There are hundreds of free applications to administer databases in a general way , but we must look for integral solutions that help to better control each aspect of these, that is, as administrators or IT personnel the control over databases is simple. but complete..
One of the best alternatives for this segment in phpMyAdmin and it is for this reason that today in TechnoWikis we will make a complete analysis of how to install this valuable application and thus centralize the management of the databases.
What is phpMyAdmin
phpMyAdmin is a free software tool that has been written in PHP, which aims primarily to provide MySQL administration through the Web intuitively and with extensive features.
phpMyAdmin is compatible with various operations in MySQL and MariaDB, so frequently used operations such as the administration of databases, tables, columns, relationships, indexes, users, permissions, and more can be executed through the user interface . While at the terminal level we will have the ability to directly execute any SQL statement.
PhpMyAdmin features
Some of the features of phpMyAdmin that will be of great help for administrative tasks are:
- Support for most MySQL features such as exploring and deleting databases, tables, views, fields and indexes, creating, copying, discarding, renaming and altering databases, tables, fields and indexes
- Manage user accounts and MySQL privileges
- Manage stored procedures and triggers
- Export data to various formats such as CSV, SQL, XML, PDF, ISO / IEC 26300 - OpenDocument text and spreadsheet, Word, LATEX and more
- Creation of database design graphics in various formats
- Create complex queries using Query-by-example (QBE)
- Global search in a database or a subset of it
- Multiple Server Administration
- Ability to transform data stored in any format using a set of predefined functions
Now we will see how to install phpMyAdmin on Ubuntu 18.04 Server and for this the server must be configured with LAMP for its optimal operation, in the following link we can see how to install LAMP on Ubuntu 18.04:
LAMP UBUNTU
Package Update
The first point to execute is to update the Ubuntu 18 packages using the following command:
sudo apt update
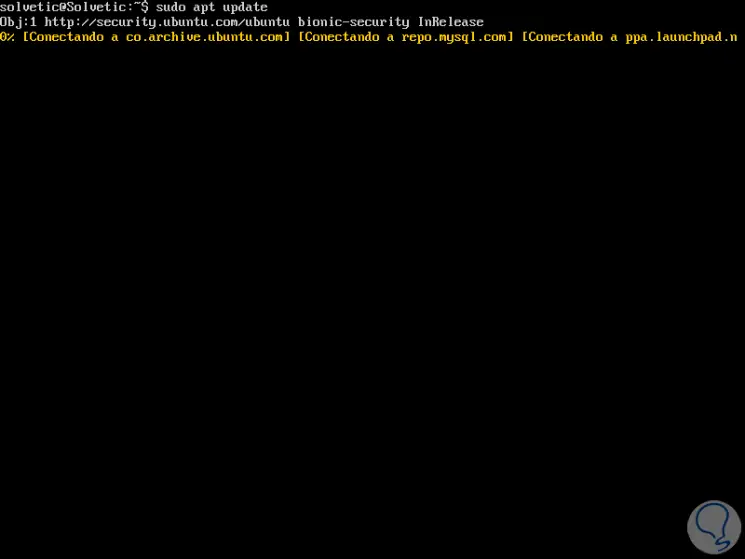
1. How to update and install phpMyAdmin
Step 1
Once this update process is finished, we will install phpMyAdmin by running the following command:
sudo apt install phpmyadmin php-mbstring php-gettext
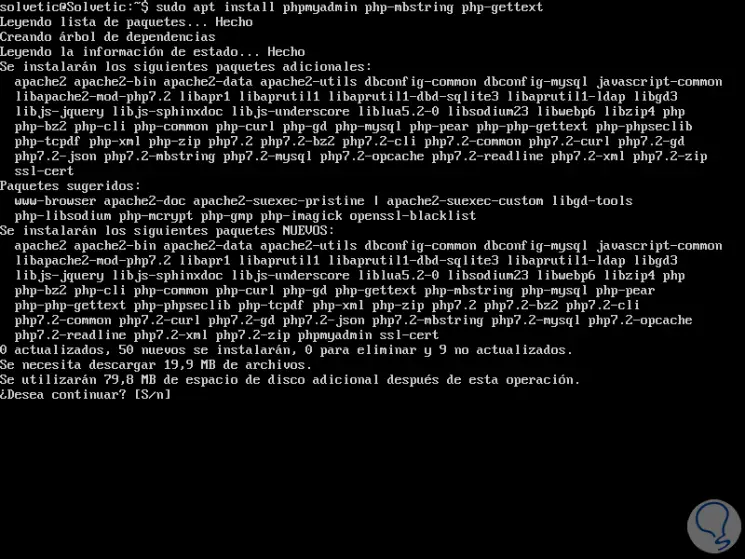
There we enter the letter S to confirm the download and installation of all phpMyAdmin dependencies..
