Managing our servers correctly is one of the most relevant tasks that, as administrators and IT personnel, we must keep in mind since having the necessary tools we will have the possibility to manage every aspect of the system in a clear, complete and fully functional way. CentOS 8, the new edition of this great and robust system, offers us a special utility called Cockpit, through which it will be possible to administer many aspects of the system on a web level both at the software and hardware level..
What is Cockpit?
Cockpit is integrated into CentOS 8 as a web-based GUI thanks to which it will be possible for all users responsible for administering CentOS 8 to have a comprehensive server management.
Cockpit Tasks
When installing and enabling Cockpit, it will be possible to execute tasks such as:
- Access system performance
- Enable or disable the firewall
- Manage aspects of the network
As you can see, it is an integral and practical utility for all of us involved in working with CentOS 8. Now TechnoWikis will explain in detail how to install and use this web administrator in CentOS 8.
1. Install Cockpit on CentOS 8
Step 1
By default, when CentOS is installed for the first time you will see that a message is embedded to enable the Cockpit service:
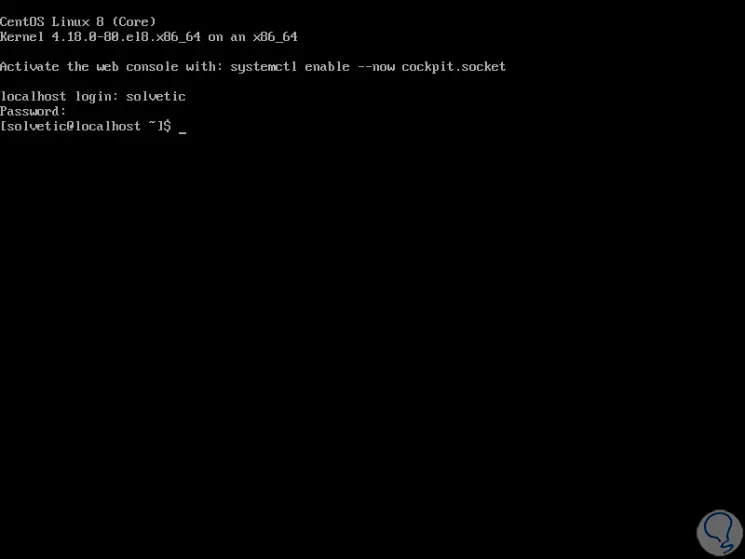
Step 2
We proceed to execute the indicated command to enable it:
systemctl enable –now cockpit.socket
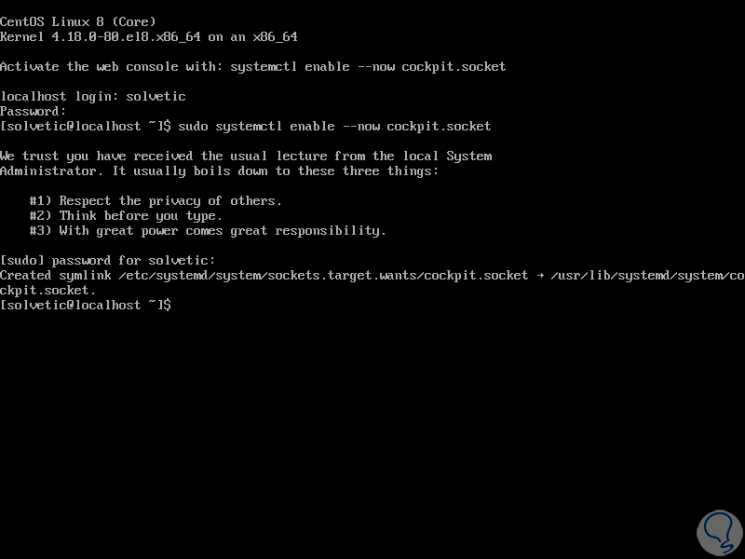
Step 3
Now is the time to install Cockpit by running the following:
yum install cockpit
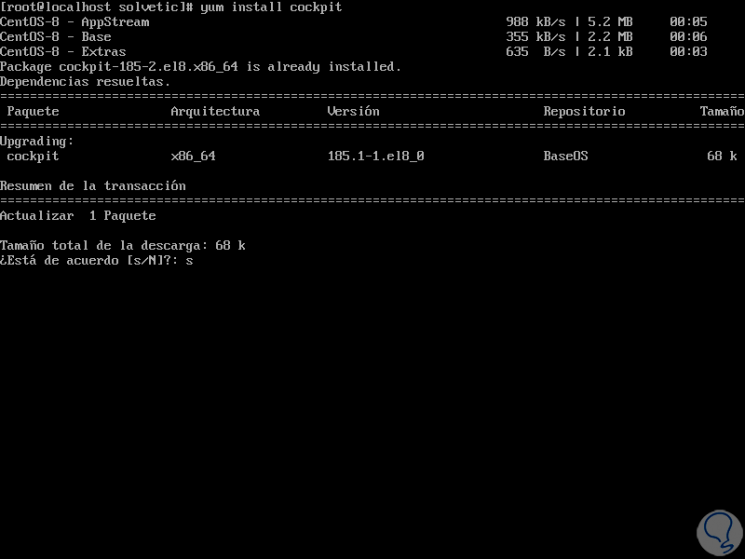
Step 4
Enter the letter "s" to confirm the download and install Cockpit in CentOS 8 and after that we must accept the import of the GPG key:
