macOS gives us various ways to maintain the integrity of our data and information and one of the most striking is the target disk on which we will explain in detail..
Using the target disk method to connect two Mac computers, we can
- Migrate data to a new Mac computer
- Access the boot disk in case macOS does not boot properly.
What is the target disk or target disk in macOS
This method of target disk, also called Target Disk Mode, has been developed as a startup mode through which it will be possible to navigate and transfer files to and from the Mac internal drive without starting the macOS system itself.
There, the volumes will be mounted virtually and the use of a cable is required with which the transfers will be faster than the traditional way of executing it. It is important to emphasize that we cannot use the destination computer while we are in the destination disk or target disk mode, so to use our equipment again it will be necessary to disconnect and restart the computer normally.
Although this mode is available for most current editions of macOS, some computers are not compatible such as iMac, Power Macintosh G3 and G4, iBook G3 models without FireWire, MacBook Air (2008-2009) and MacBook unibody
.
Requirements to use the destination mode
To carry out this process the following is required:
- Two compatible Mac computers with target disk mode
- Each of these devices must have a FireWire or Thunderbolt interface.
- A cable and the necessary adapters (such as Thunderbolt to FireWire or Thunderbolt 2 to Thunderbolt 3).
To use the destination mode it will not be possible to use the simple USB Type A connectors but the old Thunderbolt and FireWire connections work properly, a Thunderbolt 3 cable costs around USD 40, for the most recent Mac computers it is advised to use Original Thunderbolt 3 cables to get the most out of their speed and performance.
1. How to use the destination disk or target disk in macOS
This requires two teams with the following functions:
objective
This is the Mac computer that contains the disk you want to access, remember that during this process the computer will not be available as it will remain in the destination disk mode for the entire operation.
Host
This is the Mac computer that will access the drive as such, so that it will start in macOS normally to carry out the file transfer.
2. How to connect two macOS computers with target disk target disk
To start this process we must connect both computers using the respective Thunderbolt or FireWire ports. It is ideal that we connect the equipment to the current so as not to suffer some type of discharge during the transfer process:

3. How to start Target Mac in destination disk mode on macOS
To carry out this action we have the following options:
Option 1
Turn off the target Mac computer, press the power button and then press the T key and keep it pressed during this boot process, this key can be released when a Thunderbolt or FireWire icon is displayed on the computer screen.
Option 2
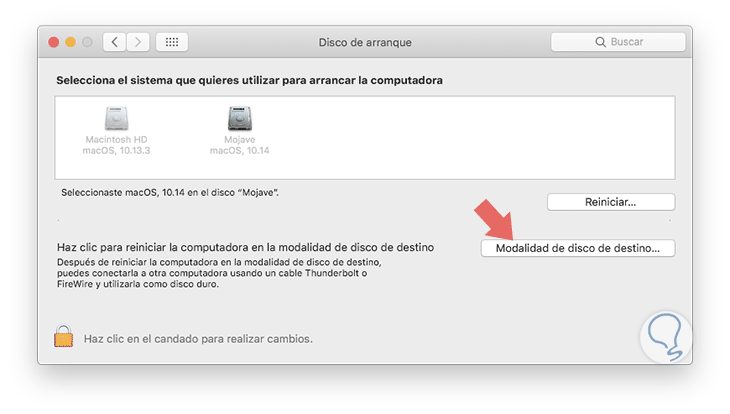
The second option is, in case the target computer is on, go to "System Preferences / Boot Disk". There we click on the "Destination disk mode" button so that the system is rebooted in that mode.
4. How to decrypt and access the disk in macOS
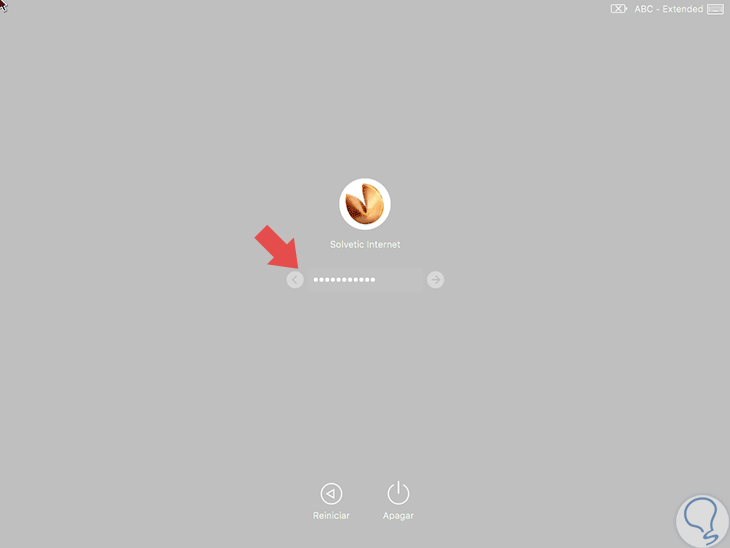
In this process we must wait for macOS to detect the Mac destination disk. In case the destination unit is encrypted with FileVault, it will be necessary to enter the password when you start the destination computer, then wait for the unit to be decrypted to That finally looks like any other external drive that we connect to macOS.
