When we work on Linux distributions we must know that services and daemons are executed in the background (nothing to do with Halloween) that have a direct impact on the way tasks are carried out in Linux, many of these services are started from the moment when we turn on the computer and in modern distributions these services are launched by systemd, and their details are stored in the path /usr/lib/systemd..
systemd has been developed as a system and service manager thanks to which it is possible to perform various tasks to manage system actions which includes services and daemons.
Systemctl is used to control the status of the system manager and systemd services and thanks to its use we can carry out different information tasks about the services or daemons that are currently running on the used system..
TechnoWikis will explain in detail how to use systemctl in Linux, for this case we will use Ubuntu 22.04 but this process applies to Systemd-based distributions, to check whether or not we use Systemd we open the terminal and execute:
ptree | head -5
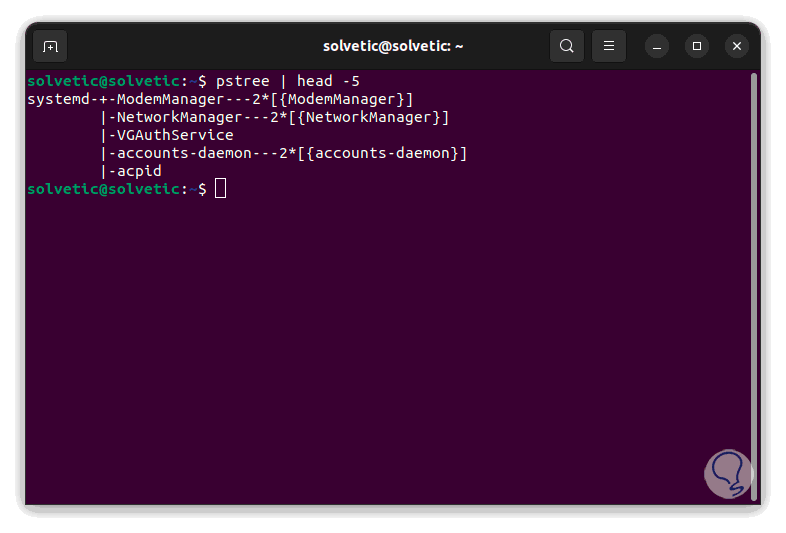
There we validate that systemd is used.
To stay up to date, remember to subscribe to our YouTube channel! SUBSCRIBE
How to use systemctl on Linux
Step 1
We list the active services with the order:
systemctl --type=service --state=running
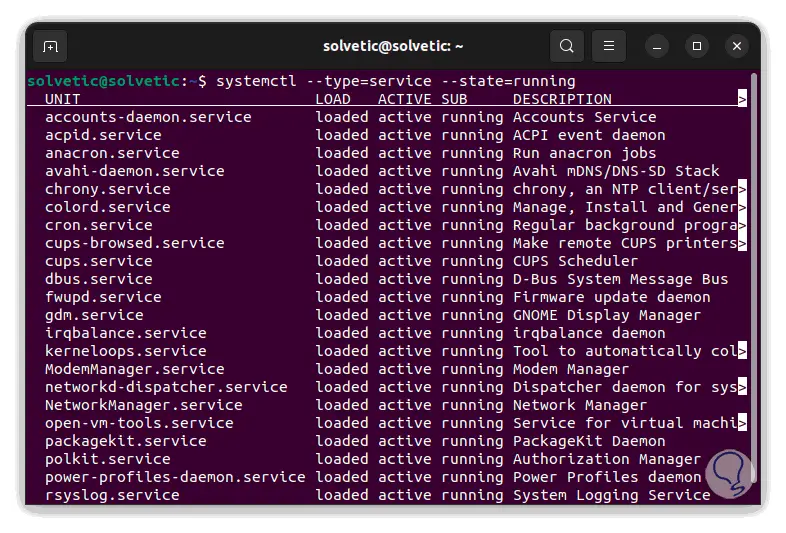
Step 2
We use the arrow keys to the right or down to see more results:
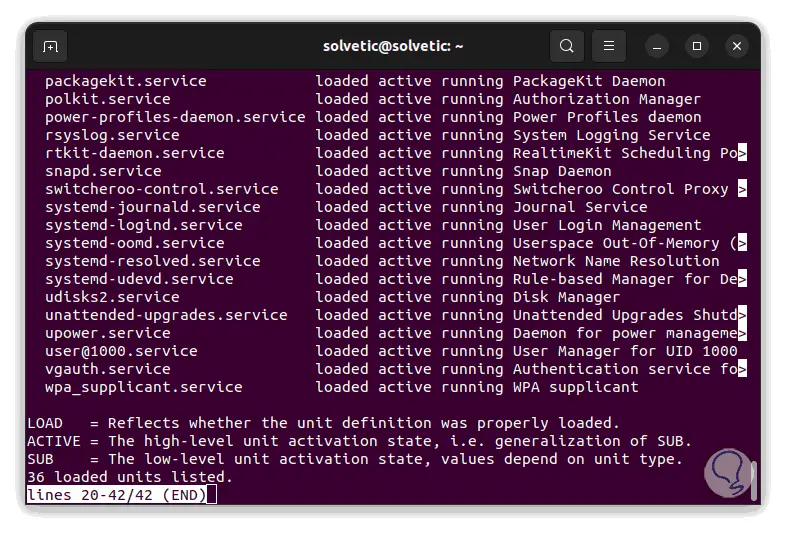
The columns displayed are:
- UNIT: is the name of the service or daemon and its name is because all its content was made through the systemd information which is in a unit file
- LOAD: is the load status of the service, the options are loaded, not-found, bad-setting, error or masked
- ACTIVE: is the current general status of the service or daemon, the options are active, reloading
- (recharging) , inactive (inactive), failed (failed) , activating (activating) or deactivating (deactivating)
- SUB: indicates the substate of the service or daemon, the options dead, exited, failed, inactive, or running
- DESCRIPTION: is a reference of the deployed service or daemon
Step 3
It is possible to search for a particular service:
systemctl --type=service --state=running | grep "service"
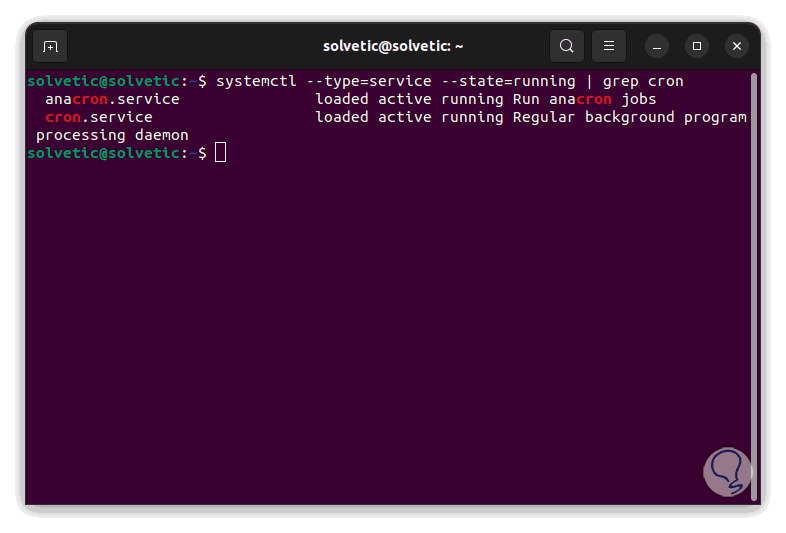
Step 4
We list the failed services:
systemctl --type=service --state=failed
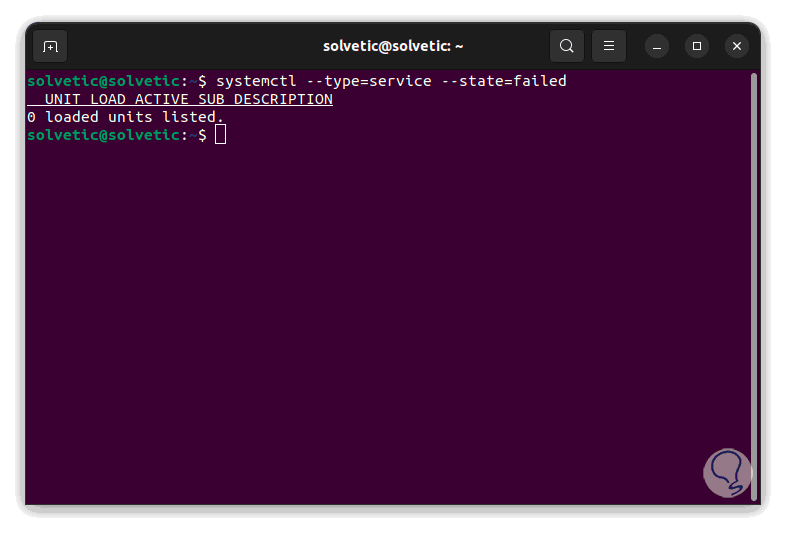
step 5
It is possible to list two states and these must be separated by commas:
systemctl --type=service --state=failed,exited
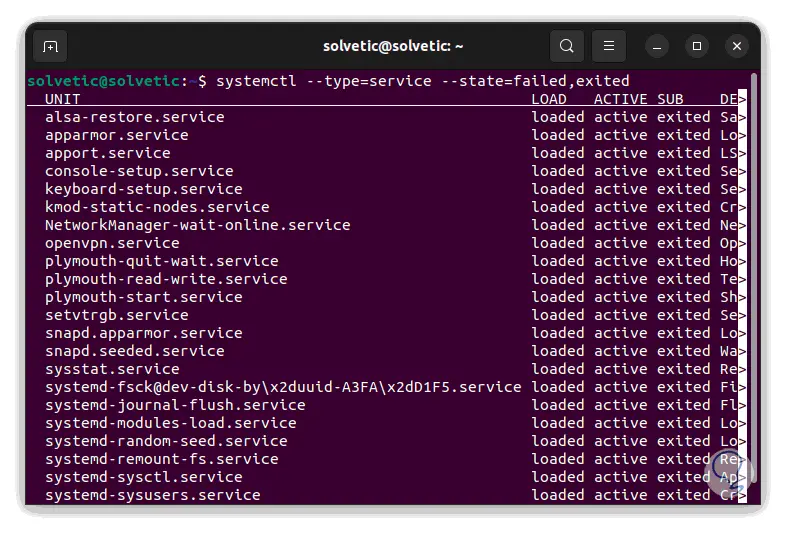
step 6
We will see the complete list of services that both states can have:
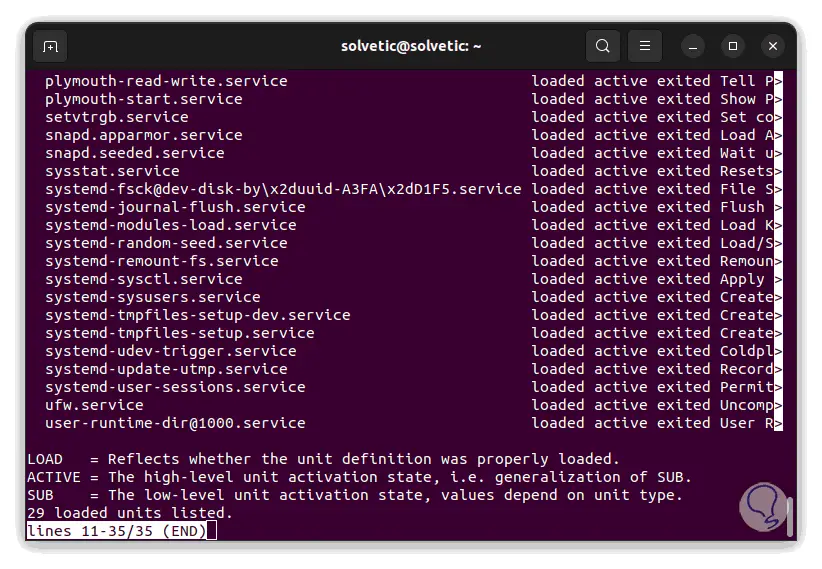
step 7
Note that the following commands produce the same result:
- sudo systemctl list-units --type=service --state=running
- sudo systemctl --type=service --state=running
It is possible to optimize the use of the systemctl command using the option list-unit-files, thanks to it it is possible to list all the unit files installed on the system and integrating the details of the services and daemons in use.
We list the file units:
systemctl list-unit-files --state=enabled
The result will have colors for a better understanding of these:
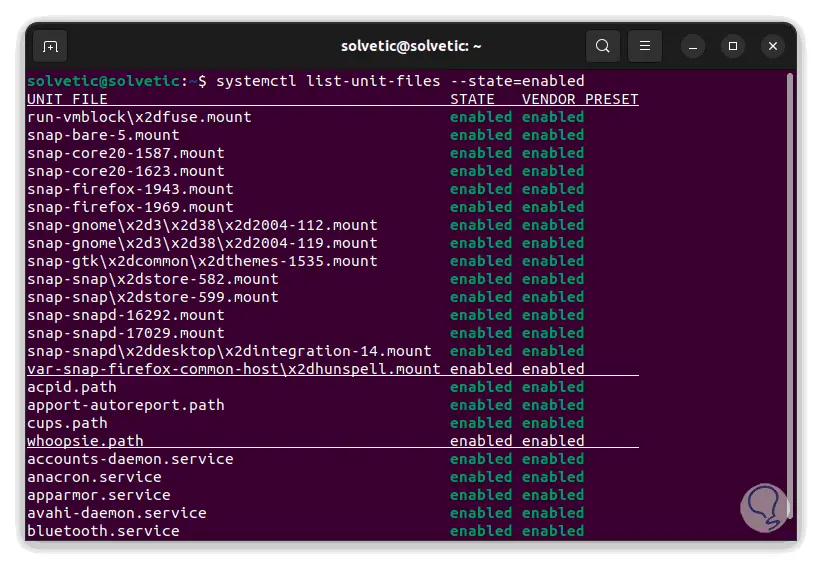
step 8
We find details like:
There we can go to the end to see all the units:
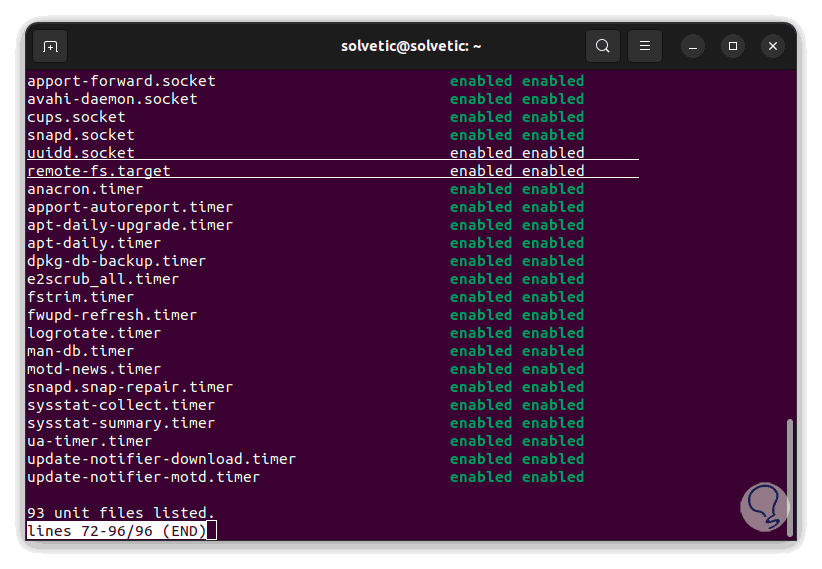
step 9
List all file drives without specifying their status:
systemctl list-unit-files
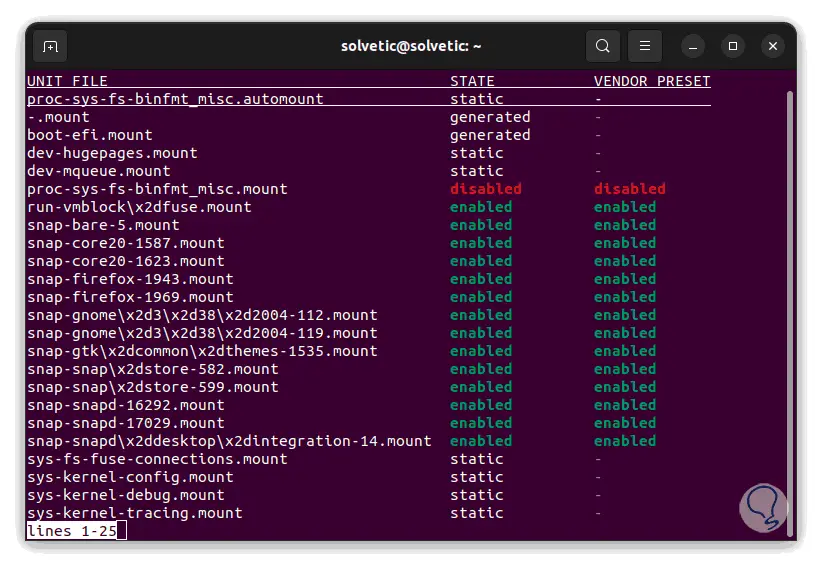
We can see that there are all the units with the different states available, we use the down arrow to continue validating..
step 10
It is possible to list simultaneous states separated by commas:
systemctl list-unit-files --state=enabled,failed
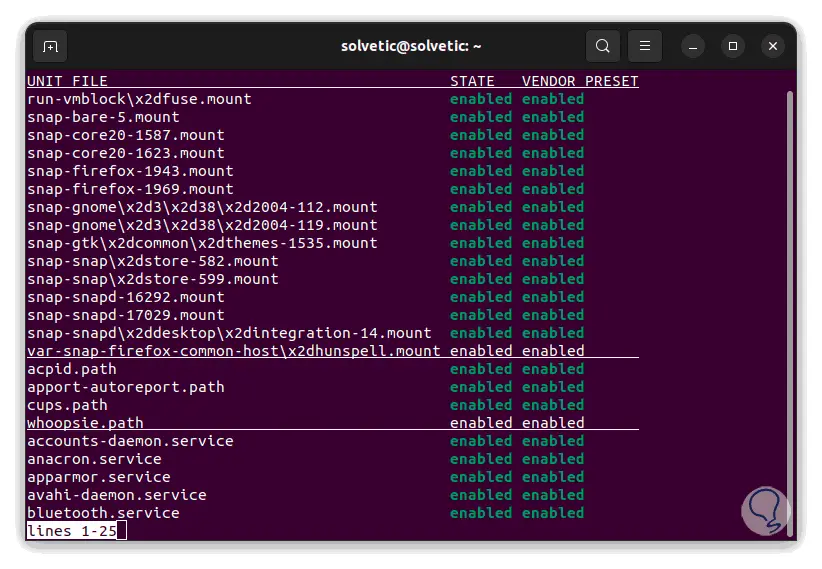
step 11
We validate the current state of a service:
systemctl status service
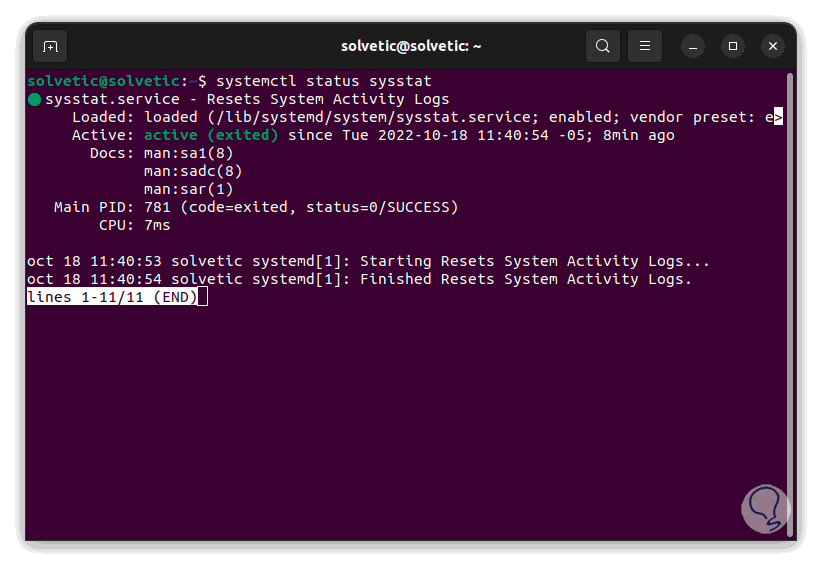
This gives us details like:
Systemctl gives us extra options such as:
list-units
Lists the drives that systemd has in memory and includes drives directly or using dependencies, drives mapped by applications, and more
list-sockets
List socket units in memory and organize them by listening state
list-timers
Lists the timer units in memory ordered by time
is active
Validates if any of the units that we have indicated is active and returns the exit code 0 if at least one is and a value other than zero if none is active.
is-failed
Validates if any of the units that have been indicated is in a "failed" state
status
Shows information about the status of the service or daemon
Show
Shows properties of one or more units
cat
Show backup files from one or more drives
list-dependencies
Displays the units required and sought by the indicated units
start
Start or activate one or more services
stop
Stops the indicated service
reload
Recharge the selected service
try-restart
Stop and then start the service
kill
Kill the process associated with the service
clean
It is responsible for removing the service's configuration, state, cache, logs, and runtime data.
set-property
Set the properties for a service
reset-failed
Resets the "failed" state of the service
Systemctl is of great help to centrally manage all services in Linux and let's remember that a faulty or misconfigured service can trigger a group of failures that destabilize from the applications used to the operating system itself, but with TechnoWikis's explanation you will be able to maintain a stable system.