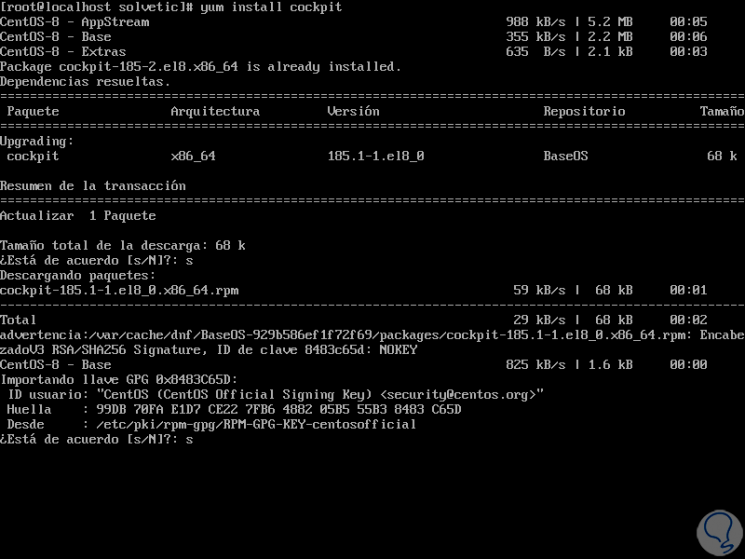
Step 5
Again we enter the letter "s" and finally we have installed Cockpit in CentOS 8:
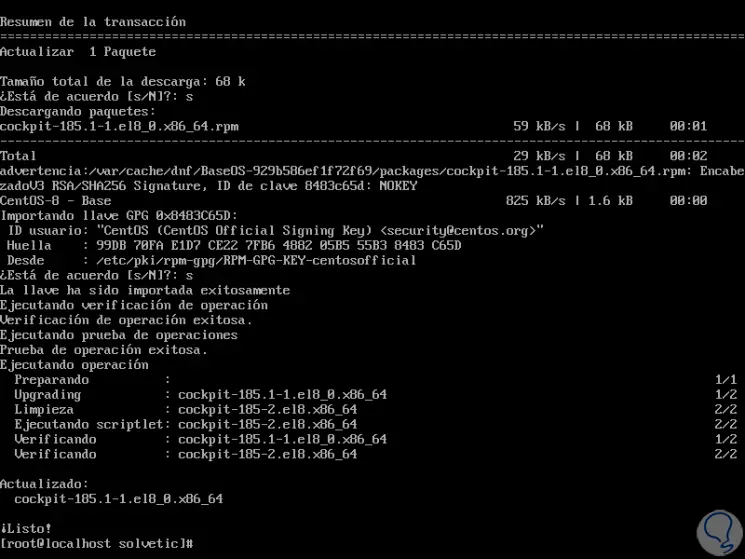
2. Start and view the status of the Cockpit service in CentOS 8
Step 1
The next step will be to start the Cockpit service in CentOS 8 by executing the following:
systemctl start cockpit.socket
Step 2
And then we can check the status of it by running:
systemctl status cockpit.socket
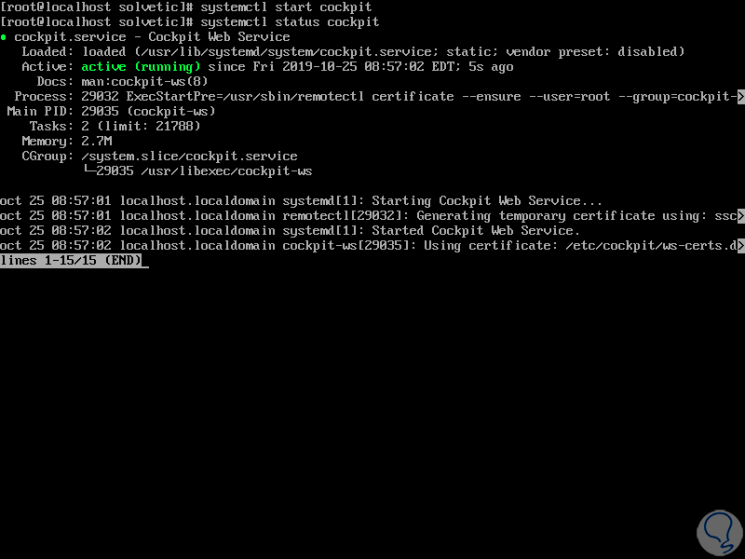
Step 3
As we see its status is active, if we want to validate the port associated with Cockpit we execute the following:
ps auxf | grep cockpit
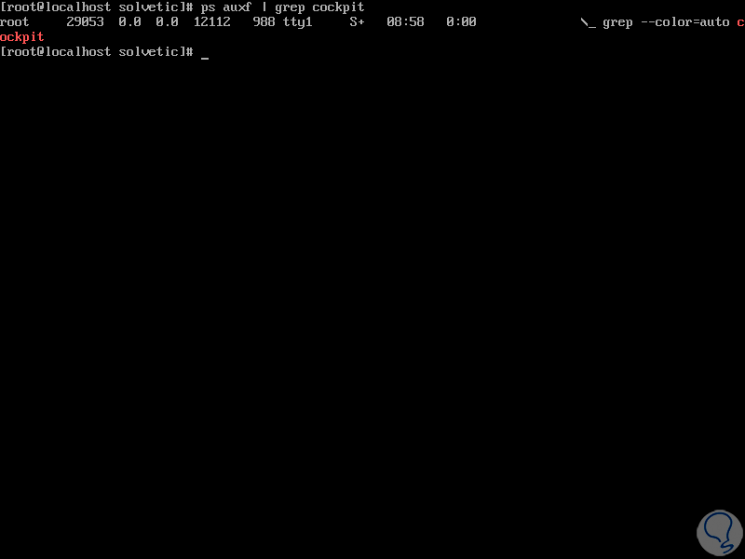
Step 4
Once we do this, we will configure the Cockpit access permissions in Firewalld by executing the following:
firewall-cmd --add-service = cockpit --permanent firewall-cmd --reload
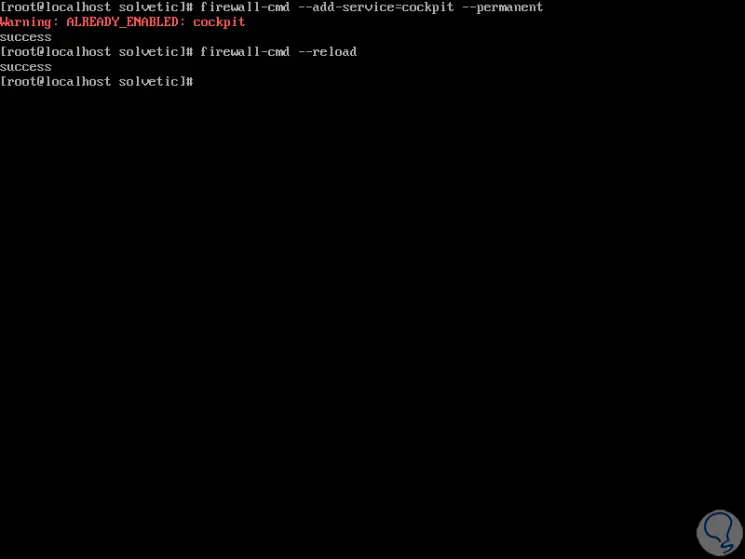
3. Access Cockpit in CentOS 8
Step 1
Configured this, we can access Cockpit either locally or remotely by executing the following syntax:
https: // Server_IP: 9090
Step 2
To know the IP of the current server we must execute the following:
ip add
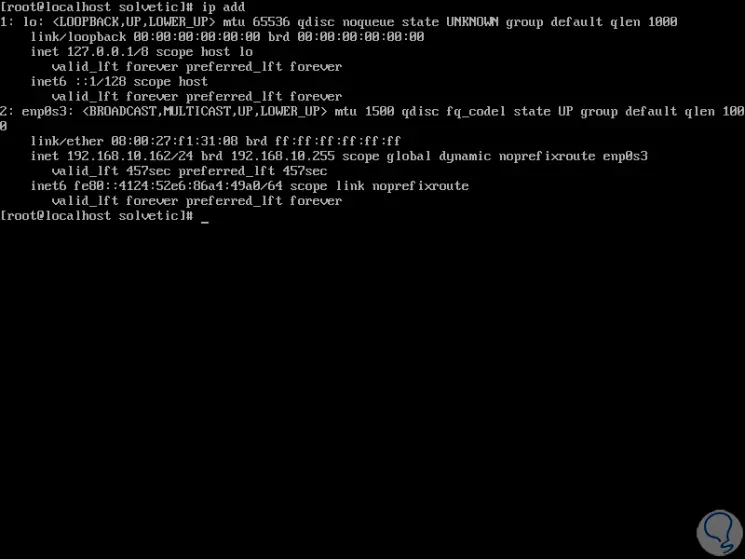
Step 3
Once we have knowledge of the IP address we proceed to access from any browser and see the following:
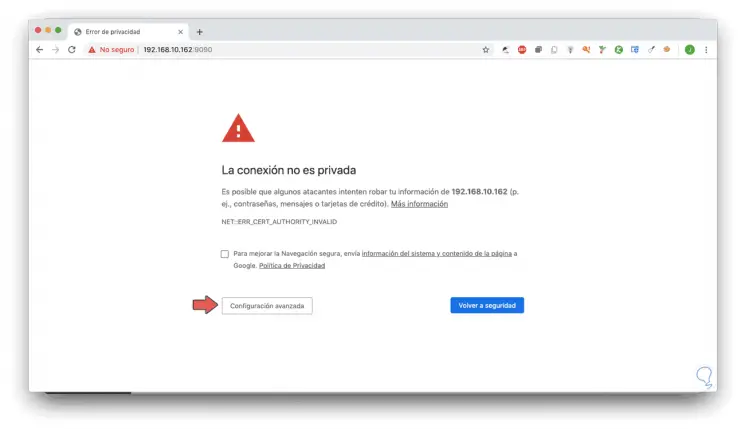
Step 4
It is a security issue, to access we click on the "Advanced Settings" button and then click on the "Continue to 192.168.xxx.xxx" line:
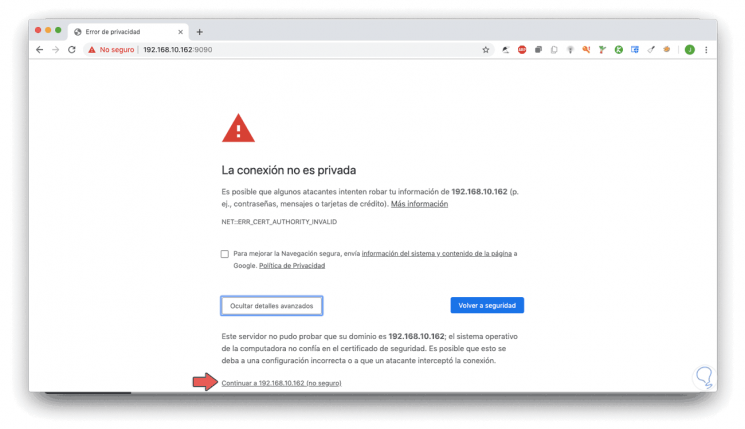
Step 5
When accessing we must enter the user with whom we want to connect to the server from Cockpit:
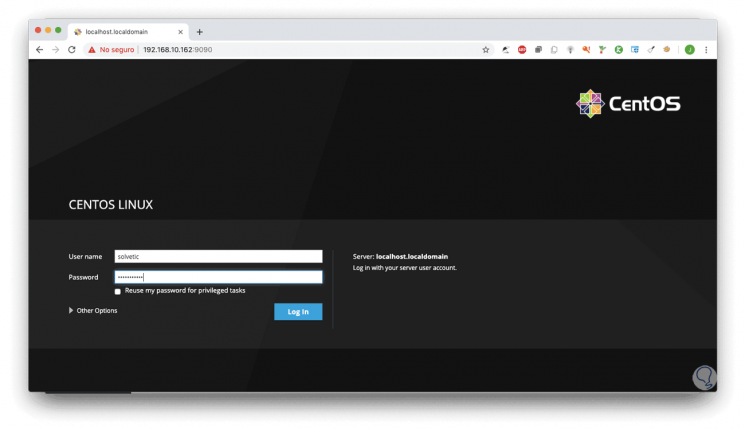
Step 6
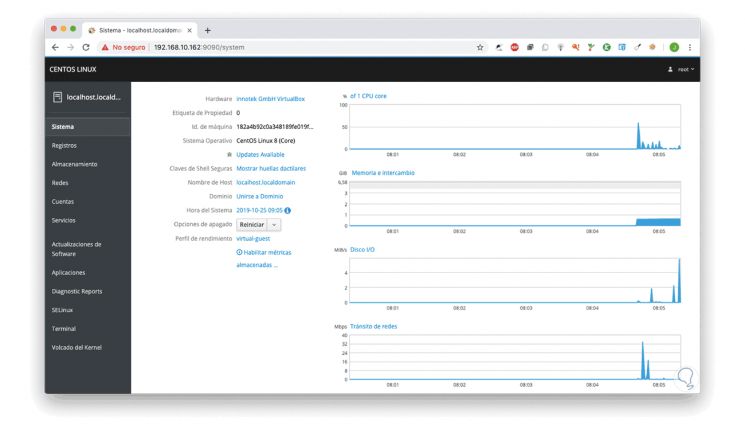
We click on Log In and we will be redirected to the Cockpit center console where we first find a general aspect of the system:
Note
The default language is English, to configure it in Spanish we will go to the account settings from the upper right corner.
4. Cockpit sections in CentOS 8
Cockpit is cataloged by a series of options which are:
System
From this menu it will be possible to access variables and aspect such as:
In addition to this we find a graphic panel where we can see the real-time status of:
Logs
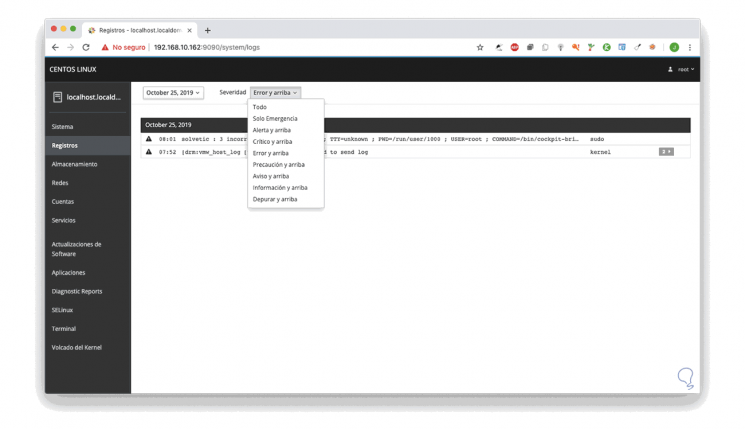
From this section we find the series of events that have happened in the system and we can filter them by a series of parameters as the case may be.