Step 2
During the process we will see certain questions, the first one that was deployed is associated with the server that is going to be configured to run phpMyAdmin:
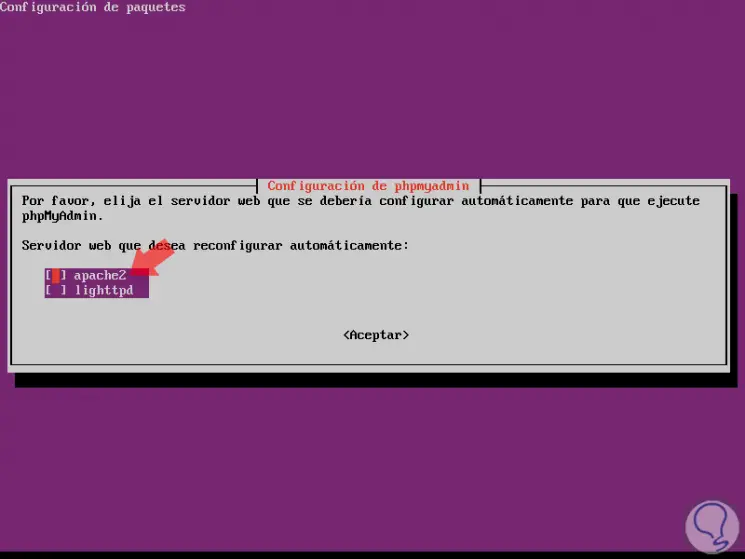
Step 3
In this case we select apache2 with the space key and click on Accept:
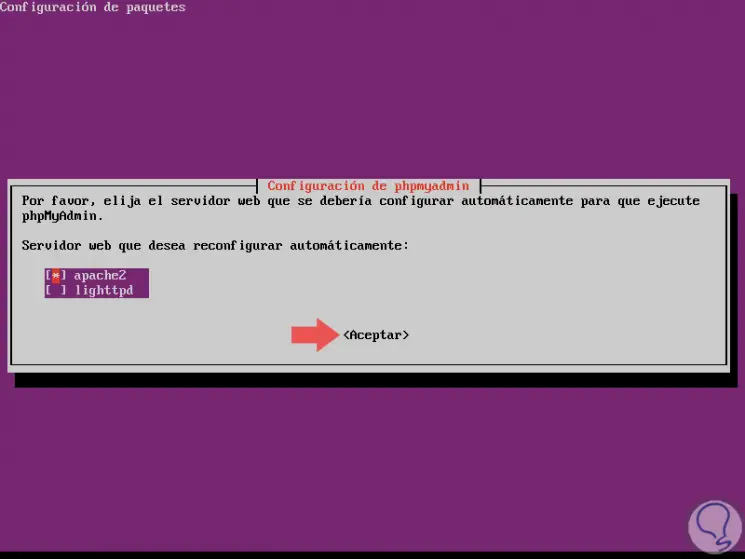
Step 4
Next, we define the database to configure phpMyAdmin:
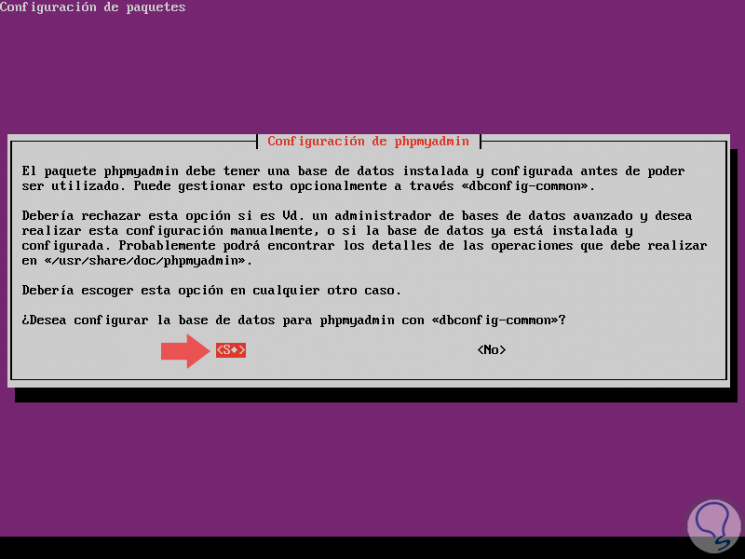
Step 5
In this case we select Yes, press Enter and now we will enter the MySQL password for phpMyAdmin:
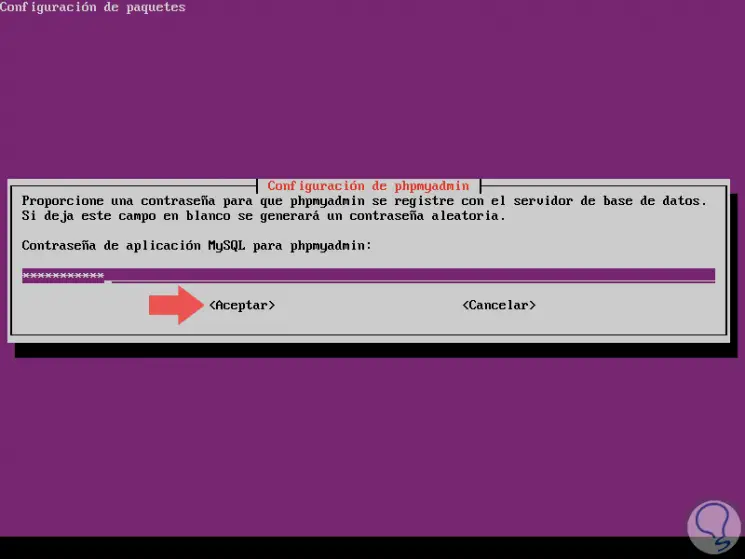
We confirm the same:
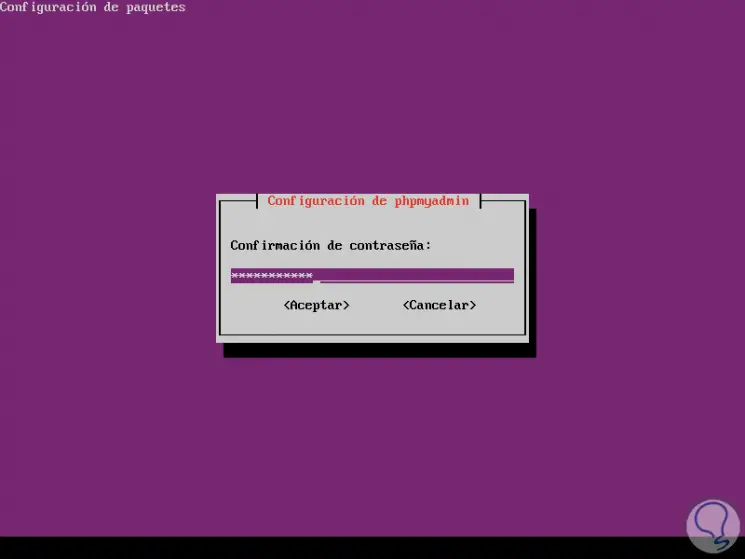
Step 6
Now we are going to assign the database administrator password:
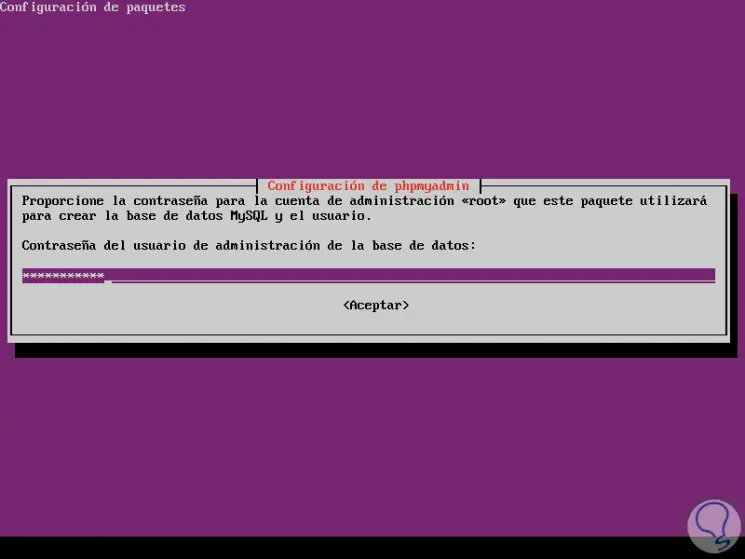
Step 7
After confirming it, press Enter and now we will define the connection form of the phpMyAdmin database:
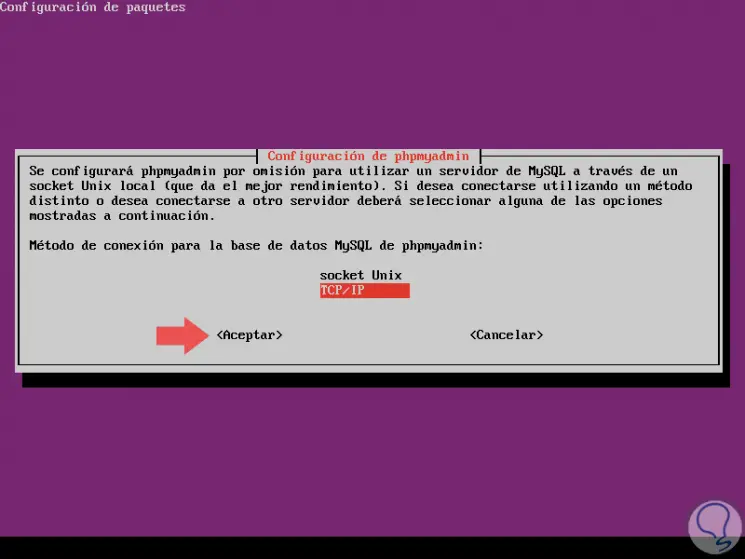
Step 8
Select the most appropriate one and press Enter to define the name of the associated server:
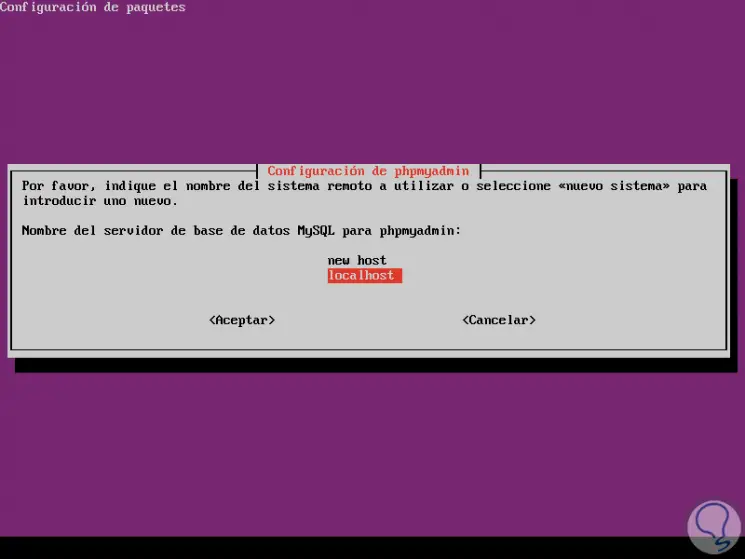
Step 9
In the next window we assign the port
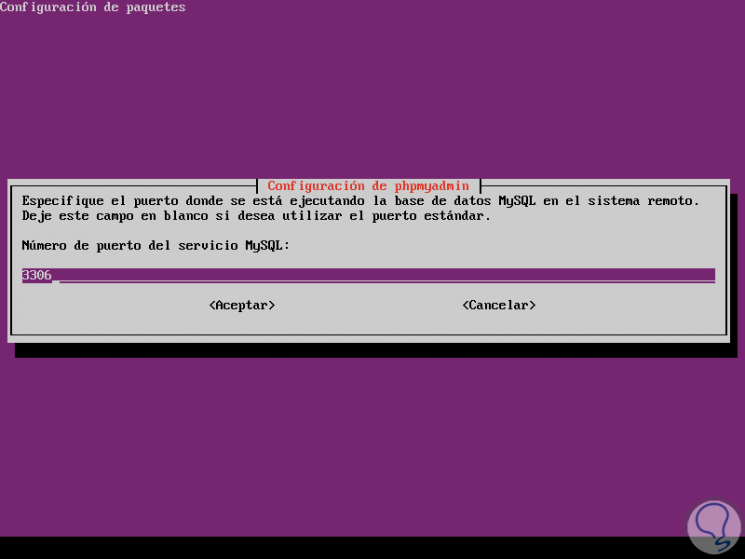
Step 10
In the following window we assign the name of the phpMyAdmin database:
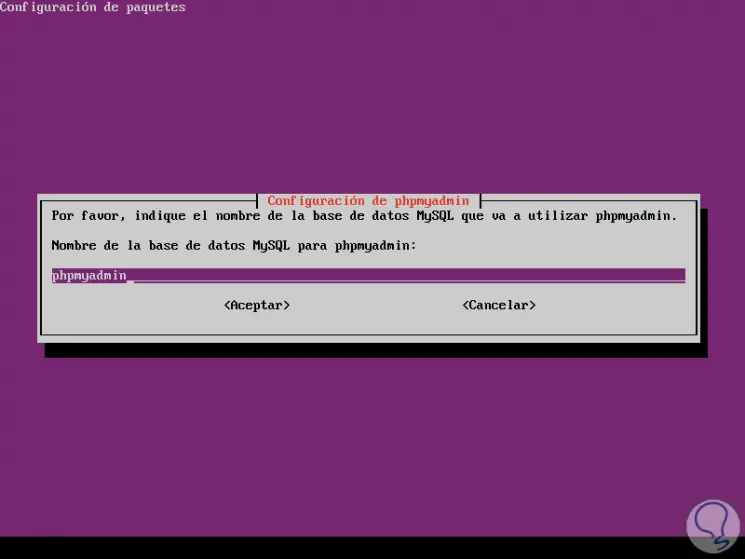
Step 11
Select OK and we will define the MySQL user for phpMyAdmin:
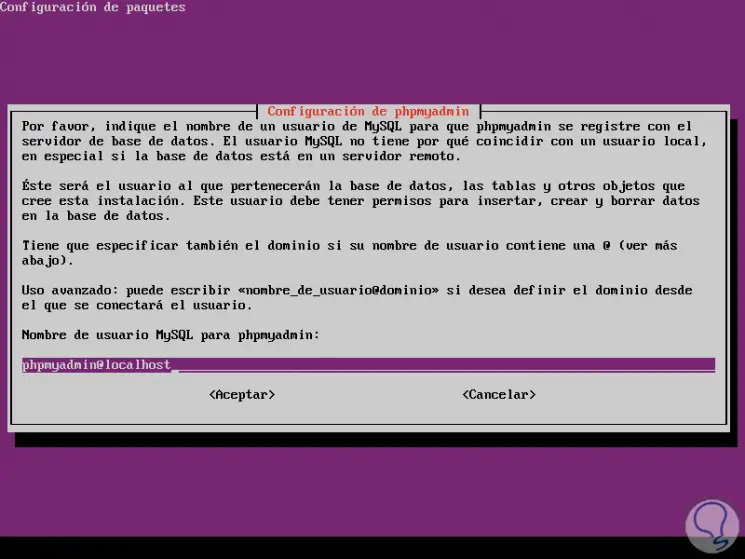
Again we assign the password:
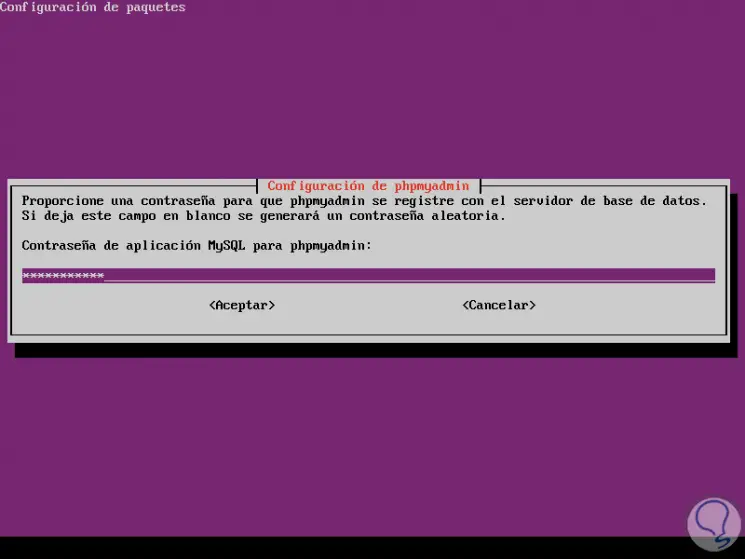
Step 12
Finally we define the user of the database where we can assign the desired one:
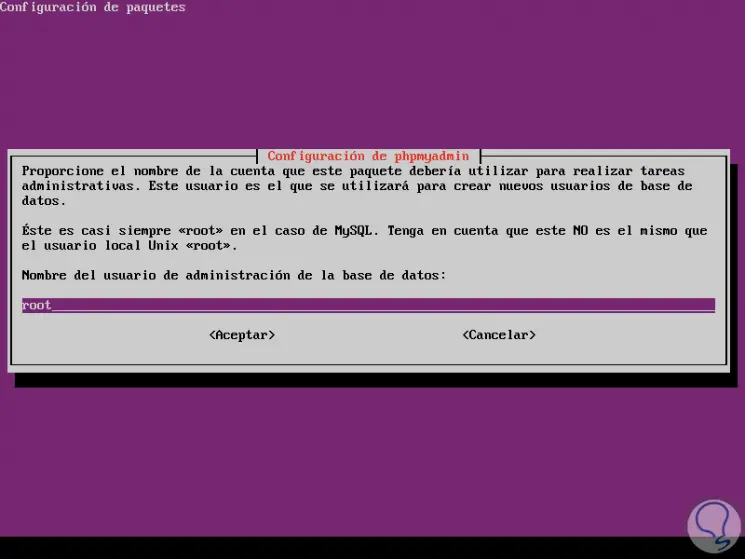
Click on OK and this way phpMyAdmin has been installed in Ubuntu 18.04.
