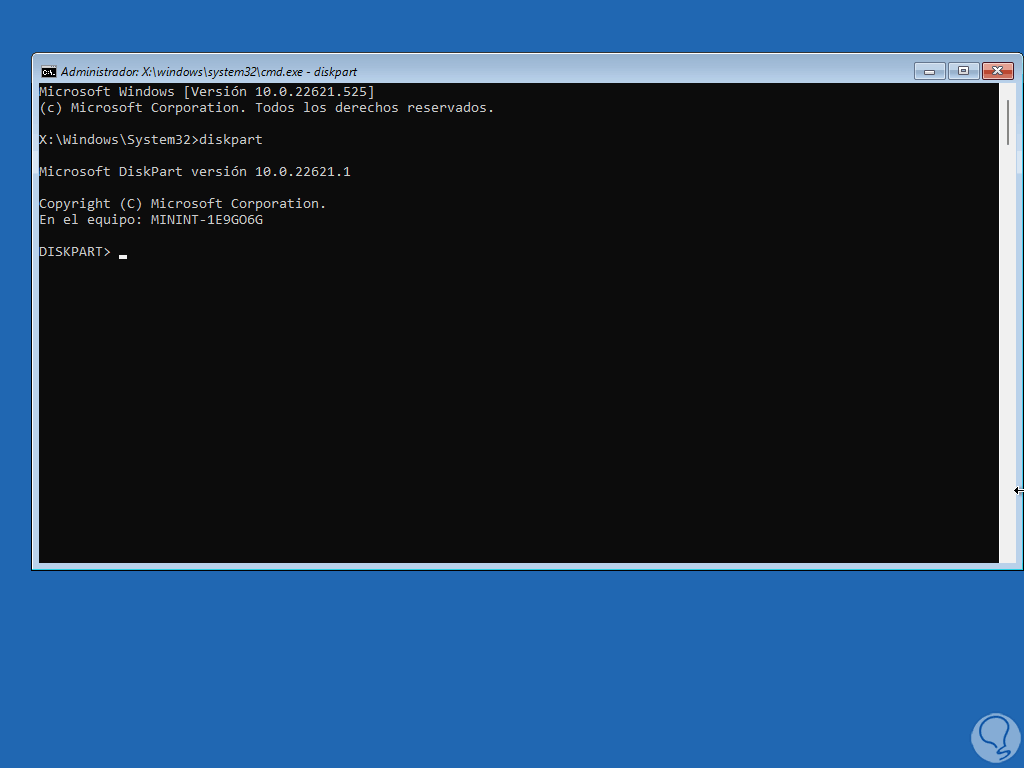
We will have access to the command prompt console, there we access the disk utility:
diskpart
step 10
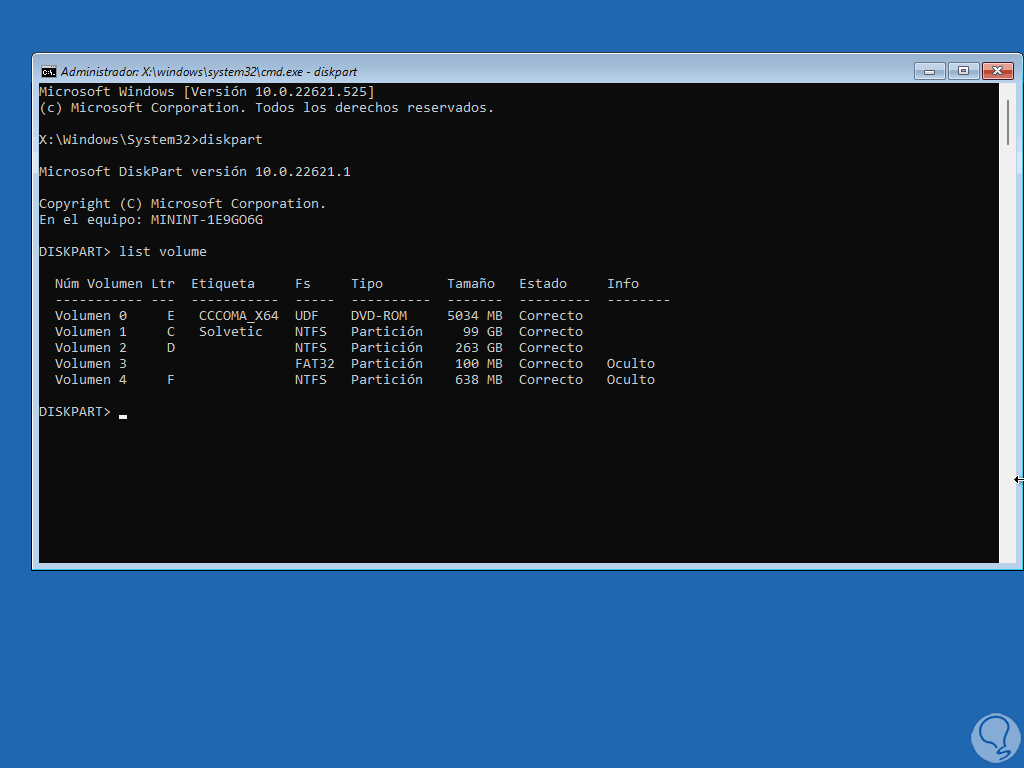
We list the volumes:
list volume
step 11
Consider the drive where Windows is installed (several gigs in size) and the reserved drive (a few megabytes in size).
