macOS is a versatile operating system from where it will be possible to manage a large part of its resources and services directly from the Mac terminal . For this, there are a large number of commands that are related based on the tasks to be executed, user information, disk validation, shutdown or reboots, etc., everything is a set of options to correctly manage the macOS system..
But only an administrator or root user, who is also known as superuser, will be able to execute most of the commands available for the administration tasks of a server or computer, this is a denominator in UNIX systems. Being an administrator allows us to make more important changes to our team, knowing that there may be significant consequences for it. Opening the Mac terminal as administrator allows us to execute commands to modify important parts of the computer.
TechnoWikis will explain in a simple way how you can execute commands in the macOS terminal as administrator or superuser..
To stay up to date, remember to subscribe to our YouTube channel! SUBSCRIBE
Open Mac terminal and run commands as Administrator or superuser
Step 1
For this we access the terminal either from Spotlight or from Applications - Utilities, when accessing the terminal we will be as the current user with whom the session was started:
Step 2
There we will execute the following:
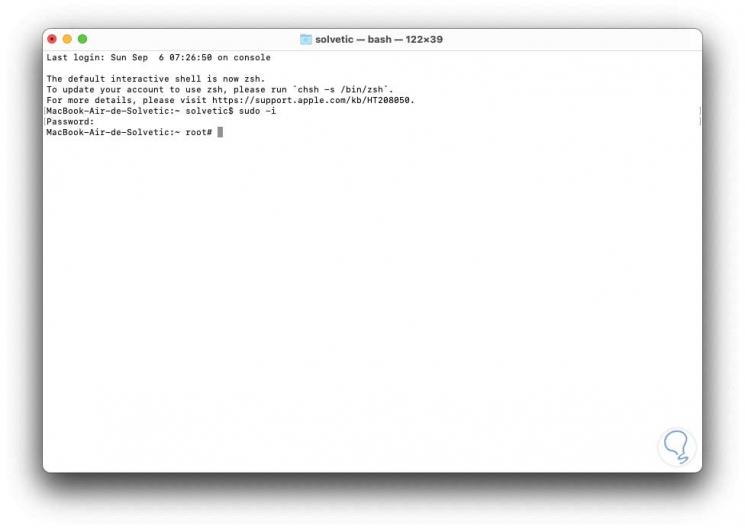
sudo -i
Step 3
We enter the team administrator password and we will see that the current user is now the root administrator user:
Step 4
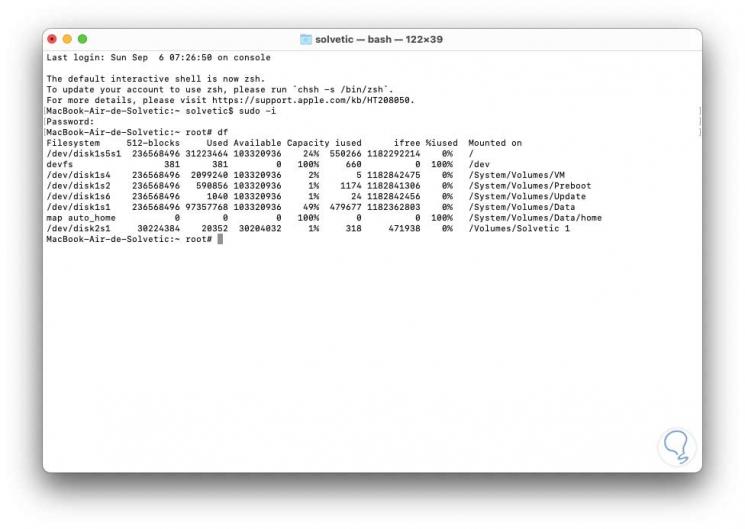
There we can execute any command with all the permissions assigned by the system:
Step 5
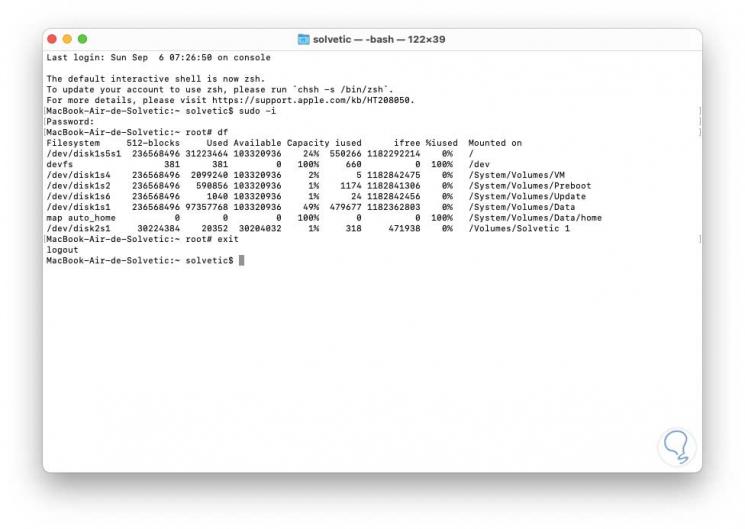
To exit the root user, for security, we can use two ways, these are. We can see that the root session is closed and we will be with the local user again.
- Closing the terminal directly
- Executing the command "exit"
This is the simple method to run commands on macOS as administrator users and is ideal for support tasks.