5. How to execute tasks on the target disk in macOS
Once we access the destination disk it will be possible to carry out the transfer tasks, for this we can use the Finder to explore files and execute the copying tasks to and from the unit, and then safely eject the unit.
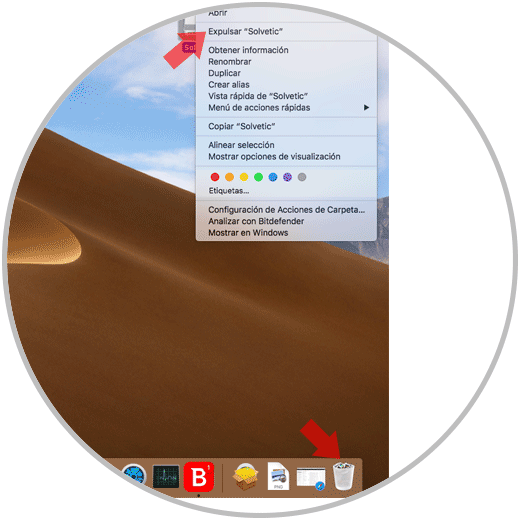
The unit can be ejected by right clicking on it and selecting the "Eject" option or dragging the icon of the Mac destination unit to the Trash / Trash..
Once the unit is ejected we can turn off the equipment or, if we wish, restart the system in the normal way.
The destination disk mode or target disk is useful in cases such as:
Quick File Transfers
This method is simpler and more practical for transferring files such as videos, media libraries, disk images, etc. since this type of cable transfer through Thunderbolt is much faster than a wireless transfer using AirDrop due to that the wireless method is exposed to connection failures or slowness.
Data transfer with macOS migration wizard
With this wizard it will be very simple to transfer all our files from an old Mac to a new one.
To do this, we must connect the destination and the host, start the target computer in the destination disk mode normally, then on the host start the "Migration Assistant" from the "System Utilities"
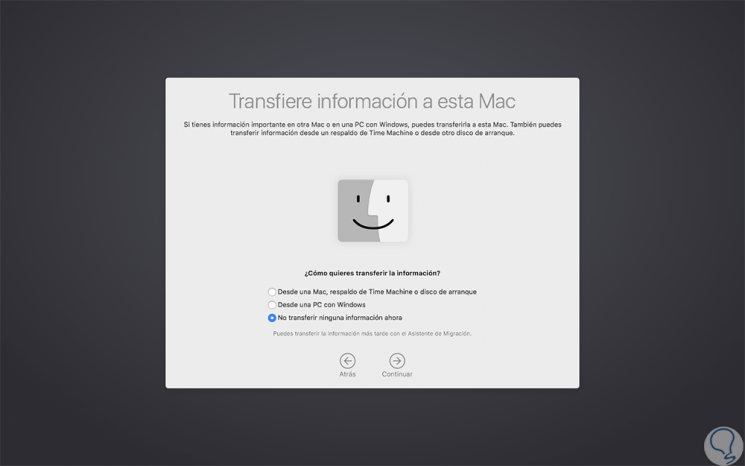
In the wizard we activate the From a Mac, Time Machine security backup or boot disk box and then follow the steps of the wizard.
File recovery when macOS does not boot properly
This is a functional method when our operating system does not start due to any hardware or software failure preventing us from accessing our information.
6. How to run the operating system of a macOS target on the host
This is another of the useful options of the destination disk, allowing us to access a computer that has some hardware failure such as its destroyed screen, corrupt keyboard or other failures.
With the destination disk mode, it is allowed to use a Mac host to boot the operating system from a target as if it were this, with it it will be possible to restore access to the computer with error to retrieve its information. To achieve this we must connect the two computers normally and boot the affected Mac computer, target, in the destination disk mode.
After this, we proceed to restart the host computer and there enter the "Startup Manager" by pressing the "Option" key while the boot process is carried out, with this, it will be possible to see the Mac destination drive in the menu of Start, there we will select it and we will have access to the information for its respective recovery..
We can see the option offered by macOS to access and perform multiple backup tasks at disk level.