We run the scan in offline mode:
sfc /scannow /offbootdir=(reserved_letter):\ /offwindir=(Windows_letter):\Windows
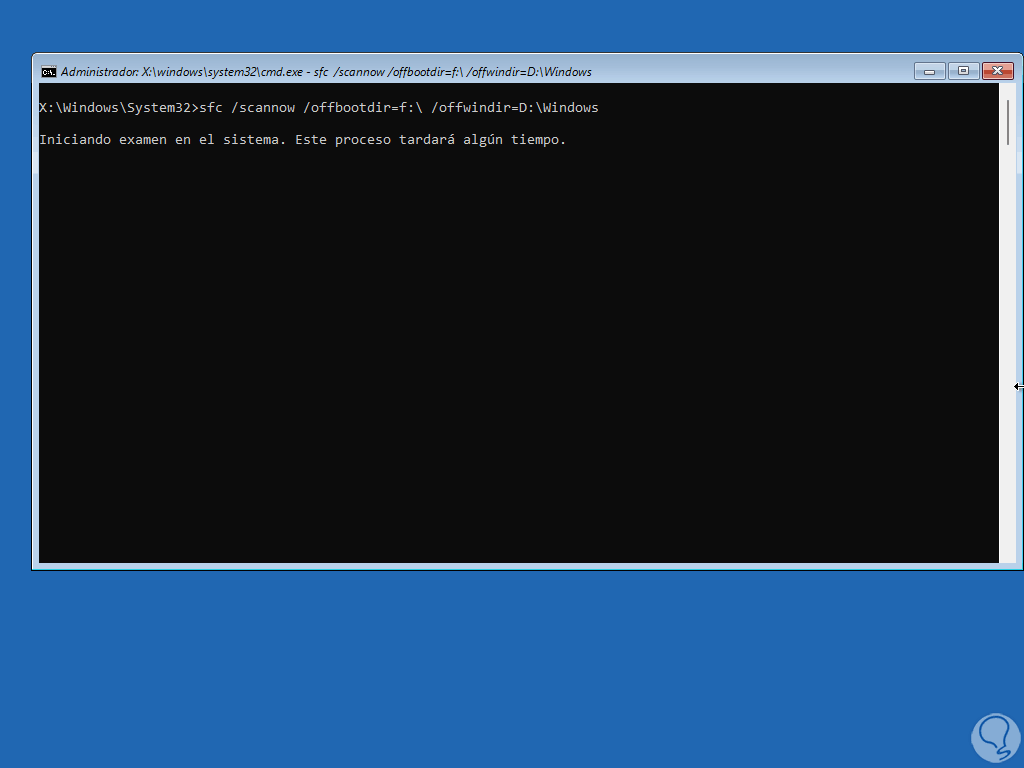
step 12
Wait for the process to finish:
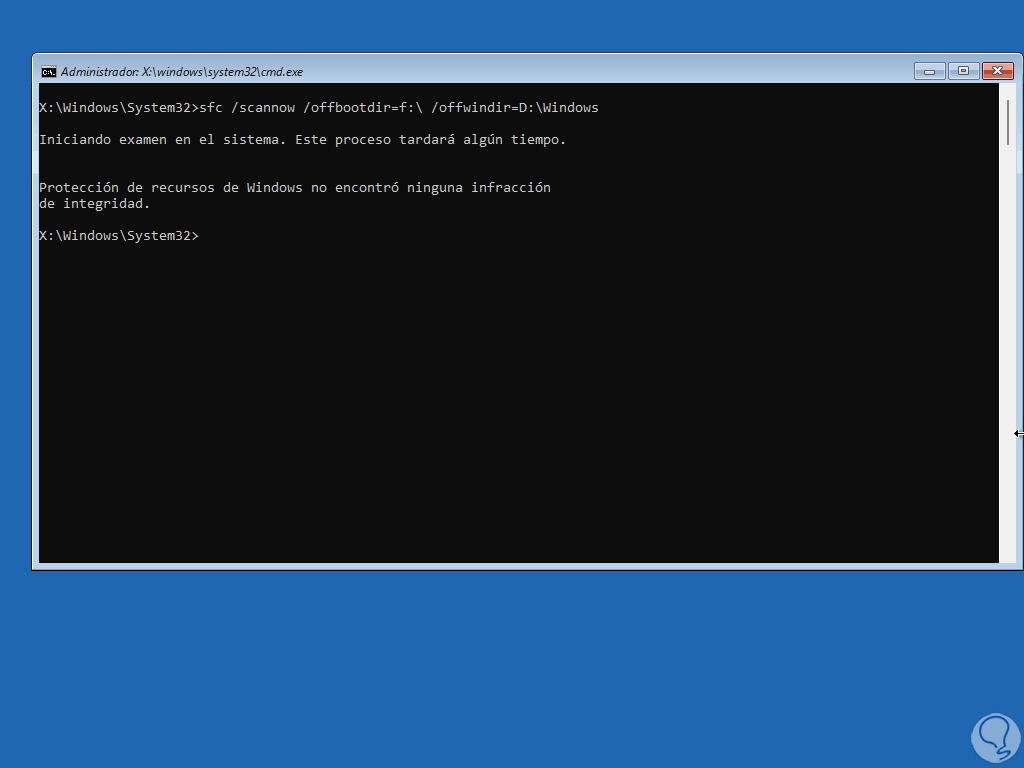
step 13
We exit the terminal and click "Continue" to access Windows 11:
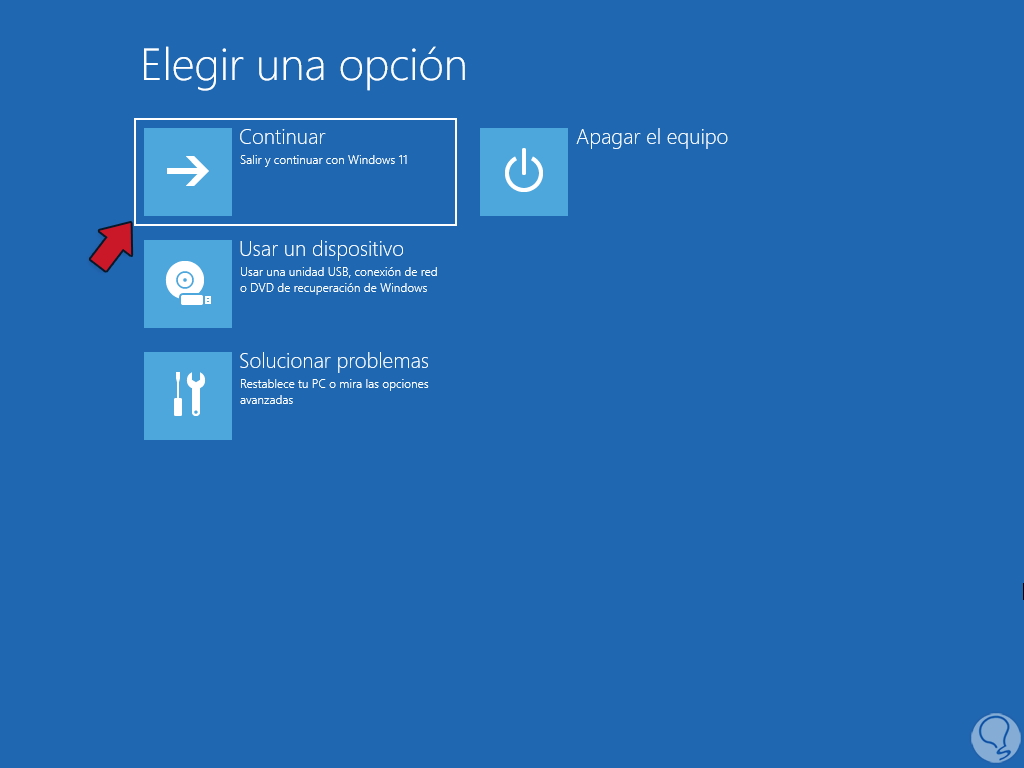