Storage
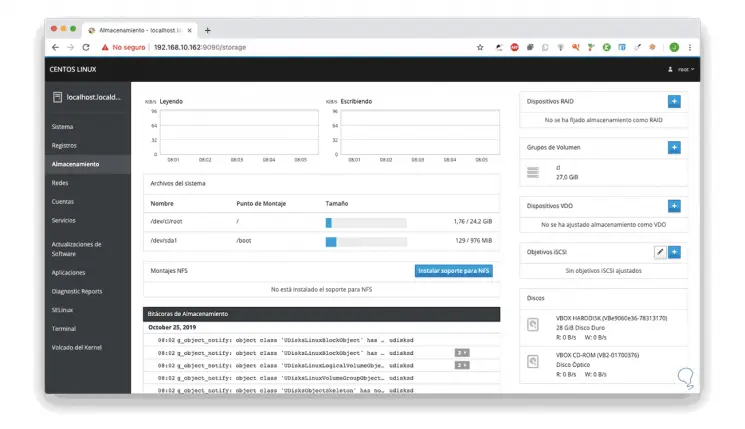
As the name implies, there are aspects such as:
- Graphics for reading and writing data to disk
- Details of installed disks
Nets
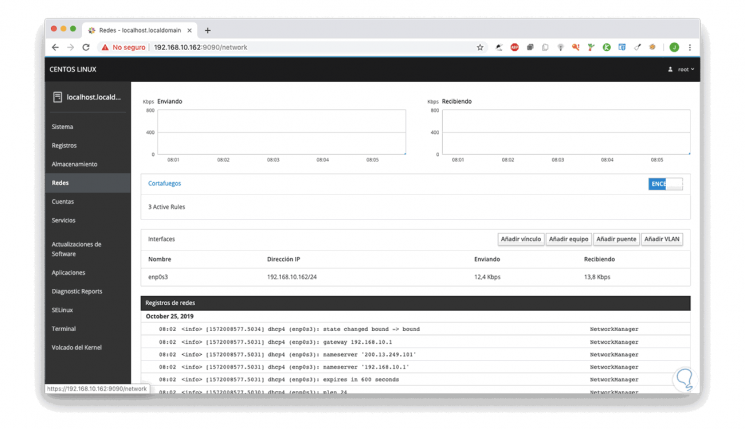
In this aspect we have network details such as:
- Transfers sent and received
- Name of the network adapter and its associated IP address
- Firewall status and active rules
Accounts
From this option it is possible to access the active CentOS 8 accounts:
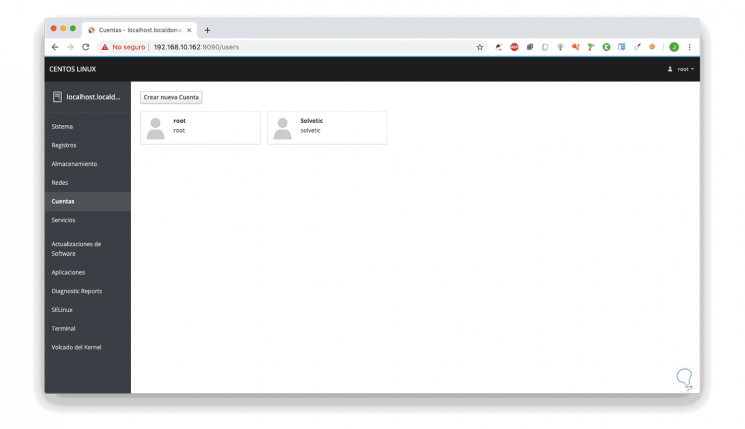
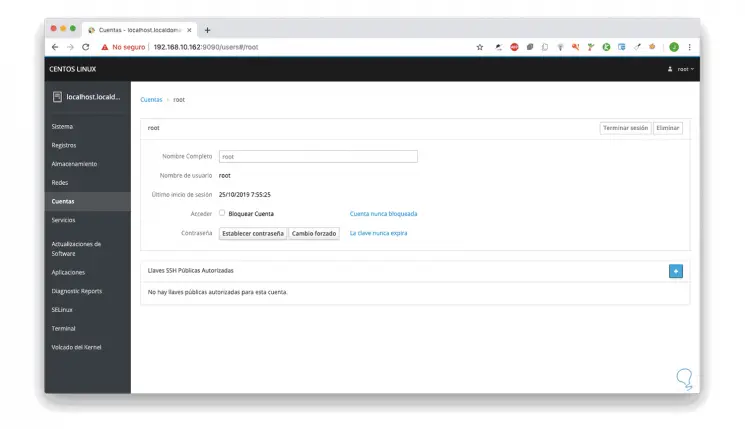
By selecting one of the accounts it is possible to access clearer details such as:
- Possibility to assign server role
- Set the account as never locked
