
PC RAM is the middle ground between microprocessor and storage. It is a memory where all the processes or programs in which the user is working are temporarily stored. For example, when you open several programs they are loaded into RAM memory. As you might guess, sufficient RAM will allow you to open multiple programs at once on your computer without slowing it down. With each activity that you carry out on the PC, for example each open tab of Google Chrome, RAM memory is consumed..
As of today, the amount of RAM that a computer should have is 16 GB. Several games and programs will already consider 8 GB insufficient for optimal performance and even more so if it is only 4 GB. If your laptop or PC has 8GB of RAM or less, increasing it could improve the user experience significantly.
Upgrading or increasing the RAM of a PC or even a laptop is quite simple. The hardest part is really knowing what RAM you should buy for your PC, that is, that it is compatible. Once you've bought it, it's a matter of removing a couple of screws and opening the latches on the RAM to remove it and then insert the new card. If you're not sure how to do this, you can always find your desktop PC's motherboard manual or maintenance manual (if it's a laptop) online to do this procedure correctly..
Upgrade RAM (replace all)
If you are going to upgrade or completely change all installed RAM modules, you need to know what format (DIMM or SODIMM), type (DDR standard) , capacity (GB) and frequency or speed (MHZ) that your motherboard and CPU support. PC, information that should be on the manufacturers website. If it is a laptop, you should consult the manufacturer's website with the technical model.
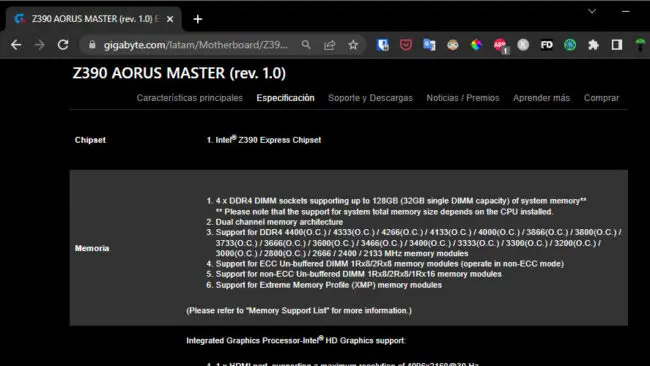
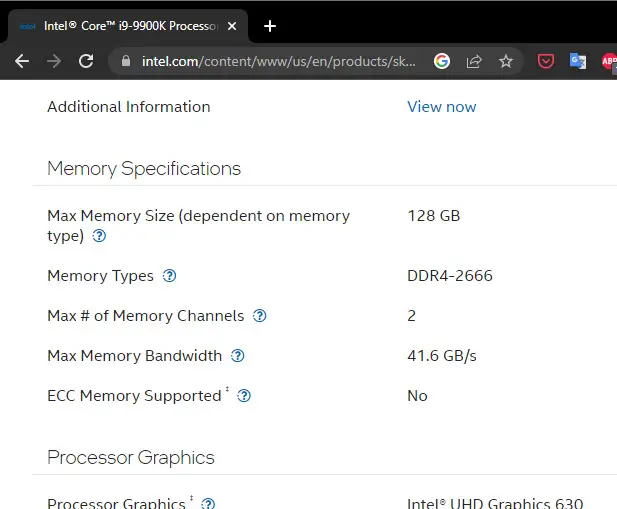
For example, on my desktop PC the installed mainboard is a Gigabyte Aorus Master Z390 and an Intel Core i9 9900k CPU. Both the card and the CPU support a maximum of 128 GB of RAM. Gigabyte indicates that the maximum speed is 4400 MHz ( higher capacity DDR4 memory does not exist anyway ) and that it only supports 32 GB per memory slot. Although the i9 9900k CPU claims to only support DDR4 memory up to 2666 MHz, this limitation could be overcome with higher frequency memories or those that support overclocking (OC), as long as the mainboard and its chipset allow this procedure. You could buy 3200 MHz memory, but if the CPU and motherboard don't allow OC, then it will run at 2666 MHz or even lower..