step 14
Windows will be started:
3 How to use SFC Scannow command with manual repair
Step 1
As administrators it is possible to manage the results of SFC to detect where the errors occur and thus be able to work directly on them, first of all, we open the File Explorer and in drive C we will see the SFC log file which we explain above how to generate:
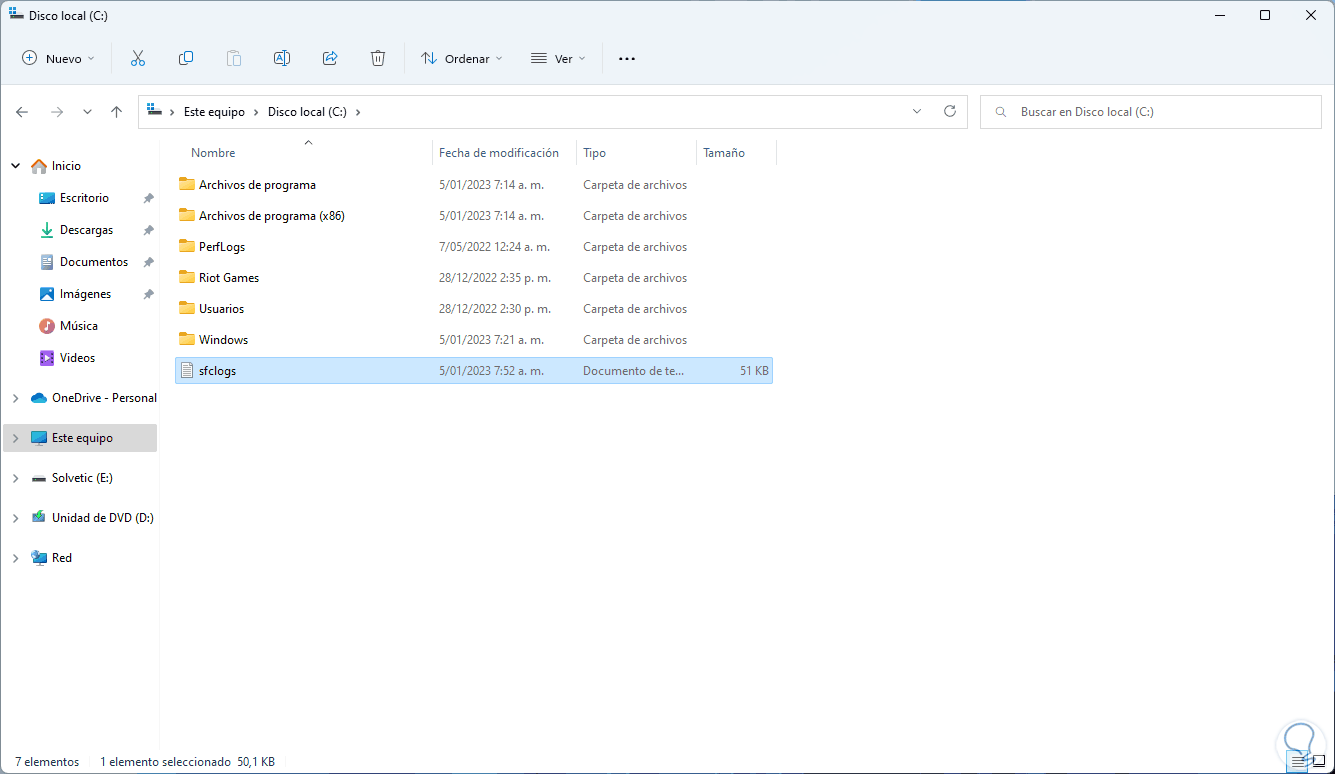
Step 2
When opening it, it is possible to find the files with error:
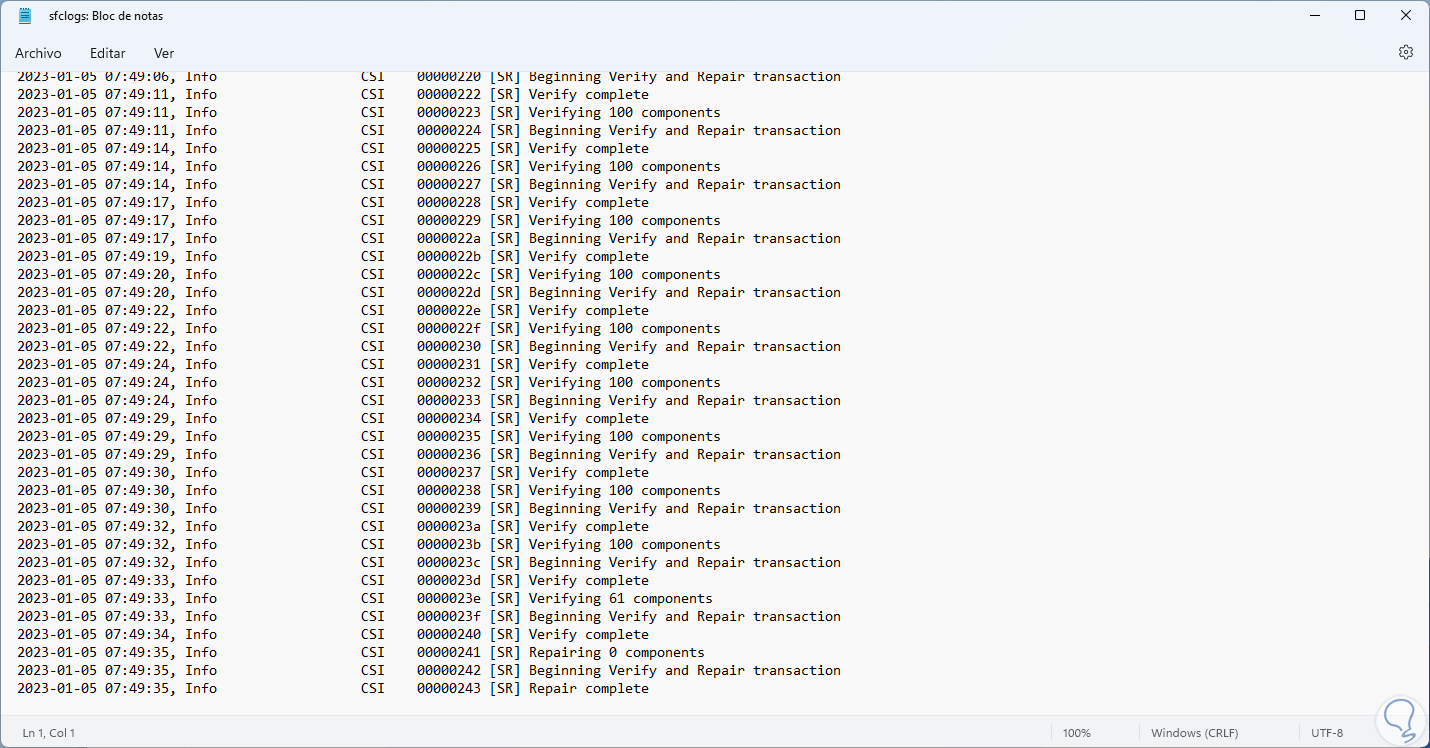
Step 3
Now we open CMD as administrator:
Step 4
We take ownership of the failed file:
takeown /f (file path)
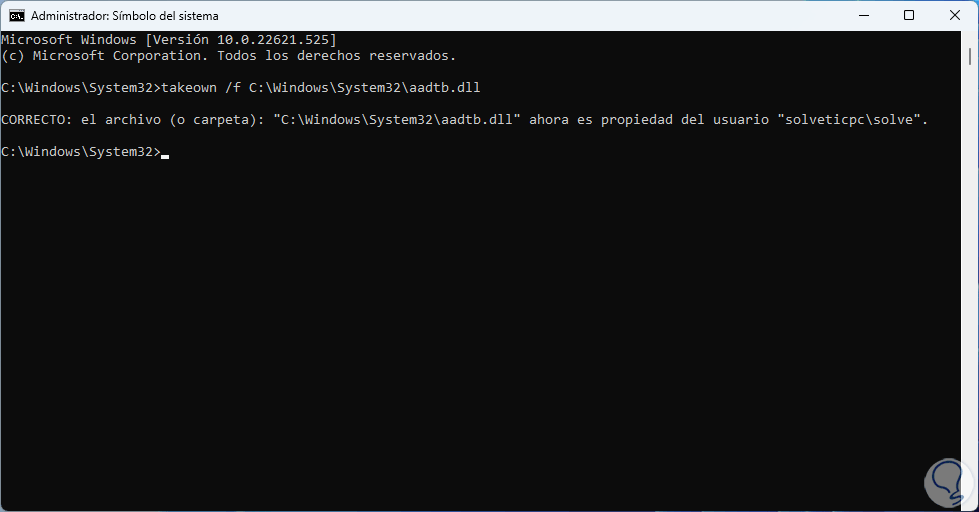
step 5