- Prevent the account from expiring
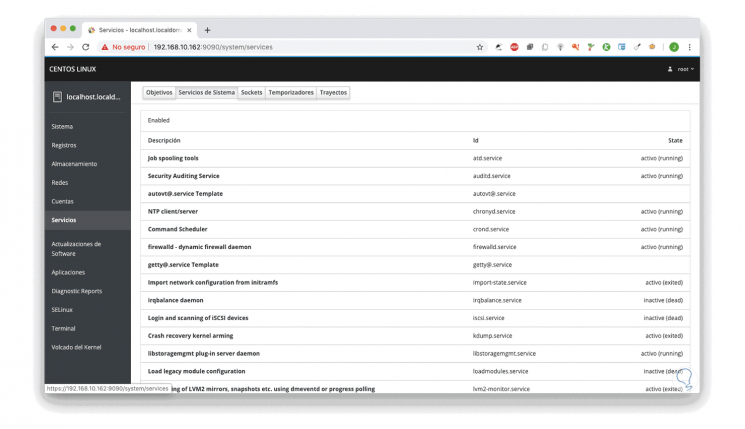
Services
From this section we can access all the services of the system, as well as its current status:
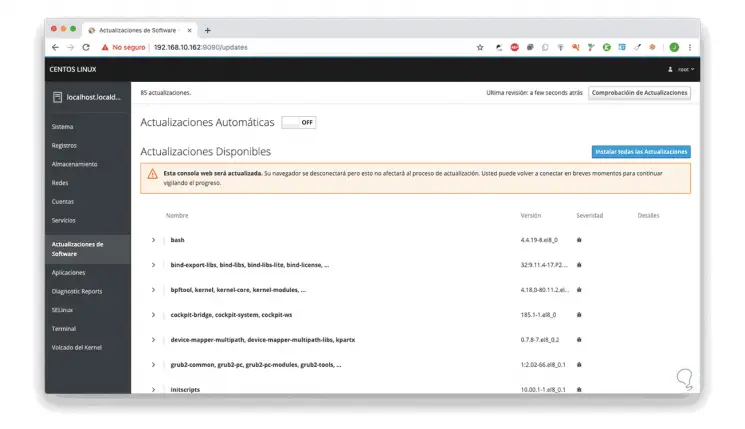
Software updates
From here we can see if there are updates for the system and be able to apply them if necessary and in addition to this we have a switch to activate automatic updates:
Applications
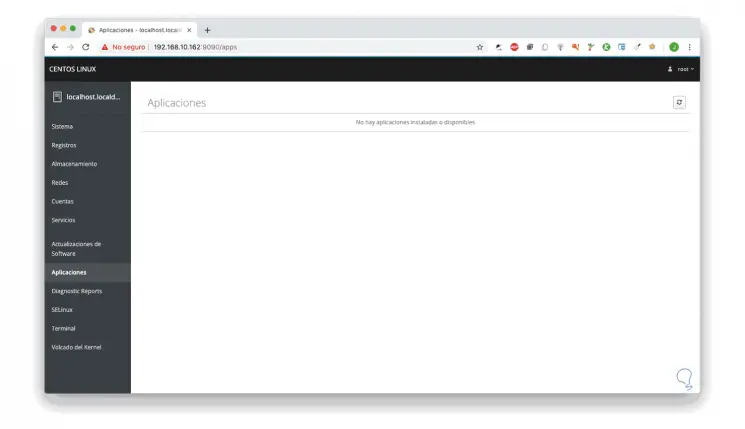
There we find available applications that have been installed in CentOS 8.
Diagnostic Reports
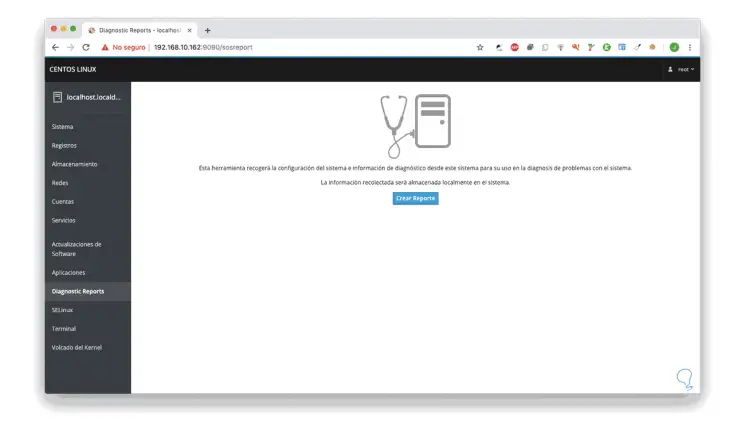
It is a diagnosis that we can generate to access explicit system information:
SELinux
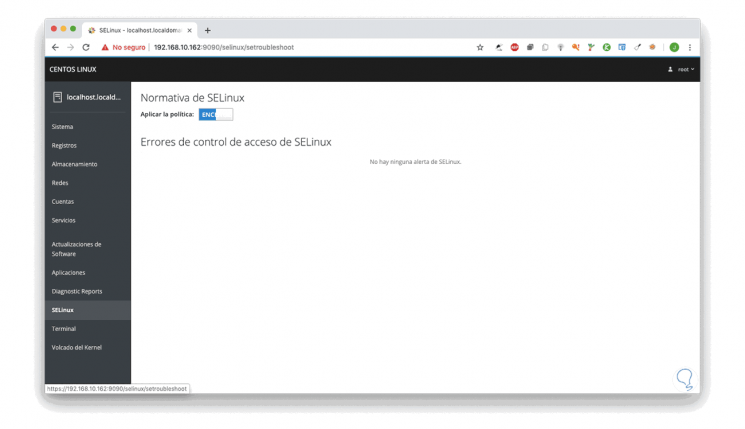