Step 12
The installation process is responsible for including the phpMyAdmin Apache configuration file in the / etc / apache2 / conf-enabled / directory, where it will be read automatically.
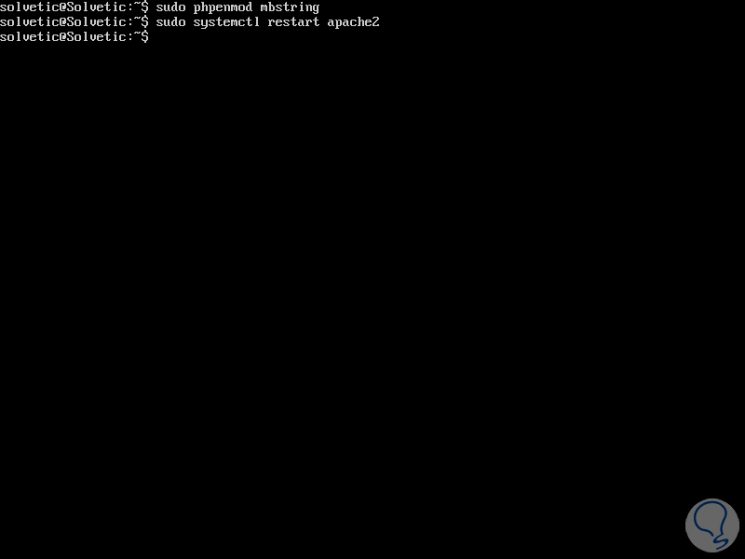
We will explicitly enable the mbstring PHP extension, with the following command:
sudo phpenmod mbstrin
Now, we will restart Apache by running:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
2. How to access phpMyAdmin
It is time to access the phpMyAdmin platform from a browser using the following syntax:
https: // IP_address / phpmyadmin
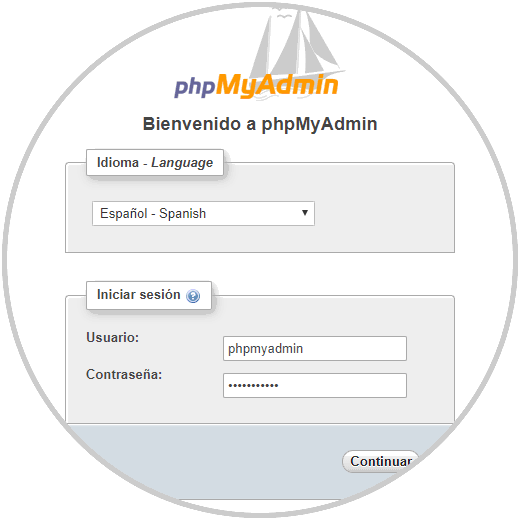
There we select the desired language and enter the respective credentials.
Once we access, this will be the phpMyAdmin environment:
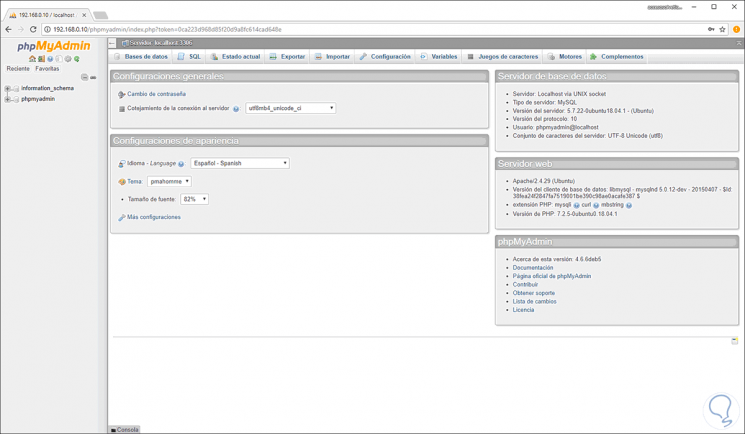
From there it will be possible to carry out all administration tasks..
3. How to secure the phpMyAdmin instance
We already have access to phpMyAdmin, but any user can access in a simple way and that is why phpMyAdmin is a simple target for attackers, in this case as administrators we must take additional security measures.
One of the simplest ways is to add a gateway to the front of the entire phpMyAdmin application, this is achieved by using the Apache authorization and authentication functions integrated.
In addition, that must be approved with the use of .htaccess file overrides by editing the Apache configuration file.
Step 1
We will access this file by running the following:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/conf-available/phpmyadmin.conf
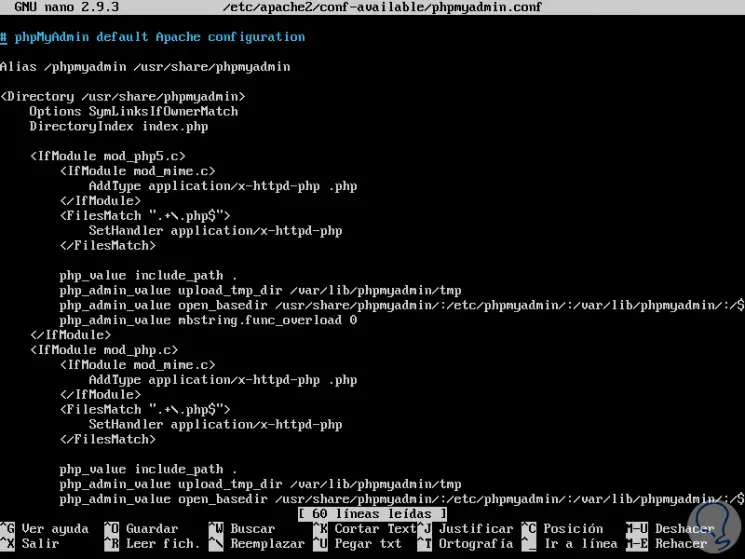
Step 2
There, we will add the AllowOverride All line at the end of the <Directory / usr / share / phpmyadmin> section:
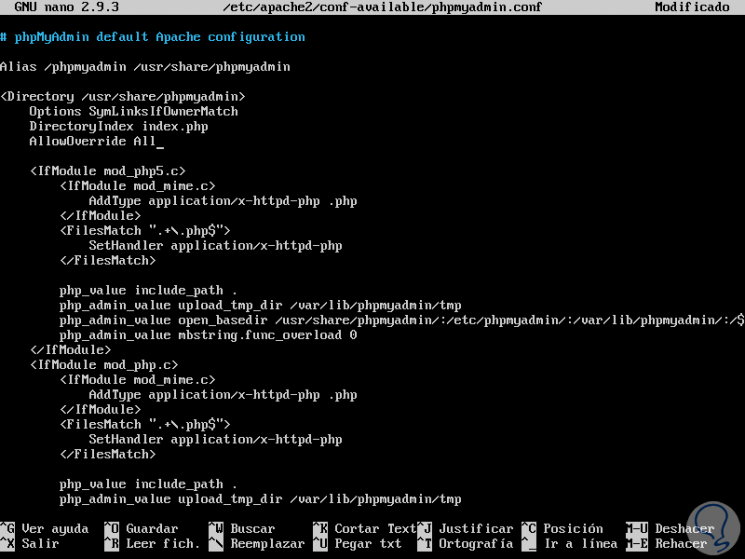
Step 3
We save the changes using the key combination Ctrl + O and exit the editor using Ctrl + X. Now, we apply the changes using the line:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
With this we have enabled the use of .htaccess for the application, but it will be necessary to create one to implement one more layer of security.
Step 4
To achieve this goal, the file must be created within the application directory, we can create the necessary file and open it with some text editor with root privileges like this:
sudo nano /usr/share/phpmyadmin/.htaccess
In this new file we will paste the following:
AuthType Basic AuthName "Restricted Files" AuthUserFile /etc/phpmyadmin/.htpasswd Require valid-user
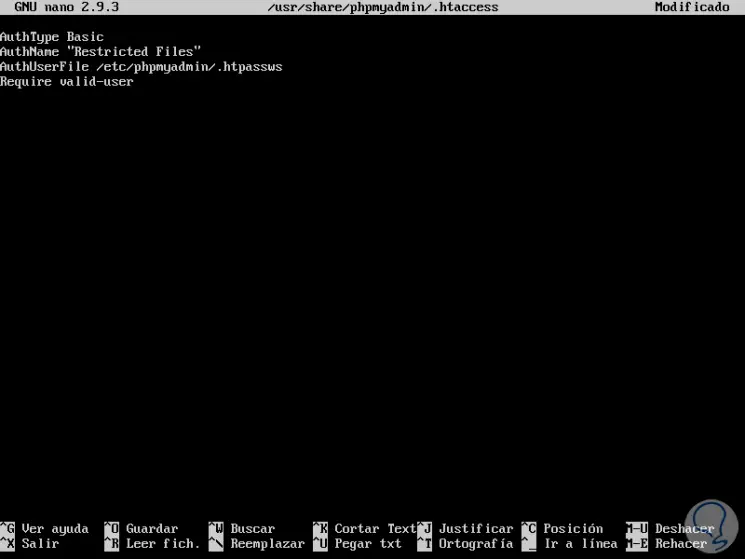
These values ​​are:
AuthType Basic
With this line the type of authentication implemented is specified. This type will implement password authentication using a password file.
AuthName
A message is set for the authentication dialog box. AuthUserFile: The location of the password file that will be used for authentication is set. This must be outside the directories to use.
Require valid-user:
This line specifies that only authenticated users should have access to the selected resource, this stops unauthorized users.
We save the changes and leave the editor.
Step 5
The location defined for the password file was /etc/phpmyadmin/.htpasswd., We are now able to create this file and with an initial user with the htpasswd utility like this:
sudo htpasswd -c /etc/phpmyadmin/.htpasswd "user"
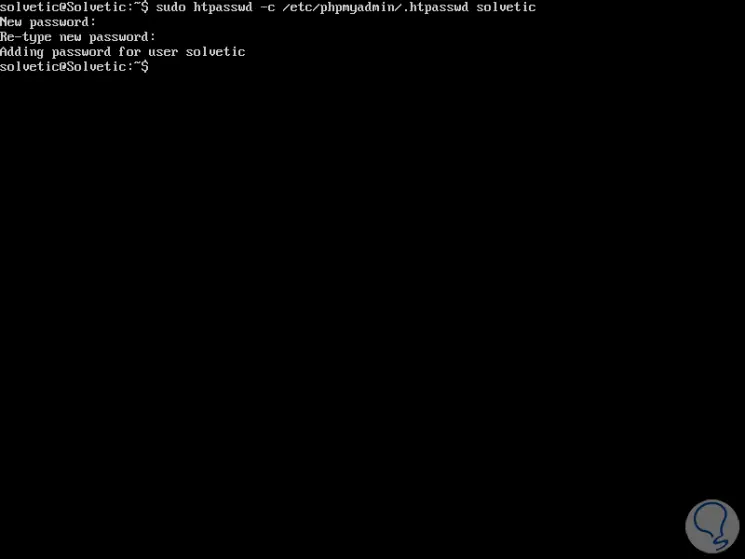
Step 6
In this example we have created the solvetic user, but we can add the desired ones, so when we try to access a subdirectory in phpMyAdmin we will see the following pop-up window where we must register the credentials of the new assigned user:
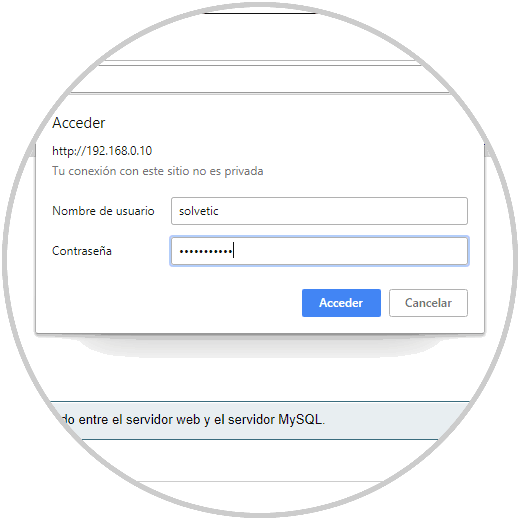
Step 7
By clicking on the Access button we can go to the various phpMyAdmin options:
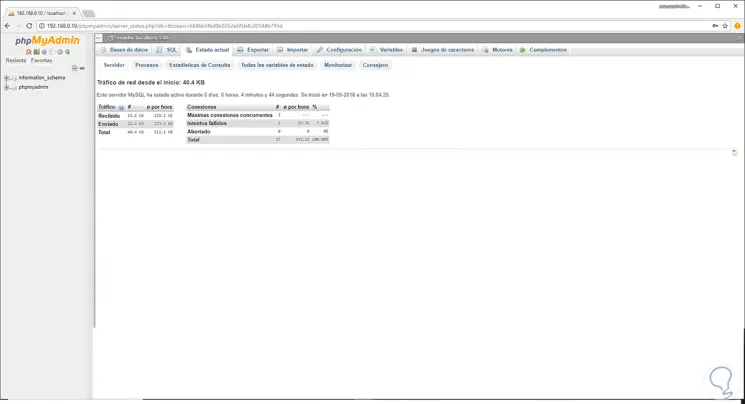
As we can see, phpMyAdmin is a comprehensive and complete solution for the entire database administration process in Linux environments and the best of all is that its interface is simple to use, but with great features.