This will give the administrative ownership of the file in question, now we are going to execute the following to have full administrator access to the system file that presents the error:
icacls (file path) /Grant Administrators:F
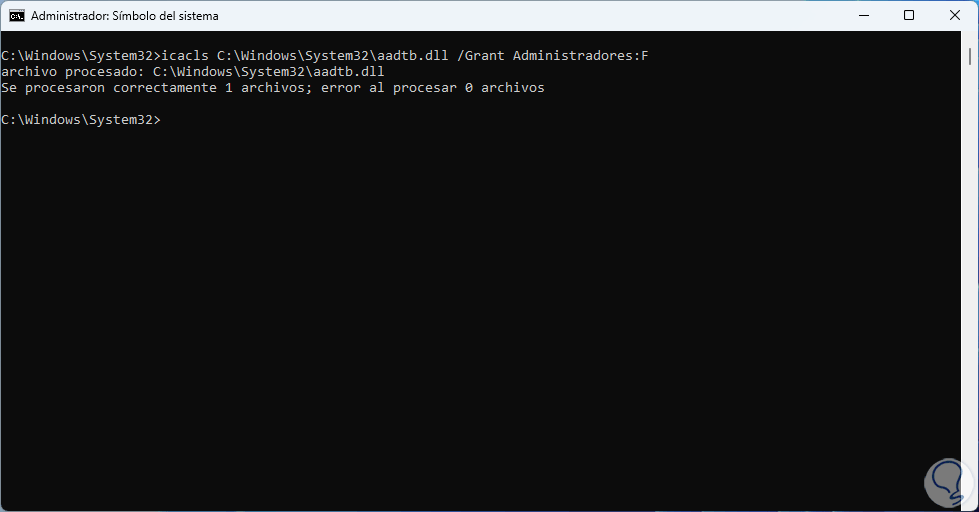
step 6
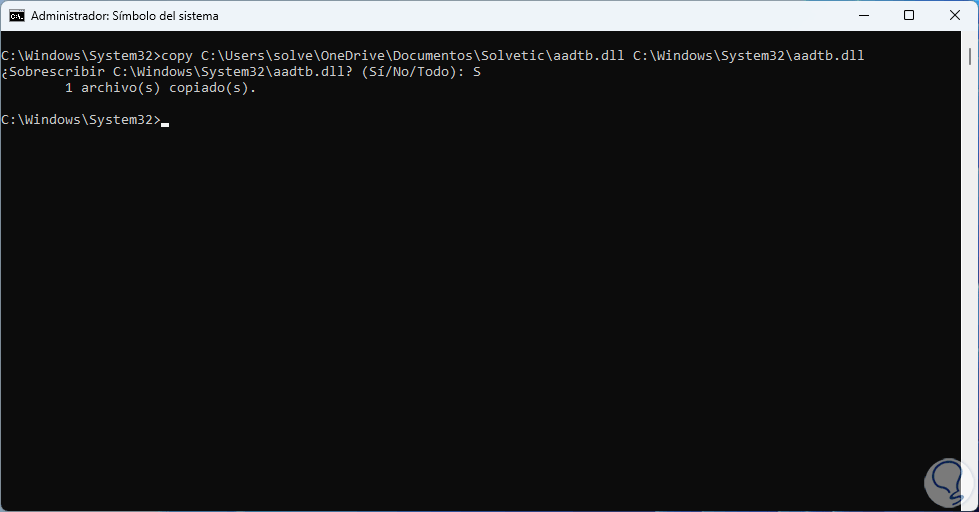
Finally we are going to replace the damaged system file with a file that is in perfect condition, we execute the following:
copy (source_path) (file path with error)
step 7
We must confirm the process by entering the letter S:
This is how SFC will help us to examine the file system in its entirety and to be able to correct errors that affect the operability of the system.