From here we can activate or not the SELinux security function:
Terminal
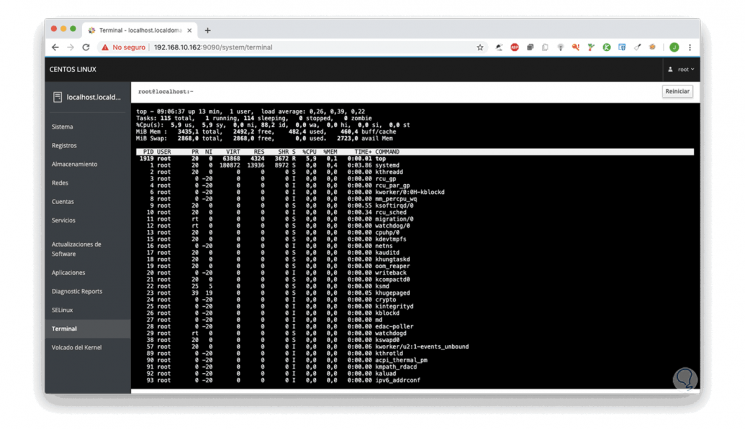
It is an option thanks to which we can access the remote terminal and execute its own commands:
Kernel Dump
There we can activate or not the kernel dump with which the tasks of the CentOS 8 core are simplified.
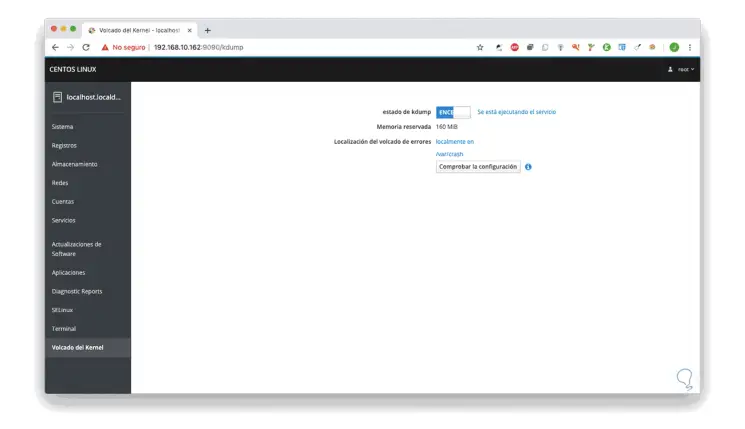
Cockpit configuration
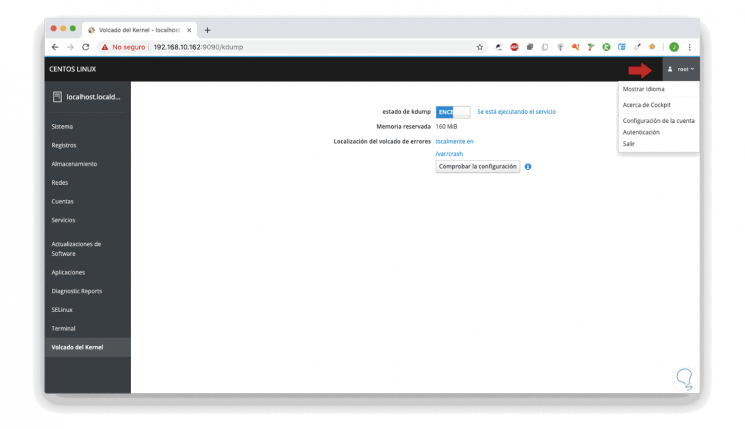
There Finally, to access the Cockpit configuration in CentOS 8 we can click on the upper right button and select the appropriate option:
Cockpit is one of the most comprehensive and functional CentOS 8 solutions for control, support and access to specific details of the operating system and its components..