Obviously in this case the RAM modules that have been installed before do not matter if they are to be removed and replaced.
Expand RAM memory (replace or add module)
This scenario is different from the previous one if you are going to add RAM to the existing one on your PC, or change one of the modules you have. In this case it is advisable to buy another RAM module of the same format , type , voltage and frequency of the RAM module already installed. If possible, you should even try to make it have the same latency (CL). To know this information, it is advisable to open the equipment (RAM modules are usually hidden only behind a cover at the bottom) to see the values on the RAM label and even investigate more with its technical model.
My Lenovo E460 laptop had its only two RAM slots already occupied with 4 and 4 GB, for a total of 8. This laptop had the Intel Core i5 6200U CPU. Although this microprocessor supports 32 GB, Lenovo indicates that this laptop or its mainboard only supports 16 GB (8 GB per module) and in this case it is the value that should be considered as the maximum.

When opening the RAM compartment, all its specifications are usually found in the same module, although sometimes under other lesser-known names as in the photograph above. From these "synonyms" we can extract the equivalences that are already familiar to us:
- PC3L: The number 3 refers to DDR3 and the letter L to Low Voltage (1.35V). That is, here we are talking about a type of DDR3L RAM.
- 12800S: The number 12800 is the data rate that corresponds to a memory of 1600 MHz frequency. The letter S stands for SODIMM format.
- The number 11 right after the 12800 data rate is the CL latency.
In other words, for this laptop you have to get a 1600 MHz DDR3L SODIMM RAM memory module and preferably CL11 latency. In this particular case, the maximum capacity that I can put is 8GB.
Voltage is important in DDR3
Low-voltage DDR3 memory, quite common in laptops, is known as DDR3L. This type of memory can work at 1.35V in addition to 1.5V, which is the standard voltage of DDR3. These memories might work on a PC that requires DDR3, but a 1.5V (NO L) DDR3 memory will not work properly on a PC that claims to work with 1.35V. This is the importance of looking at the voltage of a RAM.
Fortunately this is not a problem on DDR4 or DDR5, where there is a single working voltage of 1.2V and 1.1V respectively (voltages above these are due to overclocking). That is, there are no low-voltage versions of DDR4 or DDR5.
Mix RAM memories of different brands, frequencies and latencies
It is impossible to mix the SODIMM format with DIMMs or between DDR types due to their physical nature (different module sizes or number of pins). Mixing between RAM memories of different brands, frequencies or latencies is no longer impossible, but it is not recommended either. Although in all or at least most cases this can work , it is not optimal. If the fundamentals mentioned above are completely ignored, it is possible that there may be hiccups when turning on the PC after its installation, as well as non-ideal operation that may affect the performance of the computer or its stability.
It is quite difficult for you to get a 100% compatible RAM module or the same as the one you already have installed. For that reason manufacturers sell RAM modules wide open. However, although you can omit the same brand, the important thing is to try to install RAM modules with the same frequency and CL latency if possible. This will ensure the best possible performance when mixing RAM memories. I have mixed memories of different brands and even capacities in different PCs (eg 8GB+16GB), and the equipment has always turned on and worked without a problem, beyond the loss of performance that this may cause in very particular programs or uses.
Should I put two 8GB RAM or just one 16GB?
Whenever possible, use all available RAM slots on your PC, or at least a couple of them. Between buying a single 32 GB module or two 16 GB modules, the second option will always be better. By using the two slots, the PC will use both modules at the same time, working as a double lane of information to access the total RAM. A single module will work as a single rail, which greatly affects the performance of the computer. It is what is called Dual Channel and motherboards, when they have 4 slots, have specified pairs of modules that work together to achieve this.
Why is it bad to clean or free up RAM? Do I need a RAM booster or Task Killer?
Microsoft Hyper V, to create virtual machines in Windows 10/11
Microsoft Office 2021 with free license: Download